Abstract
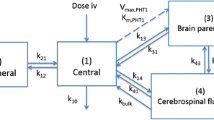
A physiological pharmacokinetic hybrid model was developed in order to predict the disposition kinetics of diphenylhydantoin (DPH) in the brain from the plasma concentration data of DPH. The model was constructed under the assumptions of well-stirred, plasma flow-limited and linear tissue disposition kinetics of DPH. DPH was administered intravenously to the rats at a dose of 10 mg/kg together with/without sodium salicylate (SA; 10 mg/kg) and the DPH concentrations in the plasma and brain were determined. Plasma protein binding of DPH was also determined using equilibrium dialysis technique. Then the model was tested for its predictability of DPH concentrations in the brian from the plasma data of DPH. It was found that the predicted values of DPH concentrations in the brian were in fair agreement with the experimental values in the rats of both treaments. The 2-fold increase in the brain concentrations of DPH by SA-coadministration was predicted well from the plasma concentration and plasma free fraction (f p) data of DPH using the model. Therefore, the hybrid model was concluded to be very useful for the prediction of the concentrations of DPH in the brain from the plasma concentration data. Finally, DPH concentrations in the human brian was calculated using this model from plasma DPH data in the literature, yet the scale-up of this model to the human is not convinced.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Yamaoka, K., Nagagawa, T. and Uno, T.: Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6, 547 (1978).
Boxenbaum, H., Riegelman, S. and Elashoff, R.: Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2, 123 (1974).
Wagner, J.: Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which has been fitted to the dataJ. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 4, 443 (1976).
King, F.G. and Dedrick, R.L.: Physiological model for the 2-deoxycofomycin in normal and leukemic mice.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 9, 519 (1981).
Terasaki, T., Iga, T., Sugiyama, Y. and Hanano, M.: Pharmacokinetic study on the metabolism mechanism of tissue distribution of doxorubicin: Inter organ and inter species variation of tissue to plasma partition coefficients in rats, rabbits, and guinea pigs.J. Pharm. Sci. 73, 1359 (1984).
Himmelstein, K.J. and Lutz, R.L.: A review of the application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7, 127 (1979).
Boxenbaum, H.: Inter species scaling, allometry, physiological time, and the ground plan of pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10, 2011 (1982).
Dedrick, R.L: Animal Scale-up.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1, 435 (1973).
Ichimura, F., Yokogawa, K., Yamana, T., Tsuji,Ji, A., Yamamoto, K., Murakami, S. and Mizukami, Y.: Physiological pharmacokinetic model for distribution and elimination of pentazocine, II. Study in rabbits and scale-up to man.Int. J. Pharmaceut. 19, 75 (1984).
Lin, J.H., Sugiyama, Y., Awazu, S. and Hanano, M.:In vitro andin vivo evaluation of the tissue to blood partition coefficient for physiological pharmacokinetic models.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10, 637 (1982).
Lin, J.H., Sugiyama, Y., Awazu, S. and Hanano, M.: Physiological pharmacokinetics of ethoxybenzamide based on biochemical data obtainedin vitro as wells as physiological data.J. Pharmacokin-Biopharm. 10, 649 (1982).
Lin, J. H., Hayashi M., Awazu, S. and Hanano, M.: Correlation betweenin vitro andin vivo metabolism rate: Oxidation of ethoxybenzamide in rat.J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 6, 327 (1978).
Weiss, M.: On pharmacokinetics in target tissues.Biopharm. Drug. Disp. 6, 57 (1985).
Joachin, H.:Routine determinations of psycoactive drugs, biological/biochemical applications of liquid chromatography, vol.4, Dekker, p.211 (1984).
Dedrick, D. L., Zaharko, D. S. and Lutz, R. L.: Transport and binding of methotrexatein vivo.J. Pharm. Sci. 62, 882 (1973).
Yamaoka, K., Nakagawa, T. Tanaka, H., Yasuhara, M. and Hori, R.: A nonlinear multiple regression program, MULTI 2 (BAYES), based on bayesian algorithm for microcomputers.J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 8, 246 (1985).
Saunders, W. B.:Handbook of biological data. p.163 (1956).
Yamaoka, K., Taniwagara, Y., Nakagawa, T. and Uno, T.: Pharmacokinetic analysis program (MULTI) for microcomputer,J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 4, 879 (1981).
Yamaoka, K. and Nakagawa, T.: A nonlinear least square program based on differential equations, MULTI (RUNGE), for microcomputers,J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 6, 595 (1983).
Guglar, R., Manion, C. V. and Azarnoff, D. L.: Phenytoin: Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 135, 19 (1976).
Evans, W. E., Schentag, J. J. and Jusko, W. J.:Applied Pharmacokinetics 2nd ed., Applied therapeutics p.493 (1986).
Loescher, W.: A comparative study of the protein binding of anticonvulsant drugs in serum of dogs and man.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 208, 429 (1979).
Benedek, I. H., Blouin, R. A. and Mcnamara, P.J.: Influence of smoking on serum protein composition and the protein binding of drugs.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 36, 214 (1984).
Kurata, D. and Wilkinson, G. R.: Erythrocyte uptake and plasma binding of diphenylhydantoin,Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16, 355 (1974).
Lunde, P. K. M., Range, A., Yaffe, S. J., Lund, L. and Sjoqvist, F.: Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin in man. Interaction with other drugs and the effect of temperature and plasma dilution.Clin. Pharm. Ther. 11, 846 (1970).
Salle, E. D., Pacini, G. M. and Morselli, P. L.: Studies on plasma protein binding of carbamazepine.Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 6, 193 (1974).
Hooper, W. D., Dubetz, D. K., Bochner, F., Cotter L. M., Smith, G. A., Eadie, M. J. and Tyrer, J. H.: Plasma protein binding of carbamazepine.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 17, 433 (1975).
Loescher, W.: Serum protein binding and pharmacokinetics of valproate in dog and mouse.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 204 255 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, SH., Shim, CK., Lee, MH. et al. Prediction of the concentration of diphenylhydantoin in the brain using a physiological pharmacokinetic hybrid model. Arch. Pharm. Res. 13, 221–226 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856525
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856525