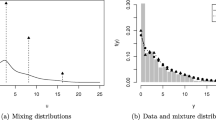
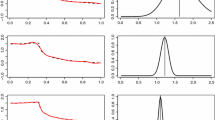
Summary
Computational constrains often limit the practical applicability of coherent Bayes solutions to unsupervised sequential learning problems. These problems arise when attempts are made to learn about parameters on the basic of unclassified observations, each stemming from any one ofk classes (k≥2).
In this paper, the difficulties of the Bayes procedure will be discussed and existing approximate learning procedures will be reviewed for broad types of problems involving mixtures of probability densities. In particular a quasi-Bayes approximate learning procedure will be motivated and defined and its convergence properties will be reported for several special cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AGRAWALA, A. K., (1970). Learning with a probabilistic teacher.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-16, 373–379.
AGRAWALA, A. K. (1973). Learning with various types of teachers.Proc. 1st. Int. Joint Conf. Pattern Recognition, 453–461.
ATHANS, M., WHITING, R.H. & GRUBER, M., (1977). A suboptimal estimation algorithm with probabilistic editing for false measurements with application to target tracking with wake phenomena.IEEE Trans. on Automat. Contr. AC-22, 372–384.
COOPER, D.B. (1975). On some convergence properties of ‘learning with a probabilistic teacher’ algorithms.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-21, 699–702.
DAVISSON, L.D. (1970). Convergence probability bounds for stochastic approximation.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-16, 680–685.
DAVISSON, L.D. and SCHWARTZ, S.C., (1970). Analysis of a decision directed receiver with unknown priors.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-16, 270–276.
FRALICK, S.C. (1967). Learning to recognize patterns without a teacher.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory IT-13, 57–64.
FU, K.S. (1968).Sequential Methods in Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York: Academic Press.
GLADYSHEV, E.G. (1965). On stochastic approximation.Theory of Prob. and its Appl.10, 275–278.
HARRISON, P.J. and STEVENS, C.P. (1976). bayesian forecasting.J. R. Statist. Soc. B. 38 205–247.
HO, Y.C. and AGRAWALA, A.K. (1968). On pattern classification algorithms; introduction and survey.Proc. IEEE 56, 2102–2114.
KATOPIS, A. and SCHWARTZ, S.C. (1972). Decision directed learning using stochastic approximation.Proc. Modelling and Simulation Conf.,-473–481.
KAZAKOS, D. (1977). Recursive estimation of prior probabilities using a mixture.IEEE Trans. on Inform Theory IT-23, 203–211.
KAZAKOS, D. and DAVISSON, L.D. (1979). An improved decision-directed detector.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory Submitted to publication.
MAKOV, U.E. (1980). On the choice of gain functions in, recursive estimation of prior probabilities.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory. IT-26, 497–498.
— (1980a). A quasi-Bayes approximation for unsupervised filters.IEEE Trans. on Autom. Contr. AC-25, 842–847.
MAKOV, U.E. and SMITH, A.F.M. (1976). Quasi Bayes procedures for unsupervised learning.Proc. IEEE Conf. on Decision and Control. 408–412. New York: IEEE Inc.
— (1977). A quasi-Bayes unsupervised learning procedure for priors.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-23, 761–764.
OWEN, J.R., (1975). A Bayesian sequential procedure for quantal response in the context of adaptive mental testing.J. Amer. Statist. Assoc. 70, 351–356.
PATRICK, E.A. (1972).Fundamentals of Pattern Recognition. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
PATRICK, E.A., COSTELLO, J.P., and MONDS, F.C. (1970). Decision directed estimation for a two class decision boundary.IEEE Trans. on Computers C-19, 197–205.
QUANDT, R.E. and RAMSEY, J.B. (1978). Estimating mixture of normal distributions and swithching regressions.J. Amer. Statist. Assoc. 73, 730–738.
ROBBINS, H. and MONRO, S. (1951). A stochastic approximation method.Ann. Math. Statist. 25, 400–407.
SCHWARTZ, S.C. and KATOPIS, A. (1977). Modified stochastic approximation to enhance unsupervised learning.,Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Decision and Control. 1067–1069.
SCUDDER, H.J. (1965). Probability of error of some adaptive pattern-recognition machines.IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory IT-11, 363–371.
SILVERMAN, B.W. (1979). Some asymptotic properties of the probabilistic teacher.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory. IT-26, 296–249.
SMITH, A.F.M. and MAKOV, U.E. (1978). A quasi-Bayes sequential procedure for mixtures.J. Roy. Statist. Soc. B 40, 106–112.
— (1980). Bayesian detection and estimation of jumps in linear systems.Proceedings of the IMA Conference on the Analysis and Optimization of Stochastic Systems (O.L.R. Jacobset.al., eds), 333–346. New York: Academic Press.
SMITH, A.F.M., (1981). Approximation to Bayes learning procedures.IEEE Trans. on Inform., Theory To appear.
SPRAGINS, J. (1966). Learning without a teacher.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory IT-12, 223–230.
TITTERINGTON, D.M. (1976). Updating a diagnostic system using unconfirmed, cases.Appl. Statist. 25, 238–347.
YAKOWITZ, S.J. (1970). Unsupervised learning and the identification of finite mixtures.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory IT-16, 330–338.
YOUNG, T.Y. and CORALUPPI, G., (1970). Stochastic estimation of a mixture of normal density functions using an information criterion.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory IT-16, 258–263.
YOUNG, T.Y. and FARJO, A.A (1972). On decision directed estimation and stochastic approximation.IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory IT-18, 671–673.
YOUNG, T.Y. and CALVERT, T.W. (1974).Classification, Estimation and Pattern Recognition. New York: American Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makov, U.E. Approximations of unsupervised Bayes learning procedures. Trabajos de Estadistica Y de Investigacion Operativa 31, 69–81 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888347
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888347