Abstract
Three isolates of strawberry mottle agent (SMA) from strawberry plants were regularly maintained and multiplied by mechanical inoculation onChenopodium quinoa plants showing mosaic and mottle symptoms. The use of 5 mM borate buffer pH 8.6 or tap water pH 6.6-7.9 with 4 % (m/v) charcoal for homogenization resulted usually in 100 % infection. The total of 2090 plants were infected from 2264 inoculated ones under the same conditions. The infectivity of SMA isolates in crude sap ofC. quinoa was retained from 48 h to 72 h at 20 °C. The dilution end points of SMA isolates were 10-3 while the inactivation temperatures were between 50 and 55 °C. The infectivity of SMA isolates in frozen leaves ofC. quinoa was detected still after six months.
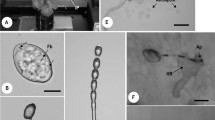
Purification procedure of SMA is based on using low molar 25 mM borate buffer pH 8.3 with cysteine hydrochloride, DIECA and Tween 20 for homogenization of infectedC. quinoa leaves, polyethyleneglycol precipitation, clarification with octanol, low and high speed centrifugation and sucrose density-gradient centrifugation. Partially purified preparations are highly infectious, causing mosaic, mottling and tip necrosis ofC. quinoa plants. The agent could not be completely separated from host proteins and it could not be concentrated to a high extent. Isometric virus-like particles 14-16 nm were observed in partially purified preparations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, A. N., Barbara, D. J.: Transmission of a virus fromFragaria vesca infected with strawberry mottle virus toChenopodium quinoa. -Acta Hort.186: 71–76, 1986.
Frazier, N. W.: Transmission of strawberry mottle virus by juice and aphids to herbaceous plants. -Plant Dis. Rep.52: 64–67, 1968.
Frazier, N. W., Posnette, A. F.: Relationships of the strawberry viruses of England and California.-Hilgardia27: 455–514, 1958.
Harris, R. V.: A bibliographical note on the distinction between mild and severe strawberry crincle. -East Mailing Res. Sta. Rep.1937: 201–202, 1938.
Hepp, R. V., Converse, R. H.: Transmission of strawberry mottle virus betweenChenopodium quinoa andFragaria vesca by aphid and sap inoculation. -Phytopathology77: 1239, 1987.
Kitajima, E. W., Betti, J. A., Costa, A. S.: Isometric, virus-like particles in leaf tissues ofFragaria vesca L. infected with strawberry mottle virus. -Cien. Cult.23: 649–655, 1971.
Leistner, H. U., Graichen, K.: Nachweis isometrischer Partikeln in Phloemgewebe vonFragaria vesca L. cv.semperflorens nach Infektion mit dem Blattscheckungs-Virus der Erdbeere (strawberry mottle virus). -Arch. Phytopathol. Pflanzenschutz22: 511–515, 1986.
Polák, J., Bezpalcová, H.: [Diagnostic methods, the incidence and spreading of strawberry mottle virus in the Czech Socialist Republic] In Czech. -Sbor. ÚVTIZ-Zahradnictví14:259–266, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polák, J., Van der Meer, F.A. & Huttinga, H. Attempts at Multiplication, Purification, Electron Microscopy, and Characterisation of Three Isolates of the Strawberry Mottle Agent. Biol Plant 33, 377–385 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897689
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897689