Abstract
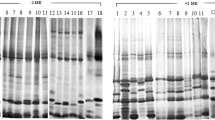
Electrophoretic and serological studies with proteins extracted from the pollen of 12 races of maize (Zea mays) have proved valuable in distinguishing among these races. Both sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and double immunodffusion (Ouchterlony method) were used to analyze the extracted pollen proteins. Jaccard's similarity coefficient was calculated from the data generated by 2-state scoring of the band patterns obtained in each system. Average linkage cluster analysis of the similarity matrices was used to construct phenograms illustrating the similarity among the extracts. The racial groupings indicated in these pheno grams, when compared with those of several morphological studies, show some general agreement. However, there are differences, the most notable being that Chalqueno appeared the most dissimilar of the races studied and that Dulce showed high similarity to Palomero Toluqueño, rather than being an exceptional race as it is usually considered. The possible bearing of the groupings of the races in these phenograms with respect to genetic lineage and selection of maize is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bird, R. McK., and M. M. Goodman. 1977. The races of maize V: Grouping maize races on the basis of ear morphology. Econ. Bot. 31: 471–481.
Brown, W. L., and M. M. Goodman. 1977. Races of corn.In Corn and Corn Improvement. G. F. Sprague, ed. pp. 49–88. Amer. Soc. Agron., Madison, WI.
Buettner-Janush, J., and R. L. Hill. 1965. Molecules and monkeys. Science 147: 836–842.
Cervantes S., T., M. M. Goodman, E.Casas D., and J. O. Rawlins. 1978. Use of genetic effects and genotype by environmental interactions for the classification of Mexican races of maize. Genetics 90: 339–348.
Cherry, L. M., S. M. Case, and A. C. Wilson. 1978. Frog perspective on the morphological difference between humans and chimpanzees. Science 200: 209–211.
Clarkson, R. B. 1973. Chemosystemic (protein) research at West Virginia University. Bull. Serol. Mus. No. 49: 8.
Crowle, A. J. 1961. Immunodiffusion. Academic Press, New York.
Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Rebers, and F. Smith. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356.
Fairbrothers, D. E. 1968. Chemosystematics with emphasis on systemic serology. In Modern Methods in Plant Taxonomy, V. H. Heywood, ed. pp. 141–174. Academic Press, London.
—, T. J. Mabry, R. L. Scogin, and B. L. Turner. 1975. The basis of angiosperm phylogeny: chemotaxonomy. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 62: 765–800.
Goodman, M. M. 1972. Distance analysis in biology. Syst. Zool. 21: 174–186.
—, and R. McK. Bird. 1977. The races of maize IV: Tentative grouping of 219 Latin American races. Econ. Bot. 31: 204–221.
Harlan, J. R. 1975. Our vanishing genetic resources. Science 188: 618–621.
Hawkes, J. G. 1968. Chemotaxonomy and Serotaxonomy. Academic Press, London.
Hernandez X., E., and G. Alanis Flores. 1970. Estudio morfológico de cinco nuevas razas de maíz de la Sierra Madre Occidental de Mexico: Implicaciones filogenéticas y fitogeográficas. Agrociencia 5: 3–30.
Jardine, N., and R. Sibson. 1971. Mathematical Taxonomy. Wiley, London.
Johnson, R. G., and D. E. Fairbrothers. 1975. A comparative disc electrophoretic study of pollen proteins ofBetula populifolia. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 3: 205–208.
King, M. C, and A. C. Wilson. 1975. Evolution at two levels in humans and chimpanzees. Science 188: 107–116.
Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Longley, A. E., and T. A. Kato Y. 1965. Chromosome morphology of certain races of maize in Latin America. Research Bull. No. 1. International Center for the Improvement of Maize and Wheat. Chapingo, Mexico.
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall. 1951. Protein measurement with the folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
McClintock, B. 1960. Chromosome constitution of Mexican and Guatemalan races of maizes. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Year Book 59: 461–472.
—. 1978. Significance of chromosome constitutions in tracing the origin and migration of races of maize in the Americas.In Maize Breeding and Genetics, David B. Walden, ed. pp. 159–184. Wiley, New York.
Mohagheghpour, N., and C. A. Leone. 1969. An immunological study of the relationships of nonhuman primates to man. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 31: 437–452.
Ouchterlony, O. 1958. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis.In Progress in Allergy, Vol. V. P. Kallos, ed. pp. 1–78. Karger, Basel and New York.
Payne, R. C, and D. E. Fairbrothers. 1973. Disc electrophoretic study of pollen proteins from natural populations ofBetula populifolia in New Jersey. Amer. J. Bot. 60: 182–189.
Pickering, J. L., and D. E. Fairbrothers. 1970. A serological comparison of Umbelliferae subfamilies. Amer. J. Bot. 57: 988–992.
Schneider, S. H., with L. E. Mesirow. 1976. The Genesis Strategy. Plenum, New York.
Smith, J. S. C, and R. N. Lester. 1980. Biochemical systemics and evolution ofZea, Tripsacum and related genera. Econ. Bot. 34: 201–218.
Sneath, P. H. A., and R. R. Sokal. 1973. Numerical Taxonomy. The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification. Freeman, San Francisco.
Urano, K., S. Sakaguchi, and T. Machida. 1965. Phytoimmunological studies inZea mays on varieties-specific antigen. Jap. J. Breeding 15: 158–162.
Vaughn, J. G. 1973. Studies ofBrassica taxonomy using serological and other protein separation methods. Bull. Serol. Mus. No. 49: 1–2.
Villamil, C. B., and D. E. Fairbrothers. 1974. Comparative protein population investigation of theAlnus serrulata-rugosa complex. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2: 15–20. or]Wellhausen, E. J., L. M. Roberts, and E. Hernández Xolocotzin, en colaboracion con P. C. Man-gelsdorf. 1951. Razas de maíz en Mexico. Su origen, caracteristicas y distributeón. Folleto Técnico No. 5, Secretaría de Agriculture y Ganadería. México, D.F.
Wilson, A. C, S. S. Carlson, and T. J. White. 1977. Biochemical evolution. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 46: 573–639.
Wright, C. A., ed.. 1974. Biochemical and Immunological Taxonomy of Animals. Academic Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greenhouse, V.Y., Xolocotzin, E.H., de Cuadra, C.R. et al. Electrophoretic and immunological characterization of pollen protein ofZea mays races. Econ Bot 36, 113–123 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858706
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858706