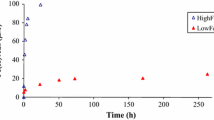
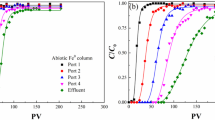
Abstract
Formation of Fe(II)-containing mineral through microbial processes may play an important role in iron and carbon geochemistry in subsurface environments. Fe(III)-reducing bacteria form Fe(II)-containing minerals such as siderite, magnetive, vivianite, and green rust using iron oxides. A psychrotolerant Fe(III)-reducing bacterium,Shewanella alga (PV-4), was used to examine the reduction and biomineralization of a poorly crystalline iron oxide, akaganeite (β-FeOOH), in the absence of a soluble electron shuttle, anthraquinone disulphonate (AQDS), under different atmospheric compositions as well as in HCO −3 buffered medium (30 to 210 mM). Iron biomineralization was also examined under different growth conditions such as incubation time, electron donors, and electron acceptors. The Fe(III)-reducing bacterium, PV-4, reduced akaganeite, Fe(III)-citrate, and Co(III)-EDTA using lactate or H2 as an electron donor. The iron biomineralization of Fe(III) oxide, akaganeite—as it undergos reduction by an iron reducing bacterium—is a complex process influenced by biogeochemical factors including microorganisms, bicarbonate buffer concentration, atmospheric composition, electron donors/acceptors, incubation time, and Eh/pH. From this research we found that microorganisms do participate in the formation of diverse iron minerals and that microbial iron biomineralization may affect Fe and C biogeochemistry in subsurface environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cairins-Smith, A.G., Hall, A.J. and Russell, M.J., 1992, Mineral theories of the origin of life and an iron sulfide example. Origins of Life Evolution, Biosph, 22, 161–180.
Chapelle, F.J., 1994, Groundwater microbiology and geochemistry. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Childs, C.W., 1992, Ferrihydrite: A review of structure, properties, and occurrence in relation to soils. Z Pfanzenernbhr Bndenk, 155, 441–448.
Dong, H., Fredriokson, J.K., Kennedy, D.W., Zachara, J.M., Kukkadapu, R.K. and Onstott, T.C., 2000, Mineral transformations associated with the microbial reduction of magnetite. Chemical Geology, 169, 299–318.
Emerson, S., 1976, Early diagenesis in anaerobic lake sediments: chemical equilibria in interstitial waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 40, 925–934.
Fredrickson, J.K., Zachara, L.N., Kennedy, D.W., Dong, H., Onstott, T.C., Hinman, N.W. and Li, S., 1998, Biogenic iron mineralization accompanying the dissimilatory reduction of hydrous ferric oxide by a groundwater bacterium. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62, 3239–3257.
Fredrickson, J.K., Zachara, J.M., Kukkadau, R.K., Gorby, Y.A., Smith, S.C. and Brown, C.F. 2001, Biotransformation of Ni-substituted hydrous ferric oxide by an Fe(III)-reducing bacterium. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 703–712.
Jenne, E.A., 1977, Trace element sorption by sediments and soil-sites and processes. In: Chappel, K.P. (ed.), Symposium on molybdenum in the environment. Marcel Dekker, New York, p. 425–553.
Karlin, R. and Levi, S., 1983, Diagenesis of magnetic minerals in recent hemipelagic sediments. Nature, 303, 327–330.
Kirchman, D., Sigda, J., Kapuscinski, R. and Mitchell, R., 1982, Statistical analysis of the direct count method for enumeration bacteria. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 44, 376–382.
Kukkadapu, R.K., Zachara, J.M., Smith, S.C., Fredrickson, J.K. and Liu, C.X., 2001, Dissimilatory bacterial reduction of Al-substituted goethite in subsurface sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 2913–2924.
Liu, S., Zhou, J., Zhang, C.L., Cole, D.R., Gajdarziska-Josifovska, M. and Phelps, T.J., 1997, Thermophilic Fe(III)-reducing bacteria from the deep subsurface: The evolutionary implications. Science, 277, 1106–1109.
Liu, C.X., Kota, S., Zachara, J.M., Fredrickson, K.K. and Brinkman, C.K., 2001, Kinetic analysis of the bacteria reduction of goethite. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 2482–2490.
Lovley, D.R., 1991, dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Microbialogical Review, 55, 259–287.
Lovley, D.R., 1993, Dissimilatory metal reduction. Annual Reviews of Microbiology, 47, 263–290.
Lovley, D.R., 1995, Bioremediation of organic and metal contaminants with dissimilatory metal reduction. Journal of Industrial Microbiology, 14, 85–93.
Mckay, D.S., Gibson, E.K., Thomas-Keprta, K.L., Vai, H., Romanek, C.S., Clemett, S.J., Maechling, C.R. and Zare, R.N., 1996, Search for past life on Mars: Possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Science, 273, 924–930.
Morita, R.Y., 1975, Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriology Review, 39, 144–167.
Mortimer, R.J.G. and Coleman, M.L., 1997, Microbial influence on the oxygen isotopic composition of diagenetic siderite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 6, 1705–1711.
