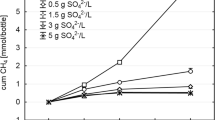
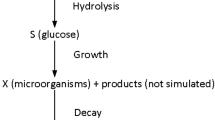
Abstract
The existing knowledge of anaerobic digestion of cellulose-containing wastes and methane formation is reviewed. Mutual relationships between the individual phases of this complex process and the mechanism of methane biosynthesis are discussed in three sections: (1) Non-methanogenic phase and digestion of cellulose; (2) methanogenic phase and methanogenesis; (3) mixed cultures and their advantages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACTI-BOSTID-CIRNRC:Methane Generation from Human, Animal and Agricultural Wastes. Nat. Acad. Sci., Washington, D.C., p. 28, 1977.
Barker H.A.:Bacterial Fermentation, p. 1. John Wiley and Sons, New York 1956.
Brandon D.G.: Isolation of an anaerobic cellulolytic mixed culture.Europ. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 7, 281 (1976).
Braun M., Hayer F., Gottschalk G.:Clostridium aceticum (Wieringa), a microorganism producing acetic acid from molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide.Arch. Microbiol. 128, 288 (1981).
Cooney C.L., Wise D.L.: Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of solid wastes for fuel gas production.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 17, 1119 (1975).
Daniels L., Fulton G., Spencer B.W., Orme-Johnson W.H.: Origin of hydrogen in methane produced byMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum.J. Bacteriol. 141, 694 (1980).
Delafontaine M.J., Naveau H.P., Nyns E.J.: Fluorimetric monitoring of methanogenesis in anaerobic digestors.Biotech. Lett. 1, 71 (1979).
Diekert G., Jaenchen R., Thauer R.K.: Biosynthetic evidence for a nickel tetrapyrrole structure of factor F430 fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum.FEBS Lett. 119, 118 (1980).
Eirich H.A., Vogels G.D., Wolfe R.S.: The structure of coenzyme F420, a novel electron carrier isolated fromMethanobacterium strain M.o.H.Biochemistry 17, 4583 (1978).
Ferry J.G., Wolfe R.S.: Nutritional and biochemical characterization ofMethanospirillum hungatii.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 34, 371 (1977).
Garcia-Martinez D.V., Shinmyo A., Midia A., Demain A.L.: Studies on cellulase production byClostridium thermocellum.Europ. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9, 189 (1980).
Gunsalus R.P., Wolfe R.S.: Methyl coenzyme M reductase fromMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Resolution and properties of the components.J. Biol.Chem. 255, 1891 (1980).
Gunsalus R.P., Wolfe R.S.: ATP activation and properties of the methyl coenzyme M reductase system inMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum.J. Bacteriol. 135, 851 (1978).
Hobson P.N.: The bacteriology of anaerobic sewage digestion.Process Biochem. 8, 19 (1973).
Hungate R.E.: The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria.Bact. Rev. 14, 1 (1950).
Jaenchen R., Diekert G., Thauer R.K.: Incorporation of methionine-derived methyl groups into factor F430 byMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum.FEBS Lett. 130, 133 (1981).
Karube I., Kuriyama S., Matsunaga T., Suzuki S.: Methane production from wastewaters by immobilized methanogenic bacteria.Biotech. Bioeng. 22, 847 (1980).
Khan A.W.: Cellulolytic enzyme system ofAcetivibrio cellulolyticus, a newly isolated anaerobe.J. Gen. Microbiol. 121, 499 (1980).
Khan A.W., Trottier T.M., Patel G.B., Martin S.M.: Nutrient requirement for the degradation of eellulose to methane by a mixed population of anaerobes.J. Gen. Microbiol. 112, 365 (1979).
Kneifel H., Sohoberth S.M.: Occurrence of polyamines in the strictly anaerobic, acetogenic bacteriumAcetobacterium woodii.FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 11, 59 (1981).
Loginova L.G., Kosmatchev A.E., Golovatcheva R.S., Seregina L.M.: The study of the thermophylic microflora of the Yangan-Tau montain in South Ural. (In Russian)Mikrobiologiya 31, 1082 (1962).
Maki L.R.: Experiments on the microbiology of cellulose decomposition in a municipal sewage plant.Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 20, 185 (1954).
Maugh T.H.: Phylogeny: Are methanogens a third class of life?Science 198, 812 (1977).
McBride B.C., Wolfe R.S.: A new coenzyme of methyltransfer; coenzymeM. Biochemistry 10, 2317-(1971).
Montenecourt B.S., Eveleigh D.E.: Production and characterization of high yielding cellulase mutants ofTrichoderma reesei.TAPPI Ann. Meet. Proc. 101 (1979).
