Summary
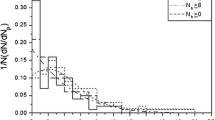
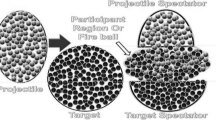
This work presents a special type of interactions produced in emulsion targets exposed to different incident beams of light ions at a few GeV per nucleon. The events characterised by multifragment break-up of the projectile nucleus which are produced via peripheral collisions or due to the effect of the Coulomb field of the target nucleus have been selected. The size of the impact parameter must be considered for determining the type of the interaction. The results are compared with other collected data at energies up to 200 GeV/nucleon. The dependence of electromagnetic dissociation cross-section on the incident projectile energy is investigated. Also, a comparison of the experimental data with the assumed virtual-photon spectrum using Weizsacker-Williams (WW) method is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroni G. et al., Nucl. Phys. A,516 (1990) 673.
Bertulani C. A. andBaur G.,Phys. Rep.,163 (1988) 299.
Heckman H. H. et al., Phys. Rev. Lett.,37 (1976) 56.
Hill J. C. et al., Phys. Rev. Lett.,60 (1988) 999.
Olson D. L. et al., Phys. Rev. C,24 (1981) 1529.
Hoopfr J. E. andKing D. T.,Philos. Mag.,41 (1950) 1194.
Powell C. F., Fowler P. H. andPerkins D. H.,The Study of Elementary Particles by the Photographic Method (Pergamon, London), 1959, p. 612.
Rybicki K.,Nuovo Cimento,49 (1967) 203.
Artru X. et al., Phys. Lett. B,40 (1972) 43.
Baroni G. et al., Nucl. Phys. A,531 (1991) 691;Baroni G. et al., CERN-PPE/92-008 (1992);Baroni G. et al., CERN-PPE/91-03 (1992).
Brechtmann C. et al., Phys. Rev. C,39 (1989) 2222.
Mercier M. T. et al., Phys. Rev. Lett,52 (1984) 898.
Mercier M. T. et al., Phys. Rev. C,33 (1986), 1655.
Moniz E. J. et al., Phys. Rev. Lett.,26 (1971) 445.
Baur G. andBertulani C. A.,Proceedings of the International School of Heavy-Ion Physics, Erice, Italy, 1986, edited byR. A. Broglia (Plenum, New York, N.Y.) 1987.
Jackson, J. D.,Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd edition (Wiley, New York, N.Y.) 1975, p. 719.
Weizsacker C. F.,Z. Phys.,88 (1934) 612;Williams E. J.,Phys. Rev.,45 (1934) 729.
Baur G. andHoffman B.,Phys. Rev. C,30 (1984) 247;Bertulani C. A. andBaur G.,Nucl. Phys. A,442 (1985) 739;458 (1986) 725.
Goldberg A.,Nucl. Phys. A,240 (1984) 636.
Barkas W. H.,Nuclear Research Emulsions, Vol.1 (Academic Press, New York, N.Y.) 1963.
Goldschmidt-Clermont Y. et al., CERN, 63-3 (1963).
Heckman H. H. et al., Phys. Rev. C,17 (1978) 1735.
Yasin M. N., Ph. D. Thesis, Cairo University (1981).
El-Nadi M. et al., Egypt J. Phys., No. 1-2 (1993).
Sengupta K. et al., Europhys. Lett.,8 (1988) 15.
Sengupta K. et al., Phys. Rev. C,41 (1990) 1000.
Sing G. andJain P. L., Internal report, August 29, 1991.
Bahk S. Y. et al., Phys. Rev. C,43 (1991) 1410.
Hill J. C. et al., Phys. Rev. C,38 (1988) 1722.
Hill J. C. et al., Phys. Rev. C,39 (1989) 524.
Adamovich M. I. et al., Phys. Rev. C,40 (1989) 66.
Sing G. andJain P. L.,Phys. Rev. C,41 (1990) 999.
Douglas Giancoli C.,Physics (Principles with Applications), 3rd edition (Prentice-Hall Int. Ed.) 1991. In this book, the data are taken from Brookhaven National Laboratory (1990).
Fuller E. G.,Phys. Rep.,127 (1985) 3;Dejager C. W. et al., Atomic Data Nucl. Data Tables,14 (1974) 479.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabil Yasin, M. Projectile multifragments break-up and the electromagnetic-field effect of target nucleus. Nuov Cim A 108, 1041–1050 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790314
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790314