Abstract
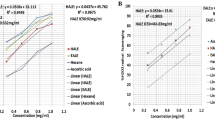
People in some tropical countries used to use some plant extracts in folklore medicine as treatment of diabetes mellitus. Of these plants isCalligonum comsum (“orta”). The present work deals with the biochemical effects of the whole plant water extract given orally to the albino rats, normals and alloxan diabetics, as to fulfil its hypoglycemic effects on rats. The results showed that “orta” extract produced a hypoglycemic effect indicated by the decrease in blood sugar level. It was observed that the diabetic state in rats treated with 300 mg/kg body weight of “orta” extract, was alleviated, showing normal levels of blood glucose, liver fat and cholesterol contents. Liver proteins were still below the normal level in the rats. Gibenclamide, a hypoglycemic drug, was used for comparison with “orta” extract. Although it did alleviate the diabetic state, yet the liver fat and cholesterol contents were still higher than those of normal. Also the liver proteins were lower than the control levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
El-Sayyad, S. and Wagner, H.: A photochemical study ofCalligonum comosum, Planta Med. 33, 262 (1978).
Augusti, K.T.: Gas chromatographic analysis of onion principles and a study on their hypoglycemic action,Indian.J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 19, 218 (1975).
Augusti, K.T.: Effect of essential oil of onion (allypropyl disulphide) (1975).
Augusti, K.T. and Benaim, M.E.: Effect of essential oil of onion (allylpropyl disulfide) on blood glucose free fatty acid and insulin levels of normal subjects.Clin. Chim. Acta,60, 121 (1975).
Mathew, P.T. and Augusti, K.T.: Studies on the effect of allicin (diallyl disulfide oxide) on alloxan diabetes (I), Hypoglycemic action and enhancement of serum insulin effect and glycogen synthesis.Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 19, 213 (1975).
Shani, J., Goldschnied, A., Joseph, B., Ahronsen, Z. and Sulman, F.G.: Hypoglycemic effect ofTrigonella foanum graeum andLupinus termis (Leguminosee) seeds and their major alkaloids in alloxan diabetic and normal rats.Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 210, 27 (1974).
Farnsworth, N.R. and Segelman, A.B.:Catharanthus alkaloids (I). Isolation of afmalicine pericalline, tetrahydroalstonine, vindalinine and ursolic acid fromCatharanthus trichophyllin roots. Tile and Till,57, 52 (1971).
Haslewood, G.A.D. and Strookman, T.A.: A method for the estimation of true sugar in 0.05 ml blood.Biochem. J. 33, 920 (1939).
MacIntyre, I. and Ralston, M.: Direct determination of serum cholesterol.Biochem. J. 56, 1954 (1954).
Lowery, D.H., Rosenbrough, N.G., Farr, L.A. and Randle, R.G.: A method for estimation of tissue proteins,J. Bio. Chem. 193, 265 (1951).
Osborne, D.R. and Voogt, P.: Food Science and Technology. The analysis of nutrients in food. Acad. Press, London (1978).
Duncan, D.B.: Multiple Range and Multiple T. Test Biometrics,11, 1 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Hawary, Z.M., Kholief, T.S. Biochemical studies on some hypoglycemic agents (II) effect ofCalligonum comosum extract. Arch. Pharm. Res. 13, 113–116 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857846
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857846