Abstract
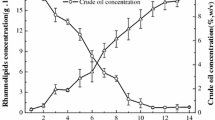
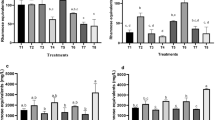
The potential biodegradation of crude oil was assessed based on the development of a fermentative process with a strain ofPseudomonas aeruginosa which produced 15.4 g/L rhamnolipids when cultured in a basal mineral medium using glycerol as a sole carbon source. However, neither cell growth nor rhamnolipid production was observed in the comparative culture system using crude oil as the sole carbon source instead. As rhamnolipid, an effective biosurfactant, has been reported to stimulate the biodegradation of hydrocarbons, 1 g/L glycerol or 0.22 g/L rhamnolipid was initially added into the medium to facilitate the biodegradation of crude oil. In both situations, more than 58% of crude oil was degraded and further converted into accumulated cell biomass and rhamnolipids. These results suggest thatPseudomonas aeruginosa could degrade most of crude oil with direct or indirect addition of rhamnolipid. And this conclusion was further supported by another adsorption experiment, where the adsorption capacity of crude oil by killed cell biomass was negligible in comparison with the biologic activities of live cell biomass.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balba, M.T., Al-Shayji, Y., Al-Awadhi, N., Yateem, A., 2002. Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant-producing bacteria from oil-contaminated soil.Soil and Sediment Contamination,11: 41–55
Beal, R., Betts, W.B., 2000. Role of rhamnolipids biosurfactants in the uptake and mineralization of hexadecane byPseudomonas aeruginosa.J. Appl. Microbiol.,89: 158–168.
Chandrasekaran, E.V., Bemiller, J.N., 1980. Constituent Analysis of Glycosaminoglycans.In: Whistler, R.L., Wolfrom, M.L. (Eds.), Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry. Academic Press, New York, p.89–96.
Chhatre, S.A., Purohit, H.J., Shanker, R., Chakrabarti, T., Khanna, P., 1996. Bacterial consortia for crude oil spill remediation.Wat Sci. Tech.,34: 187–193.
Gerson, D.F., 1993. The Biophysics of Microbial Surfactants: Growth on Insoluble Substrates.In: Kozaric, N. (Ed.), Surfactant Science Series, Biosurfactants: Production, Properties, Applications. Marcel Dekker, New York, USA, p. 269–286.
Itoh, S., Suzuki, T., 1972. Effect of rhamnolipids on growth ofPseudomonas aeruginosa mutant deficient inn-paraffin-utilizing ability.Agric. Biol. Chem.,36: 2233–2235.
Matsufuji, M., Nakata, K., Yoshimoto, A., 1997. High production of rhamnolipids byPseudomonas aeruginosa growing on ethanol.Biotechnology Letters,19: 1213–1215.
Nakahara, T., Hisatsuka, K., Minoda, Y., 1981. Effect of hydrocarbon emulsification on growth and respiration of microorganisms in hydrocarbon media.J. Ferment. Technol.,59: 415–418.
Ollis, D., 1992. Slick solutions for oil spills.Nature,358: 453–454.
Rahman, K.S.M., Banat, I.M., Thahira, J., Thayumanavan, T., Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P., 2002. Bioremediation of gasoline contaminated soil by a bacterial consortium amended with poultry litter, coir pith and rhamnolipid biosurfactant.Biores. Technol.,81: 25–32.
Urum, K., Pekdemir, T., Gopur, M., 2003. Optimum conditions for washing of crude oil-contaminated soil with biosurfactant solutions.Process Safety and Environm. Protect: Transact. of the Institut. of Chem. Engin.,81: 203–209.
Wouter, H.N., Dick, B.J., 2002. Rhamnolipid stimulates uptake of hydrophobic compounds byPseudomonas aeruginosa.Appl. and Environm. Microb.,68: 4502–4508.
Yong, K.C., Ooi, T.L., Dzulkefly, K., Wanyunus, W.M.Z., Hazimah, A.H., 2001. Characterization of glycerol residue from a palm kernel oil methyl ester plant.J. of Oil Palm Research,13 (2): 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by Science Foundation from China Petroleum and Chemical Corporation, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo-liang, Z., Yue-ting, W., Xin-ping, Q. et al. Biodegradation of crude oil byPseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of rhamnolipids. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. B 6, 725–730 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842430
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842430