Abstract
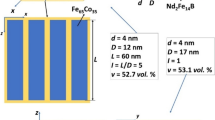
Taking Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe as example, the exchange-coupling interactions between magnetically soft and hard grains in nanocomposite permanent materials and their effects on the effective anisotropy of materials were investigated. The calculation results expressed that the exchangecoupling interactions are enhanced with the reduction of grain size, and the effective anisotropy of materials decreases with the reduction of grain size and the increase of magnetically soft phase component. The remanence and the effective anisotropy of materials possess the opposite variation trend with the change of grain size and phase ratio. The mean grain size should be in the range of 10–15 nm and the ratio of soft phase should be less than 50% for getting the magnet with high energy product.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herzer, G., Grain size dependence of coercivity and permeability in nanocrystalline ferromagnets, IEEE Trans. on Mag., 1990, 26: 1397.
Kneller, E. F., Hawig, R., The exchange-spring magnet: A new material principle for permanent magnets, IEEE Trans. on Mag., 1991, 27: 3588.
Skomski, R., Coey, J. M. D., Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets, Phys. Rev. B., 1993, 48: 15812.
Bauer, J., Seager, M., Zem, A. et al., Nanocrystalline FeNdB permanent magnets with enhanced remanence, J. Appl. Phys., 1996, 80(3): 1667.
Grössinger, R., Dehlgren, M., Exchange coupled hard magnetic materials in pulsed high magnetic field, Physica B., 1998, 246–247: 213.
Schrefl, T., Fidler, J., Finite element modeing of nanocomposite magnets, IEEE Trans. on Mag., 1999, 35(5): 3223.
Kronmüler, H., Fischer, R., Seeger, M. et al., Micromagnetism and microstructure of hard magnetic materials, J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys., 1996, 29: 2274.
Schmidts, H. F., Kronmüler, H., Magnetization process in small ferromagnetic particles with inhomogeneous demagnetizing field and uniaxial anisotropy, J. Magen. Magen. Mater., 1994, 129: 361.
Gao Youhui, Zhu Jinghan, Weng Yuqing et al., Domain structure in Fe-implanted Nd2Fe14B magnets, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1999, 74: 1749.
Sun, X. K., Zhang, J., Chu, Y. L. et al., Dependence of magnetic properties on grain size of a-Fe in nanocomposite (Nd, Dy) (Fe, Co, Nb, B)5.5/α-Fe magnets, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1999, 74: 1740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., Feng, W., Chen, W. et al. Exchange-coupling interaction and effective anisotropy in nanocomposite permanent materials. Chin. Sci. Bull. 47, 1166–1169 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907601
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907601