Summary
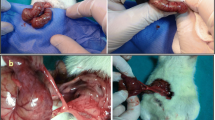
The effect of some medicaments used intraperitoneally on postoperative adhesion after “appendectomy” was studied in experiments with 318 rats and 37 rabbits. Solutions of physiological saline, chymotrypsin, urokinase, Angelica sinensis, potassium fluoro-alkylether sulfonate (F-53) and liquid paraffin were used for injection respectively in the first part of this study, and further research on F-53 was conducted in its second part. The animals in the F-53 group and chymotrypsin group yielded the highest non-adhesion rate and lowest incidence of serious adhesions, as compared with those in the control and other groups with their differences being statistically significant. The anti-adhesion effect of F-53 was definitely demonstrated in the 2nd part of the study. No toxic effects of F-53 on important organs were revealed by histopathological examination. F-53, a surfactant, when applied intraabdominally, can form a thin adsorbent film on the surface of the peritoneum, and this might be the mechanism of its anti-adhesion effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua-de, Q., Hai-an, S. Prevention of postoperative adhesions by intraperitoneal medication — An experimental study. Journal of Tongji Medical University 7, 173–175 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888213
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02888213