Abstract
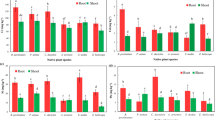
Soil samples were collected from 7 sites in the up-, mid-and down-reach along and nearby the wastewater irrigation channel, western Shenyang of China. The concentrations of selected pollutants (mineral oil, PAHs - polycycle aromatic hydrocarbons and Cd) were determined by UV spectrometer, HPLC and AAS (atomic adsorption spectrometer) spectrometer, respectively. Toxicity effects of soils were evaluated by seedling emergence test with root length of wheat as the end-point and by earthworms test with the mortality rate and inhibition rates of body weight as endpoints. Results showed accumulation of pollutants for most soils with concentration of 200.2 mg.kg−1∼1600 mg.kg−1 for mineral oil, 0.33 mg.kg−1∼1.81 mg.kg−1 for Cd and 900.16 mg.kg−1 ∼ 2737.91 mg.kg−1 for PAHs. The inhibition rates of root elongation were from −20% up to 40 %, and mortality rates of earthworms ranged from 0%∼40% from the exposure period of two weeks to eight weeks by sampling interval of two weeks, the inhibition rates of earthworm growth were from −19.36% to 34.53%, showing effects of stimulation at 2 weeks to an increasing effects of inhibition at 4, 6 and 8 weeks, respectively. Mortality rates correlated with the loss of body weight of earthworms.
This study indicated the potential risk of pollutants of environmental low content in soil by the determination of selected chemicals combined with toxicity indexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pang, J. L., Huang, C. C., Sun, J.N., Heavy metal content of sewage irrigated soil in Xi’an and its influence on tomato, Soil and Environment Sciences (in Chinese), 2001, 10(2): 94–97.
Wang, X. J., Xi, S., Special structures of trace element contents in sewage irrigated soil at the eastern suburb of Beijing, Acta Scientiae Circu. Matantiae(in Chinese), 1997, 17(4): 413–416.
Wang, X. J., Xi, S., Kriging analysis and heavy metal pollution assessment for soil from eastern suburb of Beijing City, China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 1997, 17(3): 225–227.
Sverdrup, L. E., Jensen, J., Krogh, P. H. et al., Studies on the effect of soil aging on the toxicity of pyrene and phenanthrene to a soil-dwelling springtail, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2002, 21: 489–492.
Juvonen, R., Martikainen, E., Schultz, E. et al., Abattery of toxicity tests as indicators of decontamination in composting oily waste, Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf, 2000, 47: 156–166.
Sayles, G. D., Acheson, C. M., Kupeerle, M.J. et al., Land treatment of PAH-contaminated soil: Performance measured by chemical and toxicity assays, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1999, 33: 4310–4317.
Knoke, K., Marwood, T. M., Cassidy, M. B. et al., A comparison of five bioassays to monitor toxicity during bioremediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil, Water, Air and Soil Pollut., 1999, 110: 157–169.
Mishra, A., Choudhuri, M. A., Monitoring of phytotoxicity of lead and mercury from germination and early seeding growth indices in two rice cultivars, Water Air Soil Pollut., 1999, 114: 339–346.
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development), OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals 208: Terrestrial Plants, Growth Test, Paris, France, 1984.
Chang, L. W., Meier, J. R., Smith, M. K., Application of plant and earthworm bioassays to evaluate remediation of a lead-contaminated soil, Arch Environ. Toxicol., 1997, 32: 166–171.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization), Soil quality-Effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetidae)-part 1: Determination of acute toxicity using artificial soil substance, 1993, 11268–1.
Gong, P., Sun, T. H., Beudert, G. et al., Ecological effects of combined organic or inorganic pollution on soil microbial activities, Water Air Soil Pollut., 1997, 96: 133–143.
BEP, MEPCTC (Bureau of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Environmental Protection of Construction of Town and Countries), Analysis methods of environmental monitoring, Environmental Science Press of China (in Chinese), 1986, 329–331.
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), Standard guide for conducting terrestrial plant toxicity tests, E 1963–98, West Conshohocken, PA, 1998, 1–19.
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development), Proposal for Updating Guideline 208: Terrestrial (Non-Target) Plant Test 208A-Seedling Emergence and Seedling Growth Test, Paris, France, 2000.
Song, Y. F., Chang, S. J., Li, L. et al., Accumulation and dynamic change of polycycle aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in wastewater irrigated soils, Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 1997, 8(1): 93–98.
Gong, P., Wilke, B. -M., Fleischmann, S., Soil-based phytotoxicity of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) to terrestrial higher plants, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1999, 36: 152–157.
Song, Y. F., Xu, H.X., Ren, L. P. et al., Ecotoxic effect of heavy metals on the seed germination and root elongation of turnip in soils, Chin. J. Ecol. (in Chinese), 2001a, 20: 4–8.
Song, Y. F., Xu, H. X., Ren, L. P. et al., Inhibitory effect of heavy metals on the seed germination and root elongation of tomato, China Environ Sci. (in Chinese), 2001b, 21: 390–394.
Påhlsson, A.B., Toxicity of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb) to vascular plants, Water Air Soil Pollut., 1989, 47: 287–319.
Heimbach, F., Correlations between three methods for determining the toxicity of chemicals to earthworms, Pestic. Sci., 1984, 15: 605–611.
Van Gestel, C. A. M., Ma, W.-C., Toxicity and bioaccumulation of chlorphenols in earthworms in relation to bio-availability in soil, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 1988, 15: 289–297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Zhou, Q., Gong, P. et al. Ecotoxicity of soils contaminated with industrial and domestic wastewater in western shenyang, China. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 48 (Suppl 1), 48–56 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889801
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02889801