Summary
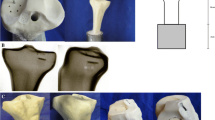
In order to investigate the effect of a new institute-designed absorbable hydroxyapatite microparticles/poly-DL-lactide (HA/PDLLA) fracture fixation devices on experimental fracture healing, 25 rabbits with a transverse transcondylar osteotomy of the distal femur were fixed intramedullary by a HA/PDLLA rod (4. 5 mm in diameter, 30–40 mm in length). The follow-up time lasted 1, 2, 4, 6 and 12 week(s). Roentgenographic, histological and ultrastructural analyses were conducted. The results showed that all osteotomies united within 6 weeks without delay. No accumulation of inflammatory cells was seen. Ultrastructural studies showed that polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages were observed mainly at the 1st week, but only few were noted at the 2nd week. The inflammatory and debridement stages were not prolonged. Large amount of active fibroblasts and some chondroblasts were observed at the 2nd week, suggesting a fibrous callus stage. The main cellularity at 4th week was osteoblasts and osteocytes. Part of osteocytes had already entered the static stage at the 6th week. Our experiment showed that the HA/PDLLA had good biocompatibility, sufficient mechanical streugth and caused no delay to the fracture healing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shikinami Y, Okuno M. Bioresorbable devices made of forged composites of hydroxyapatite (HA) particles and poly-L-lactide (PLLA): Part I. basic characteristics. Biomaterials, 1999, 20: 859
1998, 19 (2):94
Guo X D, Zheng Q X, Du J Yet al. Biodegradation and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite/poly-DL-lactide composites for fracture fixation. J Wuhan Univer Technol (Mater Sci Ed), 1998, 13(4): 9
HA/PDLLA 1999, 16(2):135
HA/PDLLA 1998, 13(6):402
DL 2000, 19(3): 80
1996, 16:653
1982, 1:18
Paivarinta U, Bostman O, Majola Aet al. Intraosseous cellular response to biodegradable fracture fixation screws made of polyglycolide or polylactide. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1993, 112: 71
Verheyen C, Kiein C, Blieckhogervorst Jet al. Evaluation of hydroxylapatite/poly (L-lactide) composites: physico-chemical properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 1993, 4: 58
Grizzi I, Garreau H, Li Set al. Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly (DL-lactic acid) size-dependence. Biomaterials, 1995, 16: 305
Verheyen C, Wijn J, Blitterswijk Cet al. Hydroxylapatite/poly (L-lactide) composites: an animal study on push-out strengths and interface histology. J Biomed Mater Res, 1993, 27: 433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 969202011) and by Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation (No. 99J053).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaodong, G., Qixin, Z., Jingyuan, D. et al. Effect of absorbable hydroxyapatite/poly-DL-lactide rods on experimental fracture healing. Current Medical Science 20, 72–76 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887683
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887683