Abstract
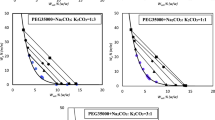
KF or K2CO3 was added into the 1-butanol-water system and two phases were formed: water-rich phase (water phase) and 1-butanol-rich phase (1-butanol phase). The liquid-liquid equilibrium (LLE) data for 1-butanol-water-Kf and 1-butanol-water K2CO3 systems were measured at 25°C and showed that 1-butanol phase contained negligible salt and water phase contained negligible 1-butanol when the concentrations of KF and K2CO3 in the water phase were equal to or higher than 27.11% and 31.68%, respectively. Thus water could be separated efficiently from 1-butanol-water by adding KF or K2CO3 into the system. A theoretical calculation of LLE data was calculated by using the Pitzer theory to get water activity in the water phase, and by the models, such as the Wilson, NRTL or the UNIQUAC for the 1-butanol phase. For 1-butanol-water-KF system, the experimental data were found in good agreement with the calculated results by using Pitzer theory and Wilson equation, while for 1-butanol-water-K2CO3 system, the experimental data were found in good agreement with the calculated results by using Pitzer theory and UNIQUAC equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gmehling J, Onken U, Arlt W.Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data Collection (Aqueous-Organic Systems). Vol. 1. Frank-Furt: Dechema Press, 1981:333–693.
Tang Zhi-gang, Zhou Rong-qi, Duan Zhan-ting. Separation of Isopropanol from Aqueous Solution by Salting-out Extraction.Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2001,76:757.
Xu Wen-you. Separation of Ethanol-Acetone-1-Butanol-Water System Using Potassium Carbonate.The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2001,1:318 (Ch).
Stephen H T.Solubilities of Inorganic Compounds, Vol. 2. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1979. 344.
Silvester L F, Pitzer K S. Thermodynamics of Electrolytes.J Phys Chem, 1977,81:1822.
Xu Wen-you. Measurement and Correlation of Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium Data for Butanone-Water-Potassium Fluoride and Butanone-Water-Potassium Carbonate Systems.Chemical Engineering, 2001,29:43 (Ch).
Roy R N, Pitzer K S. Thermodynamics of Aqueous Carbonate Solutions.J Chem Thermodynamics, 1984,16:303.
Xu Wen-you. Measurement and Correlation of Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium Data for Tetrahydrofuran-Water-KF and Tetrahydrofuran-Water-K2CO3 Systems.The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2002,2:36 (Ch).
Abrams D S, Prausnitz J M. Statistical Thermodynamics of Liquid Mixture: A New Expression for the Excess Gibbs Energy of Partly or Completely Miscible System.Aiche J, 1975,21:116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province (2005GGA06705).
Biography: XU wen-you(1963-), male, Professor, research direction: separation engineering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen-you, X., Min, J. Liquid-liquid equilibrium for 1-butanol-water-KF and 1-butanol-water-K2CO3 systems. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 10, 892–896 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832434
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832434
Key words
- 1-butanol-water-KF
- 1-butanol-water-K2CO3
- liquid-liquid equilibrium
- Pitzer equation
- Wilson equation
- NRTL equation
- UNIQUAC equation
- salting-out effect