Abstract
Objective
To compare the efficacy of conventional medical treatment versus transtympanic dexamethasone application into middle ear as treatment modality in Meniere's disease.
Study Design
Prospective randomized study.
Setting
Tertiary referral centre.
Method
Forty patients of Meniere's disease were treated, 20 by conventional method and 20 by transtympanic dexamethasone applications.
Intervention
Theraputic.
Results
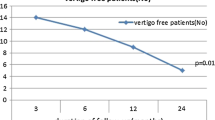
Vertigo control of 85% achieved in study group when compared to 80% in control group, 15% of patients had hearing improvement in study group while 10% had hearing improvement in control group. Aural fullness and tinnitus control were identical in both groups.
Conclusions
Both modalities of therapy were found to have almost equal efficacy, with Intra tympanic steroid (ITS) therapy having an edge over conventional therapy in cases with severe attacks and shorter duration of symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCabe BF. Antoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol 1979;88:585–90.
Cheng KC, Mastsvoka H, Lee KM, Kim NS, Krug MS, Kwon SS, et al. Proto-oncogene Raf-1 As an autoantigen in Menieres's disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Layngol 2000;1093–8.
Tomiyama S, Nonaka M, Gotoh Y, Ikezono I, Yagi I. Immunological approach to Meniere's disevase: Vestibular Immune injury following immune reaction of the endolymphatic sac. Otorhinol Laryngol J 1994;56:11–8.
Shea JJ, Xiani Ge. Dexaniethasone perfusion of the Iabyninth plus intravenous dexamethasone for Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1996;29:353–8.
Itoh A, Sakata E. Treatment of vertibular disorders. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 1991;481:617–23.
Yoshino K, Ohashi T, Urushibata T, Kenomochi M, Akagi M. Antibodies is type II collagen and immune complexes in Meniere's disease. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 1996;522:79–85.
Hall S, Higher S. Dobre Diuretic and diet effect on Meniere's disease evaluated by 1985. Committee on hearing and equilibrium guidelines. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;109:680–9.
Aantaa E. Treatment of acute vestibular vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 1991;479:44–7.
Shea J Jr, Xiafni GE. Dexamethasone perfusion of the labyrinth plus intravenous dexamethasone for Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Gun North Am 1996;29:353–8.
Sennaroglu L, Sennaroglu G, Gursel, Dml FM. Intratympanic dexamethasone, Intratympanic Gentamicin and Endolymphatic sac surgery for intractable vertigo in Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001;125:537–43.
Arriga, Goldman. Hearing results of intratympanic steroid treatment of endolymphatic hydrops. Laryngoscope 1998;108:1682–5.
Barrs D, Keyer J, Stallworth C, John T. Mc Elveen. Intratympanic steroid injections for intractable Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope 2001;111:2100–4.
Pyykko L, Magnusson M, Schalen L, Enbom H. Pharmacological treatment of vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 1998;455:77–81.
Zee DS. Perspectives on the pharmacotherapy of vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol 1985;111:609–12.
Hamid MA. Intratympanic dexamethasone perfusion in Meniere's. Presented at the spring meeting of the American Neurotology Society. Palm desert, CA. May 2001:12.
Silverstein H. Use of a new device, the Microwik TM, to deliver medication to the inner ear. Ear nose Throat J 1999;78:595–600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paragache, G., Panda, N.K., Ragunathan, M. et al. Intratympanic dexamethasone application in Meniere's disease—Is it superior to conventional therapy?. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 57, 21–23 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907620