Abstract
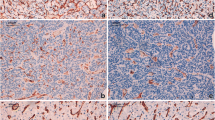
Angiogenesis seems to contribute to tumor growth and the development of metastases. There may be an association between the vascular density of individual tumors and their prognosis. In the present survey we studied 53 cases of renal cell carcinoma investigating possible relationship between histologic grade and microvessel density (MVD) measured by an image analysis system. According to our results MVD was significantly associated with the histologic grade, higher grades being accompanied with a higher MVD. Further studies are needed to investigate a possible connection of MVD with the prognostic role of grade in RCCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denekamp J, Hobson B: Endothelial-cell proliferation in experimental tumours. Br J Cancer 46: 711–720, 1982
Diaz-Cano SJ, de Miguel M, Blanes A, Galera H, Wolfe HJ: Contribution of the microvessel network to the clonal and kinetic profiles of adrenal cortical proliferative lesions. Hum Pathol 32: 1232–1239, 2001
Gelb A, Sudilovsky D, Daniel Wu C, Weiss L.M, Medeiros JL: Appraisal of intratumoral microvessel density, MIB-1 score, DNA content and p53 protein expression as prognostic indicators in patients with locally confined renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 80: 1768–1775, 1997
Ginnara JR, Ward LM, Porter FD, Wagner JR, Devor DE, Grinberg A, Emmert-Buck MR, Westphal H, Klausner RD, Linehan WM: Defective placental vasculogenesis causes embryonic lethality in VHL-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 9102–9107, 1997
Haigh JJ, Gerber HP, Ferrara N, Wagner EF: Conditional inactivation of VEGF-A in areas of collagen2ga1 expression results in embryonic lethality in the heterozygous state. Development 127: 1445–1453, 2000
Heicappell R: Cadherins in renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 19(2C): 1501–1504, 1999
Herbst C, Kosmehl H, Stiller KJ, Berndt A, Eiselt M, Schubert J, Katenkamp B: Evaluation of microvessel density by computerised image analysis in human renal cell carcinoma. Correlation to pT category, nuclear grade, proliferative activity and occurrence of metastasis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 124:141–147, 1998
Imao T, Egawa M, Takashima H, Koshida K, Namiki M: Inverse correlation of microvessel density with metastasis and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol. 1:948–953, 2004
Joo HJ, Oh DK, Kim YS, Lee KB, Kim SJ: Increased expression of caveolin-1 and microvessel density correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 93:291–296, 2004
McCue PA, Gor stein F: Genetic markers in renal cell carcinomas. Hum Pathol 32: 1027–1028, 2001
MacLennan GT, Bostwick DC: Microvessel density in renal cell carcinoma: lack of prognostic significance. Urology 46:27–30, 1995
Nativ O, Sabo E, Reiss A, Wald M, Madjar S, Moskovitz B: Clinical significance of tumor angiogenesis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Urology 51: 693–696, 1998
Pantuck A, Zeng G, Belldegrun A, Figlin R: Pathobiology, prognosis and targeted therapy for renal cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 9: 4641–4652, 2003
Paraskevakou E, Kavantzas N, Pavlopoulos PM, Delibasis A, Yova D, Davaris P: Computerized nuclear morphometry of renal cell carcinomas. Gen Diagn Pathol 142: 101–104, 1996
Rioux-Leclercq N, Epstein JI, Bansard JY, Turlin B, Botard JJ, Manunta A, Chan T, Ramee MP, Lobel B, Moulinoux JP: Clinical significance of cell proliferation, microvessel density and CD44 adhesion molecule expression in renal cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 32: 1209–1215, 2001
Tuna B, Yorukoglu K, Unlu M, Mungan MU, Kirkali Z: Association of mast cells with microvessel density in renal cell carcinomas. Eur Urol 50:530–534, 2006
Van Brussel JP, Mickisch GH: Prognostic factors in renal cell and bladder cancer. BJU Int 83: 902–908, 1999
Yagasaki H, Kawata N, Takimoto Y, Nemoto N: Histopathological analysis of angiogenic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol 10:220–227, 2003
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, Hwu P, Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Steinberg SM, Chen HX, Rosenberg SA: A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:427–434, 2003
Yoshino S, Kato M, Okada K: Clinical significance of angiogenesis, proliferation and apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 20: 591–594, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavantzas, N., Paraskevakou, H., Tseleni-Balafouta, S. et al. Association between microvessel density and histologic grade in renal cell carcinomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 13, 145–148 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893490
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893490