Abstract
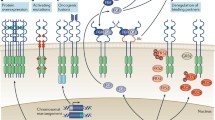
As the seventh member of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF or FGF-7) is observed to mediate epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation in a variety of tissues. In this article, such following issues within KGF research were reviewed, as (1) KGF functioning pathways: experimental results demonstrated the paracrine pathway of KGF played main role in mesenchymal-epithelial interactions whereas KGF itself was under the control of a feedback regulation, autocrine provided KGF alternative functioning way particularly in tumourogenesis; (2) KGF in apoptosis: a few of investigations recently illustrated KGF mediated cell survival was based on its mitogenic function via stimulating cell growth, moreover KGF could inhibit the ROS-induced apoptosis through Nrf-2 pathway; (3) KGF during tumourogenesis: high expression of KGF enhanced progression, motility and invasiveness of tumor cells and various cancers, in company with paracrine loop replaced by autocrine loop, meanwhile KGF clearly played the early signal in the progression of breast cancer; (4) Medical application and administration of KGF: KGF had been successfully used in several preclinical models of radiation and chemotherapy-induced mucositis, and developed into commercial medicine (i.e. Palifermin), however more effective delivery systems are still under trial.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, J.A. and Klagsbrun, M. 1996. Modulation of wound repair by members of the fibroblast growth factor family [M]. In: Clark, R.A.F. (Ed.), The molecular and cellular biology of woundrepair. 2nd edition. Plenum Press, pp. 195–248.
Alpdogan, O., Hubbard, V.M., Muriglan, S.J.,et al. 2005. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is required for post-natal thymic regeneration [J]. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation,11(2): 57 (Supplement 1).
Andreadis, S.T., Hamoen, K.E., Yarmush, M.L.,et al. 2000. Keratinocyte growth factor induces hyperproliferation and delays differentiation in a skin equivalent model system [J]. FASEB J.,15(6): 898–906.
Auf dem Keller, U., Krampert, M., Kümin, A.,et al. 2004. Keratinocyte growth factor: effects on keratinocytes and mechanisms of action [J]. European Journal of Cell Biology,83(11–12): 607–612.
Beer, H.D., Gassmann, M.G., Munz, B.,et al. 2000. Expression and function of keratinocyte growth factor and activin in skin morphogenesis and cutaneous wound repair [J]. J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc.,5(1): 34–39.
Boismenu, R. and Havran, W.L. 1994. Modulation of epithelial cell growth by intraepithelial γδT cells [J]. Science,266: 1253–1255.
Braun, S., Hanselmann, C., Gassmann, M.G.,et al. 2002. Nrf-2 transcription factor, a novel target of keratinocyte growth factor action which regulates gene expression and inflammation in the healing skin wound [J]. Mol. Cell. Biol.,22: 5492–5505.
Carrington, L.M. and Boulton, M. 2005. Hepatocyte growth factor and keratinocyte growth factor regulation of epithelial and stromal corneal wound healing [J]. Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery,31(2): 412–423.
Crescioli, C., Villari, D., Forti, G.,et al., 2002. Des (1–3) IGF-I-stimulated growth of human stromal BPH cells is inhibited by a vitamin D3 analogue [J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,198(1–2): 69–75.
Dabelsteen, S., Christensen, S., Gron, B.,et al., 2005. HGF is released from buccal fibroblasts after smokeless tobacco stimulation [J]. Oral Oncology,41(5): 509–514.
Dörr, W., Reichel, S. and Spekl, K. 2005. Effects of keratinocyte growth factor (palifermin) administration protocols on oral mucositis (mouse) induced by fractionated irradiation [J]. Radiotherapy and Oncology,75(1): 99–105.
Farrell, C.L., Rex, K.L., Chen, J.N.,et al. 2002. The effects of keratinocyte growth factor in preclinical models of mucositis [J]. Cell. Prolif.,35(1): 78–85 (Supplement 1).
Finch, P.W. and J.S. Rubin. 2004. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF/FGF7), a homeostatic factor with therapeutic potential for epithelialprotection and repair [J]. Adv. cancer Res.,91: 69–136.
