Abstracts
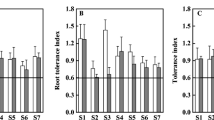
We investigated the tolerance ofHippochaete ramosissimum and the changes in physiological metabolism following exposure to copper using pot experiments and analyzing plant physiology and biochemistry. The results showed that Cu tolerance inHippochaete ramosissimum varied significantly between different populations; the tolerance of plants living in Cu polluted areas for extended periods of time exceeded that of plants living in unpolluted areas. SOD and POD activities in highly Cu tolerant plants increased noticeably following exposure to Cu. This indicates that maintaining and increasing the two kinds of protective enzyme activities are the primary foundations of plant tolerance. However, no change in CAT activity was demonstrated following Cu exposure. In summary, there existed considerable differences in physiological metabolism between different populations ofHippochaete ramosissimum following exposure to Cu.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, X. Y., Zhao, K. F., Mechanism of heavy metal injury and resistance of plants, Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2001, 7(1): 92–99.
Yang, J. R., Huang, Y., Mechanism of heavy metal tolerance of plants, Chin. J. Ecol., 1994, 13(6): 20–26.
Yang, J. R., He, J. Q., Zhang, G. X., Reaction of some enzyme activities in crops of different tolerance to the stress of Cd, Chin. Environ. Sci., 1996, 16(2): 113–117.
Yang, J. R., He, J. Q., Huang, Y., Inter- and intra-specific differences of crops in cadmium tolerance (I): Interspecific difference, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 1994, 5(2): 192–196.
Yang, J. R., Inter- and intra-specific differences of crops in cadmium tolerance (II): Intraspecific difference, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 1993, 6(suppl): 132.
Yang, J. R., Tolerance mechanism of crops to Cd pollution, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 1995, 6(1): 87–91.
Wang, Y. B., Liu, D. Y., Li, Y., Reclamation and plant colonization of copper mine tailings in Tongling, Anhui Province, Acta Botanica Sinica, 2004, 46(7): 780–787.
Li, Y., Liu, D. Y., Investigation on the vegetation of the copper tail mining wasteland in Tongling (Shizishan), Anhui, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 2003, 14(11): 1981–1984.
Lena, Q. M., Ma, L. K., A fern that hyper-accumulates arsenic, Nature, 2001, 409: 579.
Wei, Z. Y., Chen, T. B., Hyperaccumulators and phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: A review of studies in China and abroad, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2001, 21(7): 1196–1203.
Zhang, Z. L., Guide for Plant Physiology Experimentation, Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990, 160–162.
Zhu, G. L., Plant Physiology Experimentation, Beijing: Peking University Press, 1990.
Zhu, Y. J., Effects of arsenic stress on the growth and metabolism of the wheat root system, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2000, 20(4): 707–710.
Proinoke, X. H., The Methods of Analysis of Biochemistry on Plants, Beijing: Science Press, 1981, 197–209.
Sun, C. P., Radical Biology, Hefei: Chinese Science and Technology University Press, 1999, 12–84.
Celina, M. L., Claudio, A. G., Victorio, S. T., Oxidative damage caused by an excess of copper in oat leaves, Plant Cell Physiol., 1994, 35: 11–15.
Zhou, C. F., Wu, G. R., The role of antioxidant systems in Cu2+ stress resistance inAlternanthera philoxeroides, Acta Botanica Sinica, 2001, 43(4): 389–394.
Xu, Q. S., Shi, G. X., Effects of Cd and Zn combined pollution on chlorophyll content and scavenging system of activated Oxygen in leaves ofOttelia alismoides (L.) Pers, Chin. J. Ecol., 2003, 22(1): 5–8.
Huang, Y. S., Luo, G. H., Peroxidation damage of oxygen free radicals induced by cadmium to plant, Acta Botanica Sinica, 1997, 39(6): 522–526.
Luna, C. M., Gonzalez, C. A., Tripp, V. S., Oxidative damage caused by on excels of copper in oat leaves, Plant Cell Physiol., 1994, 35: 11–15.
Luo, L. X., Sun, T. Y., Le, Y. H., Accumulation of Superoxide radical in wheat leaves under Cd stress, Acta Sci. Circums., 1998, 18(5): 495–499.
Luo, L. X., Sun, T. Y., Le, Y. H., Effects of Cd stress on lipid peroxidation in wheat leaves, Chin. Environ. Sci., 1998, 18(1): 72–75.
Chis Marc, V. H., Dirk, I., Superoxide disutase and stress tolerance, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 1992, 43: 83.
Yan, B., Dai, Q.-J., Li, X.-Z., Huang, S.-B., Wang, X., Flooding induced membrane damage, lipid oxidation and activated oxygen generation in corn leaves, Plant Soil, 1996, 179: 261–268.
Vera-Estrella, R., Higgins, V. J., Blumwald, E., Plant defense response to fungal pathogens (II): G-protein mediated changes in host plasma membrane redox reaction, Plant Physiol., 1994, 106: 97–102.
Sundaresan, M., Yu, Z.-X., Ferrans, V. J., Irani, K., Finkel, T., Requirement for generation of platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction, Science, 1995, 270: 296–299.
Crane, F. L., Sun, I. L., Sun, E. E., Crowe, R. A., Plasma membrane redox and regulation of cell growth, Protoplasma, 1995, 184: 3–7.
Zhou, Q., Huang, X. H., Tu, K. G., Huang, G. Y., Zhang, J. H., Cao, Y. H., Ecophysiological effects of Laon Glycine max seedling under Cd stress, Chin. Environ. Sci., 1998, 18(5): 442–445.
Qi, Z. Z., Peng, Y. K., Song, J. X., Zhang, H., Liu, G. Q., Effects of Hg on the seeding growth and oxidases on enzymes in crops, Acta Sci. Circums., 1991, 11(3): 370–374.
Van Assche, F., Clijsters, H., Effects of metal on enzyme activity in plants, Plant Cell Environ., 1990, 13: 195–206.
Liu, D. Y., Wang, Y. B., Effect of sewage irrigation on wheat growth and its activate oxygen metabolism, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 2202, 13(10): 1319–1322.
Li, Y., Effects of cadmium and iron on the some physiological indication in leaves of tobacco, Acta Ecol. Sin. (in Chinese), 1992, 12(2): 147–154.
Ma, C. C., Hg harm on cell membrane of rape leaf and cell endogenous protection effect, Chin. J. A. Ecol. (in Chinese), 1998, 9(3): 323–326.
Wang, Y. B., Liu, D. Y., Effect of Cu, As and their combination pollution on eco-physiological index of wheat, Chin. J. A. Ecol., 2001, 12(5): 773–776.
Xu, Q. S., Effects of Cd2+ on antioxidase system and ultrastructure ofOttelia alismoides (L.), Rural Eco-Environ, (in Chinese), 2001, 17(2): 30–34.
Zhao, H. Q., Hong, F. S., The changes of activity of protective enzymes in wheat seedling under Hg stress, Agro-Enviro Protection, 1998, 17(1): 20–21.
Luna, C. M., Gonzalez, C. A., Troppi, V. S., Oxidative damage caused by an excess of copper in oat leaves, Plant Cell Physiol., 1994, 35: 11–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Li, Y., Chu, L. et al. Study of the tolerance ofHippochaete ramosissimum to Cu stress. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 48 (Suppl 1), 150–155 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889813
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889813