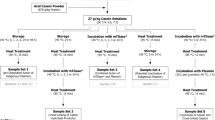
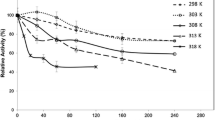
Abstract
Allyl glycidyl ether-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate copolymer with 25 % crosslink density has been functionalized with various amines. The polymer bearing a dibenzyl amino function efficiently removed the soybean trypsin inhibitor (SBTI) and lipoxygenase (LOX) from soymilk. The polymer binds SBTI and LOX efficiently (25–30 mg/g) through a combination of hydrophobic and ionic interactions and denatures them at room temperature by simple contact for 1 h. The bound proteins can be easily recovered almost quantitatively by elution with 1 % (v/v) acetic acid, and the polymer can be recycled at least 10 times without significant changes in binding capacity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayraktar H, Serilmez M, Karkaş T, Celem EB, Onal S (2011) Immobilization and stabilization of α-galactosidase on Sepabeads EC-EA and EC-H.A. Int J Biol Macromol 49:855–860
Chang YL, Liu TC, Tsai ML (2014) Selective isolation of trypsin inhibitor and lectin from soybean whey by chitosan/tripolyphosphate/genipin co-crosslinked beads. Int J Mol Sci 15:9979–9990
Diliara R, Iassonova DR, Johnson LA, Hammond EG, Beattie SE (2009) Evidence of an enzymatic source of off flavors in ‘‘lipoxygenase-null’’ soybeans. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86:59–64
Friedman M, Brandon DL (2001) Nutritional and health benefