Abstract
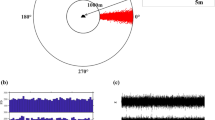
The paper analyses the characteristics of radio frequency interference (RFI) in HF surface wave radar (HF-SWR) which adopts the linear frequency modulated interrupted continuous wave (FMICW). RFI will influence all the range cells including all the positive frequency and negative frequency, and the negative frequency range cells contain only the interference information. Based on the above characteristics, we introduce and analyze a new adaptive interference mitigation beamforming algorithm using the negative frequency range cells samples to estimate the interference covariance matrix. Experimental results confirm that this general and robust algorithm can achieve effective RFI suppression using the data recorded by the HFSWR, located near Zhoushan in Zhejiang China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrick D E. Theory of HF/VHF Propagation Across the Rough Sea.Radio Science, 1971,6:517–533.
Reed I S, Mallet J D, Brennan L E. Rapid Convergence Rate in Adaptive Arrays.IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System, 1974,10(6):853–863.
Anderson S J, Abramovich Y I, Fabrizo G A. Stochastic Constraints in Nonstationary Hot Clutter Cancellation.Proceedings of ICASSP97, 1997,2:3753–3756.
Abramovich Y I, Spencer N, Anderson S J. Stochastic Constraints Method in Nonstationary Hot Clutter Cancellation—part 1: Fundeanmentals and Supervised Training Applications.IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System, 1998,34(4):1271–1292.
Abramovich Y I, Spencer N, Anderson S J. Stochastic Constraints Method in Nonstationary Hot Clutter Cancellation—part 2: Unsupervised Training Applications.IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System, 2000,36(1): 132–150.
Sevgi L, Ponsford A M, Chan H C. An Integrated Mritime Surveillance System Based on HF Surface-Wave Radars, Part II: Operational Status and System Performance.IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2001,43(5):52–63.
Fabrizio G A, Gershman A B, Turley M D. Robust Adaptive Beamforming in HF surface-Wave OTH Radar.IEEE Trans On Aerospace and Electronic System, 2004,40(2):510–524.
Gao H T, Zheng X, Li J. Adaptive Anti-Interference Technique Using Subarrays in HF Surface Wave Radar.IEE Proc Radar Sonar Navig, 2004,151(2):100–104.
Wan X R, Ke H Y, Wen B Y. Adaptive Cochannel Interference Suppression Based on Subarrays for HFSWR.IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2005,12(2):162–165.
Zhou Hao, Wen Bi-yang, Wu Si-cai. Radio Frequency Interference Suppression in HF radars.Electronics Letters, 2003,39(12):925–927.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the national Natural Science Foundation of China (60401003) and the High-Technology Research and Development Program of China (2001AA631050)
Biography: WAN Xian-rong (1975-), male, Ph. D. candidate, research direction: adaptive signal processing for HF surface wave radar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xian-rong, W., Heng-yu, K. & Feng, C. Adaptive radio frequency interference mitigation for HF surface wave radar. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 10, 851–854 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832426
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832426