Summary
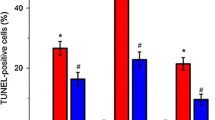
To investigate the effects of L-Tetrahydropalmatine (L-THP) on neuron apoptosis during acute cerebral ischemiareperfusion of rats and explore the effects of heat shock protein (HSP) on neuron apoptosis, Wistar rats were randomly divided into 3 groups; normal group, ischemia-reperfusion group and treatment group. The condition of neuron apoptosis, the survival state of neuron, pathological changes under an electron microscope and the number of HSP70 positive cells were measured in all groups. Results showed that the apoptosis neuron number was increased obviously at the 24th h during reperfusion and was further increased at the 48th h, the 72th h. While the number of survival neurons was decreased gradually with the prolongation of reperfusion time. Treatment with L-THP could decrease the apoptosis neuron number but increase the survival neuron number and the HSP70 positive cell number. Our study suggested that L-THP could decrease apoptosis and necrosis of neuron, up-regulate the expression of HSP70 and protect the cerebral ischemic injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona Met al. Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced respectively by mild and intense injuries with N-methyl-a-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures. Proc Natt Acad Sci USA, 1995, 75:7162
Yang G T, Wang P H, Tang Yet al. Effects of L-tetrahydropalmatine on energy metabolism, endothelin-1 and NO during acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion of rats. J Tongji Medical Univ, 1999, 19(4): 285
1998,14 (5):413
Pulsinelli W A, Brierley J B. A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke, 1979, 10:267
MacMans J P, Bucan A M, Hill I Eet al. Global ischemia can cause DNA fragmentation indicative of apoptosis in rat brain. Neuro Sci Letter, 1993, 164:89
Kihara S, Shiraishi T, Nakagawa S. Visualization of DNA double strand breaks in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 following transient ischemia. Neurosci Lett, 1994, 175:123
Sei Y, Von Lubitz K J, Basile A Set al. Interneucleosomal DNA fragmentation in gerbil hippocampus following forebrain ischemia. Neurosci Lett, 1994, 171:179
Syeller H. Mechanisms and genes of cell suicide. Science, 1995, 10:1445
1999.110
Dwyer B E, Nishimura R N. Heat shock protein in hypoxic-ischemia brain injury A perspective. J Brain Pathol, 1992, 2:245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guangtian, Y., Chonghui, J., Yan, T. et al. Effects of L-Tetrahydropalmatine on neuron apoptosis during acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion of rats. Current Medical Science 20, 106–108 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887043
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887043