Abstract
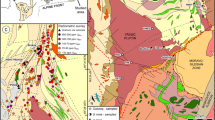
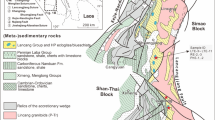
Na-rich microlite-glass is first discovered in deep-source xenoliths in alkali-rich porphyry, Liuhe village, Heqing County, Yunnan Province. It is shown that the ultramafic xenoliths originated from partial melting of primary mantle and the glass resulted from metasomatism between the xenoliths and mantle fluid derived from mantle degassing. Mantle metasomatism not only resulted in the enrichment of alkaline, large-ion elements, ore metals and volatiles but also created a favorable condition for the generation of alkaline magmas. The mantle xenoliths and their characteristics of mantle metasomatism provide important evidence for a better understanding of the petrogenesis and mineralization of the Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyry in western Yunnan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou Lingdi, Zhao Zhenhua, Petrographic and petrochemical characteristics of alkali-rich intrusions in China,Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. B, 1994, 24(10): 1093.
Deng Wanming, Huang Xuan, Zhong Dalai, Alkali-rich porphyry and its relation with intraplate deformation of northern part of Jinsha River belt in western Yunnan, China,Science in China, Ser. D, 1998, 41(3): 297.
Zhang Yuquan, Xie Yingwen, Geochronology of Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang alkali-rich intrusive rocks and their Sr and Nd isotopic characteristics,Science in China, Ser. D, 1997, 40(5): 524.
Zhao Zhenhua, Zhou Lingdi, REE geochemistry of selected alkali-rich intrusions in China,Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. B, 1994, 24(10): 1109.
Deng Wanming, Huang Xuan, Zhong Dalai, Petrographic characteristics and genesis of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyries, Western Yunnan,Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 33(4): 412.
Cai Xinping, Deep xenoliths in Cenozoic alkalic porphyries at the west margins of the Yangtze Platform and their implications,Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1992, 27(2): 183.
Geological Bureau of Yunnan Province,Regtonal Geology of Yunnan (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological fnRess, 1990, 1–28.
Sanders, A. D., Tarney, J., Weaver, S. D., Transverse geochemical variations across the Antarctic Peninsula: implications for the genesis of calc-alkaline magmas,Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., 1980, 46: 344.
Dowson, J. B., Contrasting types of upper-mantle metasomatism,Kimberlites I1: TheMantle and Crurt-Mantle Relationsship ((ed. Kornpobst, J.), Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984, 289–294.
Jones, A. P., Smith, J. V., Dawson, J. B., Glasses in mantle xenoliths from Olmani, Tanzania,Jour. Geol., 1983, 91(2): 167.
Girod, M., Dautria, J. M., De Giovanni, R., A first insight into the constitution of the upper mantle under the Hoggar Area (Southern Ageria): The lherzolite xenoliths in the alkali-hasalts,Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1981, 77: 66.
Francis, D. M., The origin of amphibole in lherzolite xenoliths from Nunivak Island, Alaska,Jow. Petrol., 1976, 17(3): 357.
Lin Chuanyong, Xu Yigang, Shi Lanbin et al., K- and Na-rich glass in mantle xenoliths: evidence of upper mantle fluid,Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1994, 39(9): 820.
Zheng Haifei, Fong Jialin, Microlite-glass in basalt xenoliths at Hannoba,Geological Review (in Chinese), 1987, 33(1): 12.
Maaloe, S., Printzlau, I., Natural partial melting of spinel lhdite,Jour. Petrol., 1979. 20(4): 727.
Schneider, M. E., Eggler, D. H., Fluids in equilibrium with peridotite minerals: implications for mantle metasomatism,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1986, 50(5): 711.
Cao Ronglong, Xia Linqi,Characters and Dynamics of Upper Mantle, China, Beijing: Earthquake Reas, 1989, 14–22.
