Abstract
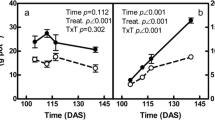
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa; L.) plants susceptible (S) and resistant (R) to the bacterial wilt were fedvia roots with a nutrient solution labelled with86Rb+, at different times after inoculating them withCorynebacterium insidiosum (McCull.) H. L. Jens. The infection did not influence86Rb+ uptake per plant in the course of a 14-day-period following inoculation, however it did affect its distribution differentially in the S- and the R-plants.86Rb+ uptake was significantly decreased due to the infection in the S-plants on the day 49 after the inoculation (a 4-h-exposure to86Rb+), with the iona also being more slowly translocated to the shoots in diseased S-plants than in diseased R-plants. Likely factors causing these effects and their relationship to alfalfa resistance to the bacterial wilt are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayres, P. G., Jones, P.: Increased transpiration and the accumulation of root absorbed86Rb in barley leaves infected byRhynchosporium secalis (leaf blotch). - Physiol. Plant Pathol.7: 49–58, 1975.
Brownell, J. R., Läuchli, A.: Measurement of β-emitters in plant material with Cerenkov radiation: correction of color-quenching. - Int. J. appl. Radiat. Isot.20: 797–798, 1969.
Clarkson, D.: Ion Transport and Cell Structure in Plants. - Mc Graw-Hill Publ., London 1974.
Cram, W. J., Pitman, M. G.: The action of abscisic acid on ion uptake and water flow in plant roots. - Aust. J. biol. Sci.25: 1125–1132, 1972.
Dimond, A. E.: Biophysics and biochemistry of the vascular wilt syndrome. - Annu. Rev. Phytopathol.8: 301–322, 1970.
Duniwey, J. M.: Water status and imbalance. - In:Heitefuss, R., Williams, P. H. (ed.): Physiological Plant Pathology. Pp. 430–449. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1976.
Epstein, E.: Mineral Nutrition of Plants: Principles and Perspectives. - John Wiley Publ., London 1972.
Graham, R. D., Ulrich, A.: Potassium deficiency-induced changes in stomatal behavior, leaf water potentials, and root system permeability inBeta vulgaris L. - Plant Physiol.49: 105 to 109, 1972.
Hanker, I., Kůdelová, A.: Changes in growth and in uptake, distribution and translocation of phosphorus in susceptible and resistant alfalfa plants induced byCorynebacterium insidiosum. - Biol. Plant.21: 136–143, 1979a.
Hanker, I., Kůdelovå, A.: Changes in phosphorus metabolism in alfalfa plants induced by bacterial wilt. - Biol. Plant.21: 144–148, 1979b.
Hooymans, J. J. M.: Role of cell compartments in the redistribution of K+ and Na+ ions absorbed by the roots of intact barley plants. - Z. Pflanzenphysiol.73: 234–242, 1974.
Kotyk, A.: [The biochemical essence of transport processes]. In Czech. - Biológia (Bratislava)33: 223–232, 1978.
Krátká, J., Kůsela, V.: Changes in alfalfa plants metabolism induced byCorynebacterium insidiosum. - Phytopathol. Z., in press 1981.
Kůdelová, A., Bergmannová, E., Kůdela, V., Taimr, L.: The effect of bacterial wilt on the uptake of manganese and zinc in alfalfa. - Acta phytopathol. Acad. Sci. hung.13: 121–132, 1978.
Läuchli, A.: Radioassay for β-emitters in biological material using Cerenkov radiation. - Int. J. appl. Radiat. Isot.20: 265–270, 1969.
Loughman, B. C.: Metabolic factors and the utilization of phosphorus by plants. - In: Phosphorus in the Environment: its Chemistry and Biochemistry. Ciba Foundation Symposium 57. Pp. 155–174. Elsevier, Excerpta Medica, North-Holland Inc. Amsterdam 1978.
Pandey, D. P., Kannan, S.: Action of ABA and some cytokinins on the transport of foliar and root absorbed Rb+ and Fe++ in bean plants. - Z. Pflanzenphysiol.78: 95–102, 1976.
Patrick, T. W., Hall, R., Fletcher, R. A.: Cytokinin levels in healthy andVerticillium-infected tomato plants. - Can. J. Bot.55: 377–382, 1977.
Pitman, M. G., Lüttge, U., Läuchli, A., Ball, E.: Action of abscisic acid on ion transport as affected by root temperature and nutrient status. - J. exp. Bot.25: 147–155, 1974.
Rüssel, R. S., Barber, D. A.: The relationship between salt uptake and the absorption of water by intact plants. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.11: 127–140, 1960.
Sawhney, B. L., Zelitch, I.: Direot determination of potassium ion accumulation in guard cells in relation to stomatal opening in light. - Plant Physiol.44: 1350–1354, 1969.
Taimr, L., Kůdelová, A., Kůdela, V., Bergmannová, E.: Effect of bacterial wilt on uptake and translocation of phosphorus, sulphur, calcium, and manganese in alfalfa plants. - Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Abt. II.130: 367–386, 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanker, I., Kdelová, A. The uptake, distribution, and translocation of86Rb in alfalfa plants susceptible and resistant to the bacterial wilt and the effect ofCorynebacterium insidiosum upon these processes. Biol Plant 23, 365–375 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877415
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877415