Abstract
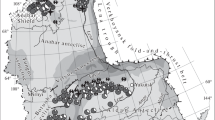
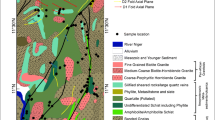
The gold deposits, occurring in the south subzone of western Qinling, are the only typical and important strata-bound gold deposits, which are associated with submarine exhalative sedimentation. The gold deposits include the La’erma ore deposit, the Qiongmo ore deposit and the Yaxiang ore occurrence. They are hosted in the Cambrian silicalite formation composed of black chert and slate. The presence of typical chert offers important evidence to evaluate the possible submarine exhalative system and its role in the formation of the gold deposits, which are closely associated with percolation and diffusion in the horizontal, vertical and axial directions. Element-assemblage zonation is clearly seen due to differences in element concentrations in different directions. Such a zonation makes gold, selenium, uranium, copper, stibium, molybdenum, mercury, etc. precipitate in the form of simple or composite orebodies. The establishment of the element-assemblage zonation is highly helpful for evaluating directly the metallogenesis of gold deposits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Jiajun and Zheng Minghua, 1992a, The first discovery of selenio-sulfantimonide mineral series: Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 37, p. 1494–1495.
Liu Jiajun, Zheng Minghua, and Lu Wenquan, 1992b, Antimonselite—no longer a synthetic mineral: Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 37, p. 1438–1439 (in Chinese).
Liu Jiajun, Zheng Minghua, and Lu Wenquan, 1993, The first discovery of a variety of famatinite—Se-famatinite: Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 38, p. 1726–1727 (in Chinese).
Liu Jiajun and Zheng Minghua, 1996, Exhalative sedimentation of the Cambrian silicalite formation in western Qinling, China: Advance in Geoscience, Chengdu, Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, p. 108–114 (in Chinese).
Ruan Tianjian and Zhu Youguang, 1985, Geochemical exploration: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, p. 54–58 (in Chinese).
Wang Chongyun, 1988, Geochemical exploration: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, p. 37–43 (in Chinese).
Zheng Minghua, Zhou Yufeng, Liu Jianming, Gu Xuexiang, Liu Jiajun, O. Schulz, and F. Vavtar, 1994, Strata-bound gold deposits of the exhalation type and turbidity type: Chengdu, Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, p. 91–110 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project is supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Sino-Austria International Cooperation Program (4880099).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zheng, M., Liu, J. et al. Element-assemblage zoning features of gold deposits in the cambrian silicalite formation, western Qinling. Chin. J. Geochem. 16, 271–277 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02870911
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02870911