Yang Keyou, Cheng Feng, Su Wenchao et al., Geological and geochemical characters and prospecting of carlin-type gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi region,Comparative Studies of Gold Deposits Between China and Canada (in Chinese), Beijing: Earthquake Press, 1994, 17–30.
Liu Congqiang, Xie Guanghong, Zheng Tianzangzhen, Geochemistry of REE and Sr, Nd isotopes of mantle xenoliths in Hannoba basalt,Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1996, 12(3): 382.
Xu Yigang, Menzies, M. A., Lin Chuanyong et al., REE composition and its petrogenetic implications of mantle xenoliths, Yitong, Jilin,Acta Petrologka Sinica (in Chinese), 1997, 13(1): 14.
Shen Weizhou,Geology of Stable Isotopes (in Chinese), Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1987, 12.
Tatsumoto, M., Basu, A. R., Huang, W. K. et al., Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes of ultramafic xenoliths in volcanic rocks of Eastern China: enriched components EMI and EMII in subcontinental lithosphere,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1992, 113: 107.
Zartman, R. E., Doe, B. R., Plumbotectonics: the model,Tectonophysics, 1981, 75: 135.
Van der Laan, S. R., MARID and mantle metasomatism,Mineralogical Magazine, 1994, 58A: 505.
Zheng Jianping, Lu Fonpiang, Cheng Zhongmei et al., Characters and genetic implications of garnet-pyroxenite xenoliths in kimberlite,Earth Science (Joml of China University of Geoscienoes) (in Chinese), 1998, 23(1): 49.
Hart, S. R., A large-scale isotope anomaly in the southern hemisphere mantle,Nature, 1984. 309: 753.
Xie Hongsen, Hou Wei, Xu Jian et al.,Introductions to Material Science in Deep Interior of the Earth (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1997, 238–244.
Bian Qiantao, Low-velocity plumes at the southwest margin of the Yangtze Craton and its implications to ultra-large ore deposits,Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. D, 1998, 28(Supplement): 92.
Bailey, D. K., Mantle metasomatism-perspective and prospect, Alkaline lgneoua Rocks ((eds. Fitton, J. C. et al.), Geological Society Special Publication, 1987, (30): 1.
Bian Qiantao, She Hongquan, Preliminary study on the relationship between the crust-mantle structure and the formation of Laowangzhai superlarge gold deposit,Science in China, Ser. D, 1998, 41(6): 561.
Du Letian, Relationship between crust fluid and mantle fluid,Earth Science Frontier (in Chinese), 1996, 3(3–4): 172.
Xie Rongju, Peng Shenlin, Potash alteration and metasomatism and their implications to mineralization,Geotectonies and Mineraltzaion (in Chinese), 1998, 22(3): 274.
Hu Ruizhong, Bi Xianwu, Turner, G. et al., He-Ar isotopic system of fluid inclusions in pyrite in copper deposit, Machangqing,Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. D, 1997, 27(6): 503.
Hu Ruizhong, Bumard, P. G., Turner, G. et al., Hilium and argon isotope systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in west Yunnan Province, China,Chemical Geology, 1998, 146: 55.
Hu Ruizhong, Bi Xianwu, He Mingyou et al., Mineralizer constraint on gold mineralization of Ailaoshan gold belt,Science in China, Ser. D, 1998. 41(Supp.): 74.
Bi Xianwu, Hu Ruizhong, He Mingyou, ESR ages and their geological implications, the Ailaoshan Gold Zone,Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1996, 41(14): 1301.
Hou Zengqian, Li Hongyang, Mantle-plume structure and mineralization—A preliminary discussion with special reference to the Sanjiang Tethys Metallogenic Province,Mined Deposits (in Chinese), 1998, 17(2): 97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhan, X., Gao, Z. et al. Deep xenoliths in alkalic porphyry, Liuhe, Yunnan, and implications to petrogenesis of alkalic porphyry and associated mineralizations. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 42, 627–635 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877790
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877790