Abstract
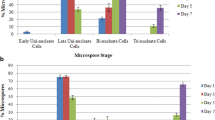
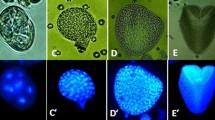
By using DNA-specific fluorescent dye and a confocal laser scanning microscope, the present study was designed to investigate the cytological characteristics of dedifferentiating initiation during pretreatment and embryogenesis during culture in freshly-isolated microspores of barley, and the difference in main developmental pathway between freshly-isolated and cold-treated microspores. The results revealed that (i) freshly-isolated microspores started the initiation within 12 h of mannitol pretreatment, whose main cytological characteristics were that: cell volume was obviously extended; the volume of nuclei and nucleoli were also greatly increased; nucleoli were extremely clear and highly condensed; N/C ratio was very high; (ii) all the pretreatment methods led to the initiation of the microspores, thus triggering the embryogenic process; (iii) pretreatment methods influenced the main developmental pathway of microspores by changing the pattern of the first mitosis. The cold-treated microspores formed main developmental pathway via A patterns, but freshly-isolated microspores via B pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, W., Comparative observation on the first mitosis of differentiation and dedifferentiation in pollen ofTriticum aestivum,Science in China, Ser. B (in Chinese), 1982, (1):25.
Xu, Z., Sunderland, N., DNA microphotometry ofHordeum Vulgare pollen during cold pretreatment and culture,Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1986, 12:140.
Shotton, D., Confocal scanning optical microscopy and its applications for biological specimens,J. Cell Sci., 1989, 94:175.
Chu, C.C., Hill, R.D., An improved anther culture method for obtaining higher frequency of pollen embryoids inTriticum asetivum L.,Plant Sci., 1988, 55:175.
Pace, G. M., Reed, J. N., Ho, L.C.et al., Anther culture of maize and the visualization of embryogenic microspores by fluorescent microscopy,Theor. Appl. Genet., 1987, 73:863.
Pescitelli, S. M., Petolino, J.F., Microspore development in cultured maize anthers,Plant Cell Rep., 1988, 7:441.
Pechan, P.M., Bartels, D., Brown, D.C.W.et al., Messenger-RNA and protein changes associated with induction ofBrassica microspore embryogenesis.Planta, 1991, 184:161.
Wei, Z. M., Kyo, M., Harada, H., Callus formation and plant regeneration through direct culture of isolated pollen ofHordeum vulgare L.cv. Sarbarlis,Theor. Appl.Genet., 1986, 72:252.
Imamura, J., Okabe, E., Kyo, M.et al., Embryogenesis and plantlet formation through direct culture of isolated pollen ofNicotiana tabacum cv. Samsum andNicotiana rustica cv. Rustica,Plant Cell Physiol., 1982, 23:713.
Liu, G.S., Li, Y., Liu, F.et al., Effects of high temperature on the cultures of isolated microspores inBrassica Camperstris ssp.,Acta Botanica Sinica (in Chinese), 1995, 37:140.
Pechan, P.M., Keller, W. A., Induction of microspore embryogenesis inBrassica napus L. by gamma irradiation and ethanol stress,In vitro Cellular & Develp. Biology, 1989, 25:1073.
Chu, C., Liu, H. T., Du, R. H., Microsphotometric determination of DNA contents of early developmental pollen grains in tobacco anther culture,Acta Botanica Sinica, 1982, 24:1.
Sunderland, N., The content of morphogenic competence to anther and pollen culture, inPlant Cell Culture in Crop Improvement, New York: Plenum Press, 1983, 125–139.
Yang, M., Chen, Y., Androgenesis inindica rice and the response to cold pretreatment and the enhancement of PH in induction medium,Plant Cell Engineering and Breeding (eds. Hu, Wang), Beijing: Beijing Polytechnic University Press, 1990, 19–23.
Shaw, P., Highett, M., Rawlins, D., Confocal microscopy and image processing in the study of plant nuclear structure,J. Microscopy, 1992, 166:87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the Bio-Rad China Limited.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Jing, J. & Hu, H. Dedifferentiating initiation and embryogenesis from freshly-isolated microspores of barley. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 40, 332–336 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879095
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879095