Abstract
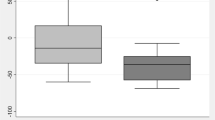
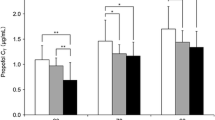
Objective: The aim of this paper is to compare the propofol concentration in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in patients scheduled for intracranial tumor removal and anaesthetized using propofol as part of a total intravenous anaesthesia technique. Methods: Twenty-seven patients (ASA I–II) scheduled for elective intracranial tumor removal were studied. Anesthesia was induced with 2 mg/kg propofol for 5 min and infused at 10 mg/(kg·h) for 5 min and then stopped. CSF and arterial blood were collected simultaneously before infusion of propofol and at different time points after infusion of propofol according to bispectral index (BIS) values. Concentrations of propofol in plasma and CSF were measured by HPLC with fluorescence detection. The correlation coefficient and regression equation between plasma and CSF concentration of propofol were worked out by linear simple regression. Results: The propofol CSF concentration that we measured was 1.46% of the plasma concentration. The coefficient of relation between plasma and CSF concentration was 76.7%. Conclusions: The propofol CSF concentration was positively correlated with and much lower than the plasma concentration. Discrepancies may result from high plasma protein binding of propofol, intracranial pathology and sampling volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawidowicz, A.L., Fijalkowska, A., Nestorowicz, A., 2001a. The influence of blood sample storage time on the propofol concentration in plasma and solid blood elements.Biomed. Chromatogr.,15:408–412.
Dawidowicz, A.L., Nestorowicz, A., Fijalkowska, A., 2001b. Propofol concentration in cerebrospinal fluid during TIVA.Minerva. Anestesiol.,67(Suppl):244–245.
Dawidowicz, A.L., Fijalkowska, A., Nestorowicz, A., 2003a. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood propofol concentration during total intravenous anaesthesia for neurosurgery.Br. J. Anaesth.,90(1):84–86.
Dawidowicz, A.L., Kalitynski, R., Fijalkowska, A., 2003b. Free and bound propofol concentrations in human cerebrospinal fluid.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.,56:545–550.
De, P.L., De, G., Testa, C., 2000. Disposition of propofol between red blood cell, plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in rabbits.Eur. J. Anaesthesiol.,17:18–22.
Dutta, S., Ebling, W.F., 1998. Formulation-dependent brain and lung distribution kinetics of propofol in rats.Anaesthesiology,89:678–685.
Dutta, S., Matsumoto, A., Muramatsu, A., 1998. Steady-state propofol brain: Plasma and brain. Blood partition coefficient and the effect-site equilibrium paradox.Br. J. Anaesth.,81:422–424.
Engdahl, O., Abrahams, M., Bjornsson, A., 1998. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of propofol during anaesthesia in humans.Br. J. Anaesth.,81:957–959.
Ghersi-Egea, J.F., Strazielle, N., 2001. Brain metabolism, and multidrug resistance at the choroid plexus.Microsc. Res. Tech.,52:83–88.
Gin, T., 1993. Pharmacodynamics of propofol and free drug concentrations.Anesthesiology,78:604.
Gumerlock, M.K., 1996. Blood-Brain Barrier and Cerebral Edema.In: Tindall, G.T., Cooper, P.R., Barrow, D.L. (Eds.), The Practice of Nuerosurgery. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p. 4–12.
Ludbrook, G.L., Upton, R.N., 1997. A physiology model of induction of anaesthesia with propofol in sheep. II. Model analysis and implications for dose requirements.Br. J. Anaesth.,79:505–513.
Mazoit, J.X., Samii, K., 1999. Binding of propofol to blood components: Implications for pharmacokinetics and for pharmacodynamics.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.,47:35–42.
Plummer, G.F., 1987. Improved method for the determination of propofol in blood by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection.J. Chromatogr.,421:171–176.
Shyr, M.H., Tsai, T.H., Tan, P.P.C., 1995. Concentration and regional distribution of propofol in brain and spinal cord during propofol anesthesia in the rat.Neurosci. Lett.,184:212–215.
Vuyk, J., Engbers, F.H.M., Lemmens, H.J.M., 1992. Pharmacodynamics of propofol in female patients.Anesthesiology 77:3–9.
Zamacona, M.K., Suarez, E., Aguilera, L., 1997. Serum protein binding of propofol in critically ill patients.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.,41:1267–1272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Zhejiang University, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Yu-hong, L., Jian-jun, Y. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma propofol concentration during total intravenous anaesthesia of patients undergoing elective intracranial tumor removal. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. B 6, 865–868 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840994
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840994