Mortimer, R.J.G., Coleman, M.L. and Rae, J.E., 1997, Effect of bacteria on the elemental composition of early diagenetic siderite: implications for paleoenvironmental interpretations. Sedimentology, 44, 759–765.
Nealson, K.H. and Myers, C.R., 1990, Iron reduction by bacteria: A potential role in the genesis of banded iron formation. American Journal of Science, 290A, 35–45.
Pedersen, K., 2000, Exploration of deep intraterrestrial microbial life: current perspectives. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 185, 9–16.
Phelps, T.J., Raione, E.G., White, D.C. and Fliermans, C.B., 1989, Microbial activity in deep subsurface environments. Geomicrobiology Journal, 7, 79–91.
Rajan, S., Mackenzie, F.T. and Glenn, C.R., 1996, A thermodynamic model for water column precipitation of siderite in the Plio-Pleistocene Black Sea. American Journal of Science, 296, 506–548.
Roden, E.E. and Zachara, J.M., 1996, Microbial reduction of crystalline Fe(III) oxides: Influence of oxide surface area and potential for cell growth. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 1618–1628.
Roh, Y., Lauf, R.J., McMillan, A.D., Zhang, C., Rawn, C.J., Bai, J. and Phelps, T.J., 2001, Microbial synthesis and the characterization of some metal-doped magnetite. Solid State Communications, 118, 529–534.
Roh, Y. and Moon, H.S., 2001, Iron reduction by a psychrotolerant Fe(III)-reducing bacterium isolated from ocean sediment. Geosciences Journal, 5, 183–190.
Roh, Y., Liu, S.V., Li, G., Huang, H., Phelps, T.J. and Zhou, J., 2002, Isolation and characterization of Metal-reducingThermoanaerobacter strains from deep subsurface environments of the Piceance Basin, Colorado. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 6013–6020.
Rosselló-Mora, R.A., Caccavo, F. Jr., Osterlehner, K., Springer, N., Springer, N., Spring, S., Schüler, D., Ludwig, W., Amann, R., Vanncanneyt, M. and Schleifer, K.H., 1994. Isolation and taxonomic characterization of a halotolerant, facultatively iron-reducting bacterium. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 17, 569–573.
Rye, K., Dickson, A.D., Schiavon, N., Coleman, M.L. and Cox, M., 1990, Formation of siderite-Mg-calcite-iron sulfide concretions in intertidal marsh and sandflat sediments, north Norfolk, England. Sedimentology, 37, 325–343.
Stookey, L.L., 1970, Ferrozine-a new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Analytical Chemistry, 42, 779–781.
Suess, E., 1979, Mineral phases formed in anoxic sediments by microbial decomposition of organic matter. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43, 339–352.
Stapleton, R.D.Jr., Sabree, Z.L., Palumbo, A.V., Moyer, C., Devol, A., Roh, Y. and Jhou, J., 2003, Metabolic capabilities and distribution ofShewanella isolates from diverse marine environments. Aquatic and Microbial Ecology (in review)
Urrutia, M.M., Roden, E.E., Fredrickson, J.M. and Zachara, J.M., 1998, Microbial and surface chemistry controls on reduction of synthetic Fe(III) oxide minerals by the dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteriumShewanella alga. Geomicrobiology Journal, 15, 269–291.
Walker, J.C.G., 1984, Suboxic diagenesis in banded iron formation. Nature, 309, 340–342.
Zachara, J.M., Fredrickson, J.K., Smith, S.C. and Gassman, P.L., 2001, Solubilization of Fe(III) oxide-bound trace metals by a dissimilatory Fe(III) reducing bacterium. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 65–73.
Zachara, J.M., Kukkadapu, R.K., Fredrickson, J.K., Gorby, Y.A. and Smith, S.C., 2002, Biomineralization of poorly crystalline Fe(III) oxides by dissimilatory metal reducing bacteria (DMRB). Geomicrobiology Journal, 19, 179–207.
Zhang, C., Liu, S., Logan, J., Mazumer, R. and Phelps, T.J., 1996, Enhancement of Fe(III), Co(III), and Cr(VI) reduction at elevated temperatures and by a thermophilic bacterium. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 57/58, 923–932.
Zhang, C., Liu, S., Phelps, T.J., Cole, D.R., Horita, J., Fortier, S.M., Elless, M. and Valley, J.W., 1997, Physiochemical, mineralogical, and isotopic characterization of magnetite-rich iron oxides formed by thermophilic iron-reducing bacteria. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 4621–4632.
Zhang, C., Vali, H., Romanek, C.S., Phelps, T.J. and Liu, S., 1988, Formation of single-domain magnetite by a thermophilic bacterium. American Mineralogist, 83, 1409–1418.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Lee, I. & Roh, Y. Biomineralization of a poorly crystalline Fe(III) oxide, akaganeite, by an anaerobic Fe(III)-reducing bacterium (Shewanella alga) isolated from marine environment. Geosci J 7, 217–226 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910288
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02910288