Abstract
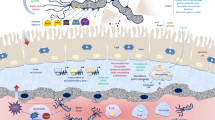
EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli (EPEC) causes severe diarrhea in young children. Upon infection, EPEC induces the assembly of highly organized pedestal-like actin structures in host epithelial cells. All the EPEC genes that are involved in inducing formation of actin pedestals are located in a unique 35 kbp chromosomal pathogenicity island, termed LEE. These genes include thesep genes that encode components of type III protein secretion system, and genes that encode proteins secreted by this system, theesp genes. This protein secretion system is activated upon contact with the host cell, resulting in increased secretion of Esp proteins. Some of these Esp proteins form the translocation apparatus while others are translocated into the cytoplasm of the host cell. Concerted activity of the LEE genes including theeae, esp and thesep genes is needed to trigger signal transduction in the host cell which results in formation of an actin pedestal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam T., Arpin M., Prevost M.C., Gounon P., Sansonetti P.J.: Cytoskeletal rearrangements and the functional role of T-plastin during entry ofShigella flexneri into HeLa cells.J. Cell Biol. 129, 367–381 (1995).
Andrade J.R.: Invasion by EPEC.Rev. Microbiol. 27, 63–66 (1996).
Baldwin T.J., Lee D.M.B., Knutton S., Williams P.H.: Calcium-calmodulin dependence of actin accretion and lethality in cultured HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenicEscherichia coli.Infect. Immun. 61, 760–763 (1993).
Baldwin T.J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P.H.: Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenicEscherichia coli.Infect. Immun. 59, 1599–1604 (1991).
Bray J.: Isolation of antigenically homogeneous strains ofBact. coli neopolitanum from summer diarrhoea of infants.J. Path. Bacteriol. 57, 239–247 (1945).
Canil C., Rosenshine I., Ruschkowski S., Donnenberg S.M., Kaper B.J., Finlay B.B.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli decreases the transepithelial electric resistance of infected polarized epithelial monolayers.Infect. Immun. 61, 2755–2762 (1993).
Donnenberg M.S., Giron J.A., Nataro J.P., Kaper J.B.: A plasmid-encoded type IV fimbrial gene of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli associated with localized adherence.Mol. Microbiol. 6, 3427–3437 (1992).
Donntenberg M.S., Calderwood S.B., Donohue R.A., Keusch G.T., Kaper J.B.: Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells.Infect. Immun. 58, 1565–1571 (1990).
Donnenberg M.S., Kaper J.B., Finlay B.B.: Interaction between enteropathogenicE. coli and host epithelial cells.Trends Microbiol. 5, 109–114 (1977).
Donnenberg M.S., Yu J., Kaper J.B.: A second chromosomal gene necessary for intimate attachment of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli to epithelial cells.J. Bacteriol. 175, 4670–4680 (1993a).
Donnenberg M.S., Tacket C.O., James S.P., Losonsky G., Nataro J.P., Wasserman S.S., Kaper J.B., Levine M.M.: Role of theeaeA gene in experimental entropathogenicEscherichia coli infection.J. Clin. Invest. 92, 1412–1417 (1993b).
Finlay B.B., Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M.S., Kaper J.B.: Cytoskeletal composition of attaching and effacing lesions associated with enteropathogenicEscherichia coli adherence to HeLa cells.Infect. Immun. 60, 2541–2543 (1992).
Foubister V., Rosenshine I., Finlay B.B.: A diarrheal pathogen, enteropathogenicEscherichia coli (EPEC), triggers a flux of inositol phosphates in infected epithelial cells.J. Exp. Med. 179, 993–998 (1994a).
Foubister V., Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M.S., Finlay B.B.: TheeaeB gene of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli is necessary for signal transduction in epithelial cells.Infect. Immun. 62, 3038–3040 (1994b).
Frankel G., Lider O., Hershkoviz R., Mould A.P., Kachalsky S.G., Candy D.C.A., Cahalon L., Humphries M.J., Dougan G.: The cell-binding domain of intimin from enteropathogenicEscherichia coli binds to β1-integrins.J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20359–20364 (1996).
Giron J.A., Ho A.S., Schoolnik G.K.: An inducible bundle-forming pilus of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli.Science 254, 710–713 (1991).
Gomez-Duarte O.G., Kaper J.B.: A plasmid-encoded regulatory region activates chromosomaleaeA expression in enteropathogenicEscherichia coli.Infect. Immun. 63, 1767–1776 (1995).
Jarvis K.G., Giron J.A., Jerse A.E., McDaniel T.K., Donnenberg M.S., Kaper J.B.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli contains a specialized secretion system necessary for the export of proteins involved in attaching and effacing lesions formation.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7996–8000 (1995).
Jerse A.E., Yu J., Tall B.D., Kaper J.B.: A genetic locus of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7839–7843 (1990).
Kenny B., Finlay B.B.: Protein secretion by enteropathogenicEscherichia coli is essential for transducing signals to epithelial cells.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7991–7995 (1995).
