Abstract
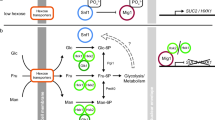
Addition of glucose to a resting cell suspension of the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae was accompanied by marked shifts of the Gα-protein subunits from the plasma membrane to the cell interior. This process was rapid with half-times between <10 and 20 s. The decrease of the plasma membrane pool of the Giα/Goα- and Gqα/G11α-protein subunits correlated with an increase in acid-sensitive forms of these proteins which was recovered in the mitochondrial and/or lysosomal membrane fraction. In contrast to cells from higher organisms glucose-stimulated yeast exhibits an extremely rapid type of the redistribution (internalization). The question remains’open as to the functional significance of the internalized forms of the G-proteins as these remain sequestered from the plasma membrane. well after glucose has been consumed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardwell L., Cook J.G., Inouye C.J., Thorner J.: Signal propagation and regulation in the mating pheromone response pathway of the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Develop. Biol. 166, 363–379 (1994).
Brandão R.L., Castro I.M., Passos J.B., Nicoli J.R., Thevelein J.M.: Glucose-induced activation of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase inFusarium oxysporum.J. Gen. Microbiol. 138, 1579–1586 (1992).
Butrynski J.E., Jones T.L., Backlund P.S., Spiegel A.M.: Differential isoprenylation of carboxy-terminal mutants of an inhibitory G protein α subunit: neither farnesylation nor geranylgeranylation is sufficient for membrane attachment.Biochemistry 31, 8030–8035 (1990).
Colombo S., Ma P., Cauwenberg L., Winderickx J., Crauwels M., Teunissen A., Teunissen A., Nauwelaers D., de Winde J.H., Gorwa M.F., Colavizza D., Thevelein J.M.: Involvement of distinct G proteins, Gpa2 and Ras, in glucose- and intracellular acidification-induced cAMP signalling in the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 17, 3326–3341 (1998).
Dohlman H.G., Song J., Apanovitch D.M., DiBello P.R., Gillen K.M.: Regulation of G protein signaling in yeast.Semin. Cell Develop. Biol. 9, 135–141 (1998).
Drmota T., Novotný J., Kim G.D., Eidne K.A., Milligan G., Svoboda P.: Agonist-induced internalization of the G protein G11α and thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor proceed on different time scales.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21699–21707 (1998).
Eraso P., Portillo F.: Molecular mechanism of regulation of yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase by glucose.J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10393–10399 (1994).
Galbiati F., Volonte D., Meani D., Milligan G., Lublin D.M., Lisanti M.P., Parenti M.: The dually acylate NH2-terminal domain of Gi1α is sufficient to target a green fluorescent protein reporter to caveolin-enriched plasma membrane domains.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5843–5850 (1999).
Iiri T., Backlud P.S., Jones T.L.Z., Wedegaertner P.B., Bourne H.R.: Reciprocal regulation of Gsα by palmitate and the βγ subunit.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 14592–14597 (1996).
Iniguez-Lluhi J.A., Simon M.I., Robishaw J.D., Gilman A.G.: G protein βγ subunits synthetized in Sf9 cells. Functional characterization and the significance of prenylation of γ.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 23409–23417 (1992).
Jones T.L., Simonds W.F., Merendino J.J., Brann M.R., Spiegel A.M.: Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein α subunit is essential for its membrane attachment.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 568–572 (1990).
Kotyk A., Georghiou G.: Both glucose-type monosaccharides and one of their metabolites are required for the activation of yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase.Cell Biol. Internat. 18, 813–817 (1994).
Linder M.E., Middleton P., Hepler J.R., Taussig R., Gilman A.G., Mumby S.M.: Lipid modifications of G proteins: α subunits are palmitoylated.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3675–3679 (1993).
McCallum J.F., Wise A., Grassie M.A., Magee A.I., Guzzi F., Parenti M., Milligan G.: The role of palmitoylation of the guanine nucleotide binding protein G11α in defining interaction with the plasma membrane.Biochem. J. 310, 1021–1027 (1994).
Mumby S.M., Heukeroth R.O., Gordon J.I., Gilman A.G.: G protein α subunit expression, myristoylation and membrane association in COS cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 728–732 (1990).
Mumby S.M., Kleuss, C., Gilman A.G.: Receptor regulation of G protein palmitoylation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 2800–2804 (1994).
Novotný J., Kvapil P., Bokosh G.M., Ransnas L.A.: Isoproterenol-induced subcellular redistribution of G protein β-subunits in S49 lymphoma cells demonstrated by a novel competitive ELISA.Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 103 202–210 (1995).
Novotný J., Bouřozá L., Málková O., Svoboda P., Kolář F.: G proteins, β-adrenoreceptors and β-adrenergic responsiveness in immature and adult rat ventricular myocardium: influence of neonatal hypo- and hyperthyroidism.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 31, 761–772 (1999).
Ransnas L.A., Svoboda P., Jasper J.R., Insel P.A.: Stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors in S49 lymphoma cells redistributes the α subunit of the stimulatory G protein between cytosol and membranes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7900–7903 (1989).
Serrano R.:In vivo glucose activation of the yeast plasma membrane ATPase.FEBS Lett. 156, 11–14 (1983).
Sigler K., Knotková A., Kotyk A.: Factors governing substrate-induced generation and extrusion of protons in the yeastSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim. Biophys.Acta 643, 572–582 (1981).
Spiegel A.M., Backlund P.S., Butrynski J.E., Jones T.L.Z., Simonds W.F.: The G protein connection: molecular basis of membrane association.Trends Biochem. Sci. 16, 338–341 (1991).
Svoboda P., Milligan G.: Agonist-induced transfer of the α subunits of the guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins Gq and G11 and of muscarinic m1 acetylcholine receptors from plasma membranes to a light-vesicular membrane fraction.Eur. J. Biochem. 224, 455–462 (1994).
Svoboda P., Gun-Do Kim, Grassie M.A., Eidne K.A., Milligan G.: Thyrotropin releasing hormone-induced subcellular redistribution and down-regelation of the guanine nucleotide binding protein G11α. Analysis of differences in agonist regulation of coexpressed G11α species variants.Mol. Pharmacol. 314, 761–768 (1996).
Svoboda P., Kim G.-D., Crassie M.A., Eidne K.A., Miligan G.: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced subcellular redistribution and down-regulation of G11α. Analysis of agonist regulation of co-expressed G11α species variants.Mol. Pharmacol. 49, 646–655 (1996).
Sychrová H., Kotyk A.: Conditions of activation of yeast plasma membrane ATPase.FEBS Lett. 183, 21–24 (1985).
Watson S., Arkinstall S.:The G-Protein-Linked Receptor Factsbook. Academic Press, London, 1994.
Wedegaertner P.B., Wilson P.T., Bourne H.: Lipid modifications of trimeric G proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 270, 503–506 (1995).
Xue Y., Battle M., Hirsch J.P.: GPR1 encodes a putative G-protein-coupled receptor that associates with the Gpa2p Gα subunit and functions in a Ras-independent pathway.EMBO J. 17, 1996–2006 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotyk, A., Ihnatovych, I., Lapatiitis, G. et al. Subcellular shifts of trimeric G-proteins following activation of Baker’s yeast by glucose. Folia Microbiol 46, 391–396 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814427
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814427