Abstract
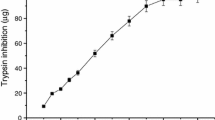
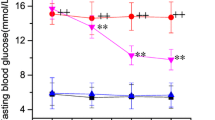
The modification of Bowman-Birk soybean protease inhibitor (BBI) with the monoaldehyde derivative of block copolymer of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide (PE),M r 2000 is described. The conjugate contains five covalently bound polymer chains per protein molecule, and retains the ability to inhibit trypsin and chymotrypsinlike proteinases. The distribution of native BBI and the BBI-PE conjugate was examined in mice. After iv injection of [125I]BBI and [125I]BBIPE, both inhibitors distributed very rapidly to the liver, kidney, and lungs, and more slowly to the brain. At the same time-points (up to 24 h), radioactivity in the blood and organs of mice injected with modified inhibitor was higher than that of the native inhibitor. The blood concentration time profile following iv administration of two BBI preparations at a dose 3 mg/kg was reasonable well described by a two-compartment open model with first-order elimination kinetics. The total clearance of BBI-PE decreased by a factor of 8, body mean residence time increased by a factor of 5 in comparison with BBI. A physiological pharmacokinetic model was developed to describe the tissue-to-blood distribution of two inhibitors. One-compartment physiological organ model (flow limited) was used to describe of timecourse profiles of BBI concentration in organs. A two-compartment physiological organ model (membrane limited) was used to predict tissue-to-blood distribution of conjugated BBI in some organs of mice (liver, lungs). The predicted concentration curves of BBI and BBI-PE in blood and organs in mice (with the exception of kidney) showed good agreement with the observed values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy, A. R. (1993), inProtease Inhibitors as Cancer Chemopreventive Agents, Troll, W. and Kennedy, A. R., eds., Plenum, New York, pp. 9–64.
Kennedy, A. R. (1993), inProtease Inhibitors as Cancer Chemopreventive Agents, Troll, W. and Kennedy, A. R., eds., Plenum, New York, pp. 65–91.
Persiani, S., Yeung, A., Shen, W. C, and Kennedy, A. R. (1991),Carcinogenesis 12, 1149–1152.
Chang, T. M. S. (1977),Biomedical Application of Immobilized Enzymes and Proteins. Plenum, New York.
Madar, Z., Gertler, A., and Birk, Y. (1979),Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62A, 1057–1061.
Billings, P. C., St. Clair, W. H., Maki, P. A., and Kennedy, A. R. (1992),Cancer Lett. 62, 191–197.
Kirillova, G. P., Mochova, E. M., Deduchova, V. I., Tarakanova, A. N., Ivanova, V. P., Efremova, N. V., and Topchieva, I. N. (1993),Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 18, 329–339.
King, F. G. and Dedrick, R. L. (1979),Cancer Treatment Rep. 63, 1939–1947.
Chen, H.-S. and Gross, J. F. (1979),Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2, 85–94.
Larionova, N. I., Gladysheva, I. P., Tikhonova, T. V., and Kazanskaya, N. F. (1993),Biochemistry (Moscow) 58, 1046–1052.
Boccu, E., Largajolly, R., and Veronese, F. M. (1983),Naturforschung 3, 94–99.
Bradford, M. M. (1976),Anal. Biochem. 181, 321–330.
McConahey, P. C. and Dixon, F. J. (1980),Methods Enzymol. 70, 221–247.
Kong, A.-Ng. and Jusko, W. (1988),J. Pharm. Sci. 77, 157–165.
Hatanaka, T., Sato, S., Endo, H. M., Katayama, K., Kakemi, M., and Koizumi, T. (1988),J. Parmacobio-Dyn. 11, 18–30.
Sato, H., Okezaki, E., and Yamamoto, S. (1988),J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 11, 386–394.
Ritschel, W. A. and Banerjee, P. S. (1986),Methods and Findings Expl. Clin. Pharmacol. 8, 603–614.
Gerlowski, L. and Jain, R. (1983),J. Pharm. Sci. 72, 1103–1127.
Ratkowski, D. A. (1983),Nonlinear Regression Modeling, Marcel Dekker, New York.
King, F. G., Dedrick, R. L., Collins, J. M., Mattews, H. B., and Birnbaum, L. S. (1983),Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 67, 390–400.
Yavelow, J., Collins, M., Birk, Y., Troll, W., and Kennedy, A. R. (1985),Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 5395–5399.
Odani, S. and Ikenaka, T. (1972),J. Biochem. 71, 839–848.
Fields, R. (1971),Biochem. J. 124, 581–590.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. S., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. (1951),J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Larionova, N. I., Topchieva, I. N., Gladysheva, I. P., and Kennedy, A. R. (1994),Cancer J. 7, 158–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larionov, N.I., Gladysheva, I.P., Polekhina, O.V. et al. Synthesis and biodistribution of bowman-birk soybean protease inhibitor conjugate with amphiphilic polyester. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 61, 139–148 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785696
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785696