Summary
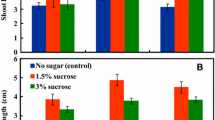
To improve proliferation of soybean cultures in liquid medium, the effects of sucrose; total inorganic nitrogen; content of No3 −, NH4 +, Ca2+, PO4 3−, K+; NH4 +/NO3 − ratio; and medium osmotic pressure were studied using cv. Jack. Sucrose concentration, osmotic pressure, total nitrogen content, and ammonium to nitrate ratio were found to be the major factors controlling proliferation of soybean embryogenic cultures. Growth decreased linearly as sucrose concentration increased from 29.7 mM to 175.3 mM. A sucrose concentration of 29.2 mM, a nitrogen content of 34.9 mM, at 1 to 4 ammonium to nitrate ratio were found to be optimal for the fastest proliferation of soybean embryogenic cultures. There was no significant effect on proliferation of cultures when concentrations of NH4 +, Ca2+, PO4 3−, and K+ were tested in the range of 3.50 to 10.50, 1.02 to 3.06, 0.68 to 2.04, and 22.30 to 36.70 mM, respectively. The relative proliferation of embryogenic cultures of four soybean genotypes was evaluated in Finer and Nagasawa medium and in the new medium formulation. Despite genotype-specific differences in growth, the genotypes tested showed a biomass increase in the new formulation equal to 278, 269, 170, and 251% for Chapman, F138, Jack, and Williams 82, respectively, relative to their growth on standard FN medium. Due to its lowered sucrose and nitrogen content, we are referring to the new medium as FN Lite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, M. A.; Boerma, H. R.; Parrott, W. A. Genotype effects on proliferative embryogenesis and plant regeneration of soybean. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 29P:102–108; 1993.
Christianson, M. L.; Warnick, D. A.; Carlson, P. S. A morphogenetically competent soybean suspension culture. Science 222:632–634; 1983.
Chu, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Su, C.-S. Establishment of an efficient medium for anther culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci. Sin. 18:659–668; 1975.
Collins, G. B.; Phillips, G. C.In vitro tissue culture and plant regeneration inTrifolium pratense L. In: Earle, E. D.; Demarly, Y., eds. Regeneration from cells and tissue culture. New York: Praeger Scientific Publishing; 1982:22–34.
Conner, A. J.; Meredith, C. P. Strategies for the selection and characterization of aluminum-resistant variants from cell cultures ofNicotiana plumbaginifolia. Planta 166:466–473; 1985.
Finer, J. J.; McMullen, M. D. Transformation of soybean via particle bombardment of embryogenic suspension cultures. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27P:175–182; 1991.
Finer, J. J.; Nagasawa, A. Development of an embryogenic suspension culture of soybean (Glycine max Merrill). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 15:125–136; 1988.
Gamborg, O. L.; Miller, R. A.; Ojima, K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 50:150–158; 1968.
Gleddie, S.; Keller, W.; Setterfield, G. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf explants and cell suspensions ofSolanum melongena (eggplant). Can. J. Bot. 61:656–666; 1983.
Kumar, A. S.; Gamborg, O. L.; Nabors, M. W. Plant regeneration from cell suspension cultures ofVigna aconitifolia. Plant Cell Rep. 7:138–141; 1988a.
Kumar, A. S.; Gamborg, O. L.; Nabors, M. W. Regeneration from long-term cell suspension cultures of tepary bean (Phaseolous acutifolius). Plant Cell Rep. 7:322–325; 1988b.
Maheswaran, G.; Williams, E. G. Direct somatic embryoid formation on immature embryos ofTrifolium repens, T. pratense andMedicago sativa, and rapid clonal propagation ofT. repens. Ann. Bot. 54:201–211; 1984.
Meijer, E. G. M.; Brown, D. C. W. Role of exogenous reduced nitrogen and sucrose in rapid high frequency somatic embryogenesis inMedicago sativa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 10:11–20; 1987.
Merkle, S. A.; Parrott, W. A.; Flinn, B. S. Morphogenetic aspects of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe, T. A., ed. In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:155–203.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Nadolska-Orczyk, A.; Orczyk, W. New aspects of soybean somatic embryogenesis. Euphytica 80:137–143; 1994.
Niedz, R. P. Growth of embryogenic sweet orange callus on media varying in the ratio of nitrate to ammonium nitrogen. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 39:1–5; 1994.
Parrott, W. A.; All, J. N.; Adang, M. J., et al. Recovery and evaluation of soybean plants transgenic for aBacillus thuringiensis var.Kurstaki insecticidal gene. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30P:144–149; 1994.
Parrott, W. A.; Durham, R. E.; Bailey, M. A. Somatic embryogenesis in legumes. In: Bajaj, Y. P. S., ed. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Vol. 31. Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed II. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1995:199–227.
Ranch, J. P.; Oglesby, L.; Zielinski, A. C. Plant regeneration from embryoderived tissue cultures of soybean by somatic embryogenesis. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 21:653–657; 1985.
Sato, S.; Newell, C.; Kolacz, K., et al. Stable transformation via particle bombardment in two different soybean regeneration systems. Plant Cell Rep. 12:408–413; 1993.
Schenk, R. U.; Hildebrandt, A. C. Medium and techniques for induction and plant growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50:199–204; 1972.
Smith, D. L.; Krikorian, A. D. Release of somatic embryogenic potential from excised zygotic embryos of carrot and maintenance of proembryonic cultures in hormone-free medium. Am. J. Bot. 76:1832–1843; 1989.
Stewart, C. N., Jr.; Adang, M. J.; All, J. N., et al. Genetic transformation, recovery, and characterization of fertile soybean transgenic for syntheticBacillus thuringiensis cryIAc gene. Plant Physiol. 112:121–129; 1996.
Thompson, M. R.; Douglas, T. J.; Obata-Sasamoto, H., et al. Mannitol metabolism in cultured plant cells. Physiol. Plant. 67:365–369; 1986.
Trigiano, R. N.; Beaty, R. M.; Graham, E. T. Somatic embryogenesis from immature embryos of redbud (Cercis canadensis). Plant Cell Rep. 7:148–150; 1988.
Walker, K. A.; Sato, S. J. Morphogenesis in callus tissue ofMedicago sativa: the role of ammonium ion in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1:109–121; 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samoylov, V.M., Tucker, D.M. & Parrott, W.A. Soybean [Glycine max (L.) merrill] embryogenic cultures: The role of sucrose and total nitrogen content on proliferation. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 34, 8–13 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823116
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823116