Abstract
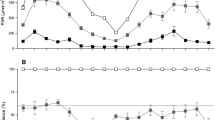
The photosynthetic response of 12-year oldPinus sylvestriformis to elevated CO2 and its influential factors were tested and analyzed in the forest region of Changbai Mountain in 1999. Trees grown at the natural condition were controlled at three levels of CO2 concentration (350 μL·L−1, 500 μL·L−1 and 700 μL·L−1) by CO2 rich settlement designed by us. Net photosynthetic rates (NPR), temperature, relative humidity, stomatal conductance, intercellular CO2 concentration and photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) were measured at 6:00, 8:00, 10:00, 14:00, 16:00 and 18:00 hours a day. Experimental results showed that the NPR ofPinus sylvestriformis increased by 32.6% and 123.0% at 500 μL·L−1 and 700 μL·L−1 CO2 concentration respectively, compared to ambient atmospheric CO2 concentration (350 μL·L−1). The relations between NPR and influential factors, including temperature, relative humidity, intercellular CO2 concentration and photosynthetic active radiation, were analyzed respectively by regression analysis at different CO2 concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazzaz, F.A. 1990. The response of natural ecosystems to the rising global CO2 levels [J]. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst.,21: 167–196.
Caemmerer, S.V. and Farquhar, G.D. 1981. Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves [J]. Planta,153: 376–387.
Han Shijie, Wang Chenrui.et al. 1999. Response of seedlings growth ofPinus sylvestriformis to atmospheric CO2 enrichment in Changbai Mountain [J]. Journal of Forestry Research,10(4): 207–208.
Hendrey, G.R.et al. 1993. Free air carbon dioxide enrichment: development, progress, results [J]. Vegetatio,104/105: 17–31.
Jiang Gaoming, Qu Chunmei. 2000. Photosynthetic response of six woody species to elevated CO2 in Quercus liaotungensis forest in the Beijing Mountainous areas [J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,24(2): 204–208.
Linden R. S., 1990. Some coolness concerning global warming. Bull. Amer. Meterorol. Soc.71: 288–299.
Pearcy, R.W., Bjorkman, O. 1993. Physiological effects. In influence of water table and atmospheric CO2 concentration on the carbon balance of arctic tundra [J]. Arctic Alpine Res.16: 331–355.
Raval, A., Ramanathan V. 1989. Observational determination of the greenhouse effect. Nature342: 758–761.
Ruan Chengjiang, Li Daiqiong. 2000. Photosynthetic characteristics ofHippophae rhamnoides L. and its influence factors in semiarid loess hilly region[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment.9(1): 16–21.
Tolbert, N. E., Zelitch, I. 1983. Carbon metabolism. In CO2 and Plants: The response of plants to rising level of atmospheric carbon dioxide, ed. E. R. Lemon. pp. 21–64. Boulder, Colo: Westview.
Wang Chenrui, Han Shijie. 1999. Effects of elevated CO2 on net photosynthetic rate of trees in Changbai Mountain [J]. Journal of Forestry Research,10(4): 211–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation Item: This project was supported by Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Biography: WANG Chen-rui (1970-), male, Assistant Research Fellow in Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Responsible editor: Chai Ruihai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen-rui, W., Shi-jie, H. & Xing-bo, L. Photosynthetic response ofPinus sylvestriformis to elevated carbon dioxide and its influential factor analysis. Journal of Forestry Research 11, 167–172 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02855518
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02855518