Summary
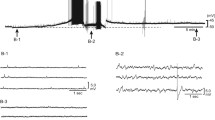
Intracellular recordings were made on perfused preparation isolated from toad dorsal root ganglion (DRG). Of the 51 neurones examined, 46 were of type A, and the remaining 5 of type C cell. The resting membrane potential of these two types of cells was ™60.06±1.30 mV (\(\bar X\)±SE).
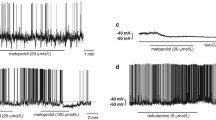
When the preparations were superfused with noradrenaline (NA; 10−4 ™ 10−3M), the changes of Rp were as follows: 1) hyperpolarization, with amplitude of 8.38 ± 1.42mV (\(\bar X\)±SE; 20/48); 2) depolarization, with amplitude of 9.39±1.24mv (\(\bar X\)±SE; 23/48); 3) no effect (5/48). The alteration in membrane potential mentioned above could be neither mimicked by application of isoproterenol, nor blocked by propranolol. Therefore, the possibility of the effect being mediated by β-adrenoceptor could be excluded.
Application of phenylephrine and clonidine induced depolarization and hyperpolarization of membrane potential respectively, while application of prazosin eand yohimbine blocked depolarization and hyperpolarization response induced by NA, respectively.
From the results mentioned above, it may be concluded that depolarization and hyperpolarization induced by NA are mediated by α1- and α2-adrenoceptors on the soma of DRG neurones respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Owman C, Santini M. Adrenergic nerves in spinal ganglia of the cat. Act.a Physiol Scand 1966; 68: 127–8.
Ru LQ, et al. Fluorescence histochemical observations on the sympathetic nerves in spinal ganglia of rat. Acta Acad Med Wuhan 1985; 5: 5–9.
Ito M. The electrical activity of spinal ganglion cells investigated with intracellular microelectrodes. Jap J Physiol 1957; 7: 297–323.
Koketsu K, et al. Effect of quaternary ammonium ions on electrical activity of spinal ganglion cells in frogs. J Neurophysiol 1959; 22: 177–94.
Morita K, Katayama Y. Two types of acetylcholine receptors on the soma of primary afferent neurons. Brain Res 1984; 290: 348–52.
Holz GG, IV et al. Serotonin depolarizes type A and C primary afferents; an intracellular study in bullfrog dorsal root ganglion. Brain Res 1985; 327: 71–9.
Harper AA, Lawson SN. Electrical properties of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones with different peripheral nerve conduction velocities. J Physiol 1985; 359: 47–63.
DeGroat WC. Depolarization of dorsal root ganglia in the cal by GABA and related amino acid: antagonism by picrotoxin and bicuculline. Brain Res 1972; 44: 273–7.
Nishi S, et al. Primary afferent neurons: the ionic mechanism of GABA-mediated depolarization. Neuropharmacology 1974; 13: 215–9.
Hunt Sp, Ninkovic M. Certain substance P-like immunoreactive dorsal root ganglion cells possess opiate and/or histamine binding sites. Br J Pharmacol 1983; 79:414P.
Ninkovic M, Hunt SP. Opiate and histamine H1 receptors are present on some substance P-containing dorsal root ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett 1985; 53: 133–7.
Ninkovic M, et al. Localization of opiate and histamine H1 receptors in the primary sensory ganglia and spinal cord. Brain Res 1982: 241: 197–206.
Werz MA, MacDonald RL. Dynorphin reduces voltage-dependent calcium conductance of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuropeptides 1984; 5: 253–6.
Kojima H, et al. Biochemical and histochemical studies on catecholamines in bullfrog spinal ganglion. J Neurochem 1981; 36: 2106–9.
Stevens RT, et al. Catecholamine varicosities in cat dorsal root ganglion and spinal ventral roots. Brain Res 1983; 216: 151–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi-wang, L., A-jing, W., Ming, L. et al. Noradrenaline depolarization and hyperpolarization mediated by alpha-adrenergic receptors in the soma of dorsal root ganglion neurons. Journal of Tongji Medical University 8, 144–149 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887837
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887837