Finch P.W., Rubin J.S., Miki T.,et al. 1989. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth [J]. Science,245: 752–755.
Galiacy, S., Planus, E., Lepetit, H.,et al., 2003. Keratinocyte growth factor promotes cell motility during alveolar epithelial repairin vitro [J]. Experimental Cell Research,283(2): 215–229.
Gillis, P., Savla, U., Volpert, O.V.,et al., 1999 Keratinocyte growth factor induces angiogenesis and protects endothelial barrier function [J]. J. cell Sci.,112(Pt 12): 2049–2057.
Groves, R.W. and Schmidt-Lucke, J.A. 2000. Recombinant human GM-CSF in the treatment of poorly healing wounds [J]. Adv. Skin. Wound Care,13: 107–112.
Haddad, J.J. 2004. Redox and oxidant-mediated regulation of apoptosis signaling pathways: immuno-pharmaco-redox conception of oxidative siege versus cell death commitment [J]. International Immunopharmacology,4(4), 475–493.
Hofmann, B., Hecht, H.J. and Flohe, L. 2002. Peroxiredoxins [J]. Biol. Chem.,383: 347–364.
Hovey, R.C., Davey, H.W., Vonderhaar, B.K.,et al., 2001. Paracrine action of keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) during ruminant mammogenesis [J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,181(1–2): 47–56.
Johnson D.E. and Williams, L.T. 1993. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family [J]. Adv. Cancer. Res.,60: 1–41.
Kamata, T., Hattori, Y., Hamada, H.,et al., 2002. Keratinocyte growth factor regulates proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic cells expressing the receptor gene K-sam [J]. Experimental Hematology,30(4): 297–305.
Kanzler, M.H., Gorsulowsky, D.C., and Swanson, N.A. 1986. Basic mechanisms in the healing cutaneouus wound [J]. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol.,12: 1156–1164.
Steenfos, H.H. 1994. Growth factors and wound healing [J]. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg.,28(2): 95–105.
Karvinen, S., Pasonen-Seppanen, S., Hyttinen, J.M.,et al., 2003. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates migration and hyaluronan synthesis in the epidermis by activation of keratinocyte hyaluronan synthases 2 and 3 [J]. J. Biol. Chem.,278(49): 495–504.
Koos, R.D., Banks, P.K., Inkster, S.E.,et al., 1993. Detection of aromatase and keratinocyte growth factor expression in breast tumors using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction [J]. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,45(4): 217–225.
Kopp, J., Wang, G.Y., Kulmburg, P.,et al., 2004. Accelerated Wound Healing by In vivo Application of Keratinocytes Overexpressing KGF [J]. Molecular Therapy,10(1): 86–96.
Lin, M.P., Marti, G.P., Dieb, R.,et al., 2004. Electroporation improves transfection efficiency in rat wound healing model [J]. Journal of the American College of Surgeons,199(3): 58–59 (Supplement 1).
Marti, G.P., Lin, M.P., Qaiser, R.,et al., 2004. KGF-1 plasmid delivered with electroporation accelerates wound closure in diabetic mice [J]. Journal of the American College of Surgeons,199(3): 59 (Supplement 1).
Marti, G.P., Makary, M.A., Ferguson, M.,et al., 2004. Transfection with keratinocyte growth factor 1 cDNA with electroporation improves wounds healing in an aged mouse model [J]. Journal of Surgical Research,121(2): 320–321.
McGarvey, T.W. and Stearns, M.E. 1995. Keratinocyte Growth Factor and receptor mRNA expression in benign and malignant human prostate [J]. Experimental and Molecular Pathology,63(1), 52–62.
Michelson, P.H., Tigue, M., Panos, R.J.,et al., 1999. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates bronchial epithelia cell proliferationin vitro andin vivo [J]. Am. J. Physiol.,211(4 Pt 1): L737–742.
Min, D., Taylor, P.A., Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.,et al., 2002. Protection from thymic epithelial cell injury by keratinocyte growth factor: a new approach to improve thymic and peripheral T-cell reconstitution after bone marrow transplantation [J]. Blood,99: 4592–4600.
