Abstract
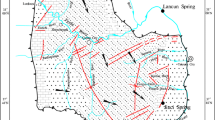
Using the hydrogeochemical modeling method, the groundwater chemical environmental problems of the Hebei Plain which involve increasing of hardness and total dissolved solids in piedmont area and mixing of saline water with fresh water in middle-eastern area are studied. The water-rock interactions and mass transfer along a ground-water flow path and in mixing processes are calculated. Thus the evolution mechanisms of the groundwater chemical environment are brought to light.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nordstrom, O.K., Plummer, L. N., Wiglcy, T. M. L., A comparison of computerized chemical models for equilibrium calculations in aqueous systems,American Chemical Society Symposium Series, 1979, (93): 857.
Hummer, L. N., Back, W., The mass balance approach: Application to interpreting the chemical evolutions of hydrologic systems.Amer. J. Sci., 1980, 280: 130.
Plummer, L. N., John, F. B., Roger, W. L., Geochemical modeling of the Madison aquifer in part of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota,Water Resources Research, 1990, 26(9): 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Srience Foundation of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Shen, Z. & Zhong, Z. Hydrogeochemical modeling of groundwater chemical environmental evolution in Hebei Plain. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 40, 502–508 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877616
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877616