Kenny B., Lai L.C., Finlay B.B., Donnenberg M.S.: EspA, a protein secreted by enteropathogenicEscherichia coli, is required to induce signals in epithelial cells.Mol Microbiol. 20, 313–323 (1996).
Kenny B., Finlay B.B.: Intimin-dependent binding of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli to host cell triggers novel signaling event, including tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-γ.Infect. Immun. 60, 2528–2536 (1997).
Kenny B., DeVinney R., Stein M., Reinscheid D.J., Frey E.A., Finlay B.B.: EnteropathogenicE. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells.Cell 91, 511–520 (1997).
Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P.H., McNeish A.S.: Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagicEscherichia coli.Infect. Immun. 57, 1290–1298 (1989).
Knutton S., Rosenshine I., Pallen M.J., Nisan I., Neves B.C., Bain C., Wolff C., Dougan G., Frankel G.: A novel EspA-associated surface organelle of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli involved in translacation of EspB into eukaryotic cells.EMBO J., in press (1998).
Levine M.M., Edelman R.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis.Epidemiol. Rev. 6, 31–51 (1984).
Manjarrez-Hernandez H.A., Amess B., Selers L., Baldwin T.J., Knutton S., Williams P.H., Aitken A.: Purification of a 20-kDa phosphoprotein from epithelial cells and identification as a myosin light chain-phosphorylation induced by enteropathogenicEscherichia coli and phorbol ester.FEMS Lett. 292, 121–127 (1991).
Manjarrez-Hernandez H.A., Baldwin T.J., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P.H.: Intestinal epithelial cell protein phosphorylation in enteropathogenicEscherichia coli diarrhoea.Lancet 339, 521–523 (1992).
McDaniel T.K., Jarvis K.G., Donnenberg M.S., Kaper J.B.: A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1664–1668 (1995).
McDaniel T.K., Kaper J.B.: A cloned pathogenicity island from enteropathogenicEscherichia coli confers the attaching and effacing phenotype onE. coli K-12.Mol. Microbiol. 23, 399–407 (1977).
Moon H.W., Whipp S.C., Argenzio R.A., Levine M.M., Giannella R.A.: Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenicEscherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines.Infect. Immun. 41, 1340–1351 (1983).
Paulozzi L.J., Johnson K.E., Kamahele L.M., Clausen C.R., Riley L.W., Helgerson S.D.: Diarrhea associated with adherent enteropathogenicEscherichia coli in an infant and toddler center, Seattle, Washington.Pediatrics 77, 296–300 (1986).
Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M.S., Kaper J.B., Finlay B.B.: Signal transduction between enteropathogenicEscherichia coli (EPEC) and epithelial cells: EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of host cell proteins to initiate cytoskeletal rearrangement and bacterial uptake.EMBO J. 11, 3551–3560 (1992).
Rosenshine I., Ruschkowski S., Stein M., Reinsceid D., Mills D.S., Finlay B.B.: A pathogenic bacterium triggers epithelial signals to form a functional bacterial receptor that mediates pseudopod formation.EMBO J. 15, 2613–2624 (1996).
Sanger J.M., Chang R., Ashton F., Kaper J.B., Sanger J.W.: Novel form of actin-based motility transports bacteria on the surfaces of infected cells.Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 34, 279–287 (1996).
Senerwa D., Olsvik O., Mutanda L.N., Lindqvist K.J., Gathuma J.M., Fossum K., Wachsmuth K.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli serotype O111: HNT isolated from preterm neonates in Nairobi, Kenya.J. Clin. Microbiol. 27, 1307–1311 (1989).
Sohel I., Puente J.L., Ramer S.W., Bieber D., Wu C.Y., Schoolnik G.K.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli: identification of a gene cluster coding for bundle-forming pilus morphogenesis.J. Bacteriol. 178, 2613–2628 (1996).
Stein M.A., Mathers D.A., Yan H., Baimbridge K.G., Finlay B.B.: EnteropathogenicEscherichia coli markedley decreases the resting membrane potential of Caco-2 and HeLa human epithelial cells.Infect. Immun. 64, 4820–4825 (1996).
Stone K.D., Zhang H.Z., Carlson L.K., Donnenberg M.S.: A cluster of fourteen genes from enteropathogenicEscherichia coli is sufficient for the biogenesis of a type IV pilus.Mol. Microbiol. 20, 325–337 (1996)
Tobe T., Schoolnik G.K., Sohel I., Bustamante V.H., Puente J.L.: Cloning and characterization ofbfpTVW, genes required for the transcriptional activation ofbfpA in enteropathogenicEscherichia coli.Mol. Microbiol. 21, 963–975 (1996).
Wolff C., Nisan I., Hanski E., Frankel G., Rosenshine I.: Protein translocation into host epithelial cells by infecting enteropathogenicEscherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol., in press (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisan, I., Wolff, C., Hanski, E. et al. Interaction of enteropathogenicEscherichia coli with host epithelial cells. Folia Microbiol 43, 247–252 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02818609
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02818609