Nguyen, T., Zang, X. and Pento, J.T. 2002. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates the migration and proliferation of breast cancer cells in a culture wounding model [J]. Pharmacological Research,46(2): 179–183.
Ornitz, D.M. and Itoh, N. 2001. Fibroblast growth factors [J]. Genome Biol. Reviews,2(3): 3005.1–3005.2.
Ornitz, D.M., Xu, J., Colvin, J.S.,et al., 1996. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family [J]. J. Biol. Chem.,271: 15292–15297.
Panosm, R.J., Bak, P.M., Simonet, W.S.,et al. 1995. Intratracheal instillation of keratinocyte growth factor decreases hyperoxia-induced mortality in rats [J]. J. Clin. Invest.,96: 2026–2033.
Parrott, J.A., Doraiswamy, V., Kim, G.,et al., 2001. Expression and actions of both the follicle stimulating hormone receptor and the luteinizing hormone receptor in normal ovarian surface epithelium and ovarian cancer [J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,172(1–2): 213–222.
Parrott, J.A., Kim, G., Mosher, R.,et al., 2001. Expression and action of keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) in normal ovarian surface epithelium and ovarian cancer [J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,167(1–2): 77–87.
Ray, P., Devaux, Y., Stolz, D.B.,et al. 2003. Inducible expression of keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) in mice inhibits lung epithelial cell death induced by hyperoxia [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA.100: 6098–6103.
Rossi, S., Blazar, B.R., Farrell, C.L.,et al., 2002. Keratinocyte growth factor preserves normal thymopoiesis and thymic microen- vironment during experimental graft-versus-host disease [J]. Blood,100: 682–691.
Siddiqi, I., Funatomi, H., Kobrin, M.S.,et al., 1995. Increased expression of Keratinocyte Growth Factor in human pancreatic cancer [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,215(1): 309–315.
Slonina, D., Hoinkis, C. and Dorr, W. 2001. Effect of keratinocyte growth factor on radiation survival and colony size of human epidermal keratinocytesin vitro [J]. Radiat. Res.,156(6): 761–766.
Steiling, H., Wustefeld, T., Bugnon, P.,et al., 2003. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling is crucial for liver homeostasis and repair [J]. Oncogene,22: 4380–4388.
Velagaleti, G.V.N., Tapper, J.K., Panova, N.E.,et al., 2003. Cytogenetic findings in a case of nodular fasciitis of subelavicular region [J]. Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics,14(2): 160–163.
Wei, C., Chen, W., Wang, Y.,et al., 2005. Detection of IL-20 and its receptors on psoriatic skin [J]. Clinical Immunology,117(1): 65–72.
Werner, S. and Smola, H. 2001. Paracrine regulation of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation [J]. Trends in Cell Biology,11(4): 143–146.
Werner, S., Peters, K.G., Longaker, M.T.,et al., 1992. Large induction of keratinocyte growth factor expression in the dermis during wound healing [J]. Proc. Natl Acad Sci U.S.A.89: 6896–6900.
Wildhaber, B.E., Yang, H. and Teitelbaum, D.H. 2003. Total parenteral nutrition-induced apoptosis in mouse intestinal epithelium: modulation by keratinocyte growth factor [J]. Journal of Surgical Research,112(2): 144–151.
Witte, R.P. and Kao, W.J. 2005. Keratinocyte-fibroblast paracrine interaction: the effects of substrate and culture condition [J]. Biomaterials,26(17): 3673–3682.
Werner, S. 1998. Keratinocyte growth factor: a unique player in epithelial repair processes [J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.,9(2): 153–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This work was supported by the scientific scholarship of NEFU to D. ZHENG, the EYTIF fund of NEFU to X.LIU, and partial supported by the grant of the Ministration of Education (020-413229) to D. ZHENG.
Biography: ZHENG Wen-jing (1982-), female. Graduate of Physiology in College of Wildlife Resources, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China.
Responsible editor: Chai Ruihai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen-jing, Z., Li, Y., Xue-dong, L. et al. Issues within Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) research. Journal of Forestry Research 16, 335–338 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858203
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02858203
Keywords
- Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF or FGF-7)
- Paracrine
- Autocrine
- Apoptosis
- Tumourogenesis
- Medical administration