Summary
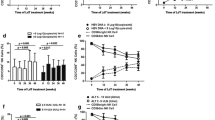
By monitoring immunobiological parameters known to be influenced by interferon (IFN), the natural killer (NK) cell activity of 10 low replication (anti-HBe) virus B-DNA (HBV-DNA) hepatitis patients receiving rIFN α-A, of 5 anti-HBe/δ positive hepatitis patients treated with rIFN α-2, and of 6 high replication (HBeAg) HBV-DNA hepatitis patients on lymphoblastoid IFN was followed-up during therapy. Overall, strong and significant (p<0.01) shift to increase segregated with the low replication subset; the δ positive subset was non-significantly increased (0.30>p>0.2); the high replication subset was depressed in a nearly significant (0.10>p>0.05) manner. Kinetic studies showed the activation of the first subset to follow an early steep rise and a subsequent plateau as fitted with a quadratic curve (p=0.02); an early rise and a depression at 2 months delineated a complex cubic model (p=0.06) in the high replication subset. The profound NK depression was clinically witnessed by a sharp rise of the aminotransferases and following drop of viremia. The study shows thati. discrete patterns of NK response as amenable to mathematical models may associate to differential patterns of virus B replication in patients responding to IFN;ii. point(s) on the NK curve may acquire clinical meaning as they coincide with a consensual or opposite shift of a clinical index.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BMDP Statistical Software. University of California Press, Los Angeles, 1981. BMDP2V, p. 359.
Bonino F., Rosina F., Rizzetto M., Rizzi R., Chiaberge E., Tardanico R., Callea F., Verme G.: Chronic hepatitis in HBsAg carriers with serum HBV-DNA and anti-HBe — Gastroenterology90, 1268, 1986.
Bukovski J. F., Woda B. A., Habu S., Okumura K., Welsh R.: NK depletion enhances virus synthesis and virus-induced hepatitisin vivo — J. Immunol.131, 1531, 1983.
Czaja A. J.: Natural history of chronic active hepatitis. In:Czaja A. J., Dickson E. R. (Eds): Chronic active hepatitis (the Mayo Clinic experience). M. Dekker, New York, 1986; p. 9.
Dooley J. S., Davis G. L., Peters M., Waggoner J. G., Goodman Z., Hoofnagle J. H.: Pilot study of recombinant human α-interferon for chronic type B hepatitis — Gastroenterology90, 150, 1986.
Dusheiko G. M., Dibisceglie A., Bowyer S., Sacks F., Kew M. C.: Prolonged recombinant leukocyte α-IFN treatment of chronic hepatitis B — Hepatology4, 158, 1984.
Ikeda T., Lever A., Thomas H. C.: Evidence for a deficiency of interferon production in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection acquired in adult life — Hepatology6, 962, 1986.
Lotzova E., Savary C. A., Gutterman J. U., Hersh E. M.: Modulation of natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity by partially purified and cloned IFN-α — Cancer Res.42, 2480, 1982.
Maluish A. E., Ortaldo J. R., Sherwin S.: Depression of NK cytotoxicity afterin vivo administration of recombinant leukocyte interferon — J. Immunol.131, 503, 1983.
Martz G.: Editorial — Advanc. therapeut. Commun.1, 5, 1985.
Matsumara N., Yoshikawa T., Kondo M., Imanishi J., Kishida T.: Effect of low dosage of IFN on NK activity in patients with HBsAg-positive chronic active hepatitis — Digestion30, 195, 1984.
Neefe J. R., Sullivan J. E., Ayoob M., Phillips E., Smith F. P.: Augmented immunity in cancer patients treated with α-interferon — Cancer Res.45, 874, 1985.
Negro F., Chiaberge E., Olivero S., Hammer M., Berninger M., Canese M. G., Bonino F.: Hepatitis B virus DNA in anti-HBe positive sera — Liver4, 177, 1984.
Omata M., Imazeki F., Yokoshuka O., Ito Y., Uchiumi K., Mori J., Okuda K.: Recombinant leukocyte α-interferon treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection — Gastroenterology88, 870, 1985.
Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B.: Cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes culturedin vitro — J. Immunol.119, 13, 1977.
Pignatelli M., Waters J., Brown D.: HLA class I antigens on the hepatocyte membrane during recovery from acute hepatitis B virus infection and during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection — Hepatology6, 349, 1986.
Rizzetto M., Shih J. W. K., Gerin J. L.: The hepatitis B virus-associated delta antigen (delta); isolation from liver, development of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay for delta/anti-delta, and partial characterization of delta — J. Immunol.125, 318, 1980.
Rizzetto M., Verme G., Recchia S., Bonino F., Farci P., Aricò S., Calzia R., Picciotto A., Colombo M., Popper H.: Chronic HBsAg hepatitis with intrahepatic expression of the delta antigen. An active and progressive disease unresponsive to immunosuppressive treatment — Ann. intern. Med.98, 437, 1983.
Sanchez-Tapias J. M., Vilar J. H., Costa J., Bruguera M., Ballesta A. M., Rodes J.: Natural history of chronic persistent hepatitis B. Relationship between hepatitis B virus replication and the course of the disease — J. Hepatol.1, 15, 1984.
Scully L. J., Brown D., Lloyd C., Shein R., Thomas H. C.: Immunologic studies before and during IFN therapy in chronic HBV infection: identification of factors predicting response — J. Hepatol. 1987. (In press).
Scully L. J., Shein R., Lok A. S. F., Karayiannis P., Thomas H. C.: Lymphoblastoid IFN therapy of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Different racial response — J. Hepatol.2, 5329, 1965. (Abstract).
Smedile A., Rizzetto M., Denniston K., Bonino F., Wells F., Verme G., Consolo F., Hoyer B., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L.: Type D hepatitis: the clinical significance of hepatitis D virus RNA in serum as detected by a hybridization based assay — Hepatology6, 1297, 1986.
Spina C. A., Fahey J. L., Durkos Smith D., Dorey F., Sarna G.: Suppression of NK cell cytotoxicity in peripheral blood of patients receiving interferon therapy — J. biol. Res. Modif.2, 450, 1983.
Warren H. S.: The generation of specific cytotoxic responses by human lymphocytes requires antigen and activities provided by a lymphokine supernatant — Scand. J. Immunol.14, 71, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Actis, G.C., Maran, E., Saracco, G. et al. Interferon treatment of chronic hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) carriers. A description of the activation profiles of natural killer cells obtained with different schedules of administration in three subsets of carriers. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 17, 331–341 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886916
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02886916