Abstract
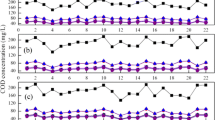
The ratio of aeration/non-aeration is a key variable in the operation of a Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) for biological nutrient removal (BNR). To determine the ratio of aeration/non-aeration, the Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP) and pH were monitored and evaluated as possible controlling factors in SBR operation. As a result of two steps, during the anaerobic phase, phosphorus release ended when the slopes of the variation curve of the pH and ORP were zero and −0.5, respectively. During the aerobic phase, the pH increased because of phosphorus uptake, suddenly decreased after phosphorus uptake, and increased again after nitrification. The result corresponded to the ammonia break point of the ORP. During the anoxic phase, the ORP bending point appeared if there were plenty of carbon sources, and the pH increased with the denitrification and decreased after the end of denitrification. It was concluded that the optimal ratio of aeration/non-aeration of SBR with a variable inflow could be determined by using ORP and pH profiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charpential, J., Martin, H.G., and Mogno, Y. (1989). “Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) regulation as a way to optimise aeration and C, N and P removal experimental basis and various full-scale examples.”Wat. Sci. Tech., Vol. 21, No. 10/11, pp. 1209–1223.
Chen, K.C., Chen, C.Y., Peng, J.W., and Houng, J.Y. (2002). “Real-time control of an immobilized-cell reactor for wastewater treatment using ORP.”Wat. Res., Vol. 36, pp. 230–238.
Hong, W.Z., Donald, S.M., William, K.O., and Frederic, A.K. (1999). “Controlling factors for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a two-stage intermittent aeration process treating domestic sewage.”Wat. Res., Vol. 33, No. 4, pp. 961–970.
Ko, K.B. and Suh, J.S. (2002). “State evaluation of Nutrient removal in an intermittent aeration process by monitoring ORP & pH.”Journal of Korean Society on Water Quality, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 401–409.
Lee, D.S., Jeon, C.O., and Park, J.M. (2001). “Biological nitrogen removal with enhanced phosphorus uptake in a sequencing batch reactor using single sludge system.”Wat. Res., Vol. 35, No. 16, pp. 3968–3976.
Sasaki, K., Yamamoto, Y., Tsumura, K., Hatsumata, S., and Tatewaki, M. (1993). “Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in intermittently aerated 2-tank activated sludge process using DO and ORP-bending-point control.”Wat. Sci. Tech., Vol. 28, No. 11-12, pp. 513–521.
Spagni, A., Buday, J., Ratini, P., and Bortone, G. (2000). “Experimental considerations on monitoring ORP, pH, Conductivity and dissolved oxygen in nitrogen and phosphorus biological removal process.”1st World Water Congress of the International Water Association, Vol. 3, pp. 17–24.
Yu, R.F., Liaw, S.L., Chang, C.N., Lu, H.J., and Cheng, W.Y. (1997). “Monitoring and control using on-line ORP on the continuous flow activated sludge batch reactor system.”Wat. Sci. Tech., Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 57–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HT., Kim, GS., Shin, SW. et al. Application of ORP and pH as controlling factors in sequencing batch reactor. KSCE J Civ Eng 9, 73–79 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829061
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829061