Abstract
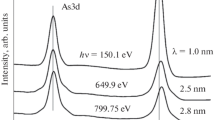
Laser Raman spectroscopy was employed as a non-destructive probe for the detection and monitoring of crystalline arsenic in the native oxide films formed during heating of GaAs in air at various temperatures. Spectroscopy of oxide films formed after successive heating and etching treatments could confirm the location of arsenic to be near the top of the GaAs: native oxide overlayer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkovits V L, Kiselev V A, Minashvili T A and Safarov V I 1988Solid State Communn. 65 385
Cape J A, Tennant W E and Hale L G 1977J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 14 921
Chang R P H and Sinha A K 1976Appl. Phys. Lett. 29 1, 56
Farrow R L, Chang R K, Mroczkowski S and Pollak F H 1977Appl. Phys. Lett. 31 768
Hasegawa H and Hartnagel H L 1976J. Electrochem. Soc. 123 5, 713
Lannin J S, Calleja J M, Cardona M 1975Phys. Rev. B12 585
Lannin J S 1977Phys. Rev. B15 3863
Mizokawa Y, Iwasaki H, Nishitani R and Nakamura A 1978Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 17 327
Murarka S P 1975Appl. Phys. Lett. 26 180
Schwartz B 1975CRC Crit. Rev. Solid State Sci. 5(4) 609
Schwartz G P, Schwartz B, Distefano D, Gualtieri G J and Griffiths J E 1979Appl. Phys. Lett. 34 205
Schwartz G P, Griffiths J E, Distefano D, Gualtieri G J and Schwartz B 1979Appl. Phys. Lett. 34 742
Takagi H, Kano G and Teramoto I 1978J. Electrochem. Soc. 125 4, 579
Trommer R, Anastassakis E and Cardona M 1976Light scattering in solids (eds) M Balkanski, R Leite and S P S Porto (Paris: Flammarion) p. 396
Zaininger K H and Revesz A G 1964J. Phys. Paris 25 208
Zitter R N 1971The physics of semimetals and narrow gap semiconductors (eds) D L Carter and R T Bate (New York: Pergamon Press) p. 285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, M., Datta, G., Venkataraman, P. et al. Detection of excess crystalline As in GaAs: Nation oxide overlayers by Raman scattering. Pramana - J. Phys. 32, 641–646 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847388
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847388