Mountfort D.O.: Effect of adenosine 5′-monophosphate on adenosine 5′-triphosphate activation of methylcoenzyme M methylreductase in cell extracts ofMethanosarcina barkeri.J. Bacteriol. 143, 1039 (1980).
Prévot A.R.: Recherches récentes sur les bactéries méthanogénes.Bull. Inst. Pasteur 78, 217 (1980).
Reddy C.A., Bryant M.P., Wolin M.J.: Ferredoxin-dependent conversion of acetaldehyde to acetate and H2 in extract of S organism.J. Bacteriol. 110, 133 (1972).
Saddler J.N., Khan A.W., Martin S.M.: Regulation of cellulase synthesis inAcetivibrio cellulolyticus.Microbios 28, 97 (1980).
Scharer J.M., Moo-Young M.: Methane generation by anaerobic digestion of cellulose-containing wastes.Adv. Biochem. Bioeng. 11, 85 (1979).
Schauer N.L., Ferry J.G.: Metabolism of formate inMethanobacterium formicicum.J. Bacteriol. 142, 800 (1980).
Smith M.R., Mah R.A.: Growth and methanogenesis byMethanosardna strain 227 on acetate and methanol.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33, 870 (1978).
Smith W.R., Yu I., Hungate R.E.: Factors affecting cellulolysis byRuminococcus albus.J. Bacteriol. 114, 729 (1973).
Smith M.R., Mah R.A.: Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion.Appl. Microbiol. 14, 368 (1966).
Smith M.R., Zinder S.H., Mah R.A.: Microbial methanogenesis from acetate.Process Biochem.15, 34(1980).
Spencer R.W., Daniels L., Fulton G., Orme-Johnson W.H.: Product isotope effects onin vivo methanogenesis byMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum.Biochemistry 19, 3678 (1980).
Suchardová O., Volfová O., Krumphanzl V., Panoš J.: Physiology of growth of a mixed culture of thermophilic bacteria on cellulose under microaerophilic conditions.Biotechnol. Lett. 3, 547 (1981).
Taylor C.D., MoBride B.C., Wolfe R.S., Bryant M.P.: Coenzyme M. essential for growth of a rumenstrain ofMethanobacterium ruminantium.J. Bacteriol. 120, 974 (1974).
Taylor C.D., Wolfe R.S.: Structure and methylation of coenzyme M.J. Biol. Chem. 249, 4879 (1974).
Taylor G.T.: The formation of methane by bacteria.Process Biochem. 10, 29 (1975).
Toerien D.F., Hattingh W.H.J.: Anaerobic digestion. I. The microbiology of anaerobic digestion.Water Res. 3, 385 (1969).
Tornabene T., Langworthy T.: Diphytanyl and dibiphytanyl glycerol ether lipids of methanogenic archaebacteria.Science 203, 51 (1979).
Tzeng S.F., Wolfe R.S., Bryant M.P.: Factor 420-dependent pyridine nucleotide-linked hydrogenase system ofMethanobacterium ruminantium.J. Bacteriol. 121, 184 (1975).
Wiegel J.: Formation of ethanol by bacteria. A pledge for the use of extreme thermophylic anaerobic bacteria in industrial ethanol fermentation processes.Experientia 36, 1434 (1980).
Winter J.U.: Glucose fermentation to methane and CO2 by defined mixed ceultures.Zbl. Bakt. Hyg., I. Abt. Orig. C 1, 293 (1980).
Winter J.U., Wolfe R.S.: Complete degradation of carbohydrates to CO2 and methane by syntrophic cultures ofAcetobacterium woodii andMethanosarcina barkeri.Arch. Microbiol. 121, 97 (1979).
Wolfe R.S., Higgins I.J.: Microbial biochemistry of methane—a study in contrasts, p. 267 in Microbial Biochemistry, Vol. 21, part 1 (J.R. Quayale, Ed.). University Park Press, Baltimore 1979.
Wood T.M., MoCrae J.: The mechanism of cellulase action with particular reference to the C1 component, p. 111 inBioconversion of Cellulosis Substances into Energy, Chemicals and Microbial Protein (T.K. Ghose, Ed.). Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 1977.
Zeikus J.G.: The biology of methanogenic bacteria.Bacteriol. Rev. 41, 514 (1977).
Zeikus J.G., Wolfe R.S.: Fine structure ofMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: Effect of growth temperature on morphology and ultrastructure.J. Bacteriol. 113, 461 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volfová, O., Suchardová, O. & Krumphanzl, V. Anaerobic degradation of cellulose and formation of methane. Folia Microbiol 27, 354–362 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883139
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883139