Abstract
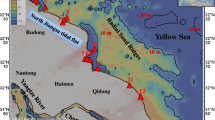
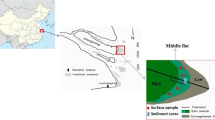
Surface and core sediments from the high, middle and low tidal flats of Shanghai coastal zone were analyzed for heavy metal (e.g. Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, Fe, Mn) concentrations. Besides Cd, the concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cr and Pb are 2–5 times higher than their background values and show serious pollution trend due to the direct discharge of industrial and municipal sewage along the Shanghai tidal flat, as well as the wet and dry depositions of industrial dusts. It seems that heavy metals prefer to accumulate and be enriched in the sediments near large sewage outlets, high flats, and the subsurface layer at the depth of 10–30 cm. Several main factors, which include the direct sewage discharge along the tidal flat, tidal hydrodynamic action, large engineering activity, early diagenesis and windstorm tide, are considered to be responsible for influencing spatial distribution patterns of heavy metals in the Shanghai tidal flat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams, T. P., Bubb, J. M., Lester, J. N., Metal accumulation within salt marsh environments: a review, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1994, 28(5): 277.
Xu, S., Tao, J., Chen, Z. et al., Dynamic accumulation of heavy metals in tidal flat sediments of Shanghai, Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 1997, 28(5): 509.
Liu, M., Xu, S., Chen, Z., The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of tidal mud flat from Nanhui, Shanghai, China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 1998,18(3): 284.
Panutrakul, S., Baeyens, W., Behavior of heavy metals in a mud flat of the Scheldt estuary, Belgium, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1991, 22(3): 128.
Bryan, G. W., Langston, W. J., Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: A review, Environmental Pollution, 1992, 76: 89
Gambrell, R. P., Trace and toxic metals in wetland—A review, Journal of Environmental Quality, 1994, 23: 883.
Emmerson, R. H. C., O’reilly-Wiese, S. B., Macleod, C. L. et al., A multivariate assessment of metal distribution in inter-tidal sediments of the Blackwater estusry, UK, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1997, 34(11): 960.
Jones, B., Turki, A., Distribution and specification of heavy metals in surfacial sediments from the Tees estuary, North-east England, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1997, 34(10): 768.
Izquierdo, C., Usero, J., Gracia, I., Specification of heavy metals in sediments from salt marshes on the Southern Atlantic Coast of Spain, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1997, 34 (2): 123.
Gerritse, R. G., Wallbrink, P. J., Murray, A. S., Accumulation of Phosphorus and heavy metals in the Swan-Canning estuary, Western Austrialia, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 47: 165.
Gerritse, R. G., Wallbrink, P. J., Murray, A. S., Accumulation of Phosphorus and heavy metals in the Peel-Harvey estuary in Western Austrialia: results of a preliminary study, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 47: 679.
Huang, H., Pang, X., Heavy metals in sediments of tidal zone from south-west Bohai Sea, Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 1992(5): 44.
Attrill, M. J., Thomes, R. M., Heavy metal concentrations in sediment from the Thames estuary, UK, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1995, 30(11): 742.
Forstner, U., Muller, G., Schwermetalle in Flussen and Seen, Berlin: Springer, 1974.
Beeftink, W. G., Nieuwenhuize, J., Stoeppler, M. et al., Heavy metal accumulation in salt marshes from the western and eastern Scheldt, The Science of the Total Environment, 1982, 25: 199.
Goldberg, E. D., Gamble, E., Griffin, J. J. et al., Pollution history of Narragansett Bay as recorded in sediments, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1977, 5: 549.
Glooschenko, W. A., Capocianco, J., Coburn, J. et al., Geochemical distribution of trace metals and organochlorine contaminants of a Lake Ontario shoreline marsh, Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 1981, 15: 197.
Xu, S., Chen, Z., Yu, L. et al., The influence of polluted bottom sediments on overlying water and reasonably dredging scale in Suzhou Creek (eds. Lin, J., Chen, Y., Wu, S.), China in 21 Century: Environment, Resource and Sustainable Developmen, Hongkong (in Chinese), Hongkong and Asia Institute of the Hongkong Chinese University, 1999, 61–76.
Netherlands Department of Soil Protection, Soil Protection Act, Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1994.
Turekian, K. K., Wedepohl, K. H., Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust, Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1961, 72: 175.
Chen, J., The Report of Comprehensire Investrgation of Shanghai Coastal Zone and Tidal Flat Resources (in Chinese), Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1988, 1–390.
Davison, W., Supply of iron and manganese to an anoxic lake basin, Nature, 1981, 290: 241.
Balistrirei, L. S., Murry, J. W., Paul, B., The cycling of iron and manganese in the water column of Lake Sammamish, Washington, Limnology and Oceanography, 1992a, 37(3): 510.
Balistrirei, L. S., Murry, J. W., Paul, B., The biogeochemical cycling of trace metals in the water column of Lake Sammamish, Washington: response to seasonally anoxic condition, Limnology and Oceanography, 1992b, 37(3): 529.
Chen, Z., Pu, Y., Huang, R. et al., Seasonal release of iron and manganese at the sediment-water interface in Aha Lake, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41(16): 1395
Xu, S., Storm Deposits in the Yangtze Delta (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1997, 1–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Liu, P., Xu, S. et al. Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in tidal flat sediments of Shanghai coastal zone. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 44 (Suppl 1), 197–208 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884828
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884828