Abstract
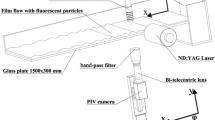
Rupture of a subcooled water film flowing down an inclined plate with a 150×150 mm heater is studied using a fiber optical thickness probe. The main governing parameters of the experiment and their respective values are: Reynolds number (3.2–30.2), plate inclination angle from the horizon (3–90 deg), heat flux (0–1.53 W/cm2). The effect of the heat flux on the film flow leads to the formation of periodically flowing rivulets and thin film between them. As the heat flux grows the film thickness between rivulets gradually decreases, but, upon reaching a certain critical thickness, the film spontaneously ruptures. The critical film thickness is practically independent on the film Reynolds number as well as on the plate inclination angle and lies in the neighborhood of 60 µm (initial film thickness varies from 93 to 368 µm). The heater surface temperature prior to rupture is also independent of Re and Θ, and is about 45°C (initial film temperature is 24°C). The process of rupture involves two stages: 1) abrupt film thinning down to a very thin residual film remaining on the heater; 2) rupture and dryout of the residual film. The threshold heat flux required for film rupture is scarcely affected by the plate inclination angle but grows with the Reynolds number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oron A., Davis S.H., Bankoff S.G., 1997, “Long-Scale Evolution of Thin Liquid Films”, Rev Mod Phys, 69, 931–980
Burelbach J. P., Bankoff S. G., Davis S. H., 1990, “Steady thermocapillary flows of thin liquid layers. II. Experiment”, Phys. Fluids A 2, 321–333
Chinnov E.A., Kabov O.A., Marchuk I.V., Zaitsev D.V., 2002, “Heat transfer and breakdown of subcooled falling water film on a vertical middle size heater”, Int J Heat Tech, 20, 69–78
Chinnov E.A., Kabov O.A., 2003, “Jet formation in gravitational flow of a heated wavy liquid film”, J Appl Mech Tech Phys, 44, 708–715
Zaitsev D.V., Kabov O.A., 2005, “Study of the thermocapillary effect on a wavy falling film using a fiber optical thickness probe”, Exp Fluids, 39, 4, 712–721
Zaitsev D.V., Kabov O.A., Evseev A.R., 2003, “Measurement of locally heated liquid film thickness by a double-fiber optical probe”, Exp Fluids, 34, 6, 748–754
Zaitsev D.V., Chinnov E.A., Kabov O.A., Marchuk I.V., 2004, “Experimental study of the wave flow of a liquid film on a heated surface”, Tech Phys Letters 30, 3, 231–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper was presented on the Second International Topical Team Workshop on TWO-PHASE SYSTEMS FOR GROUND AND SPACE APPLICATIONS October 26–28, 2007, Kyoto, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitsev, D.V., Rodionov, D.A. & Kabov, O.A. Study of thermocapillary film rupture using a fiber optical thickness probe. Microgravity Sci. Technol 19, 100–103 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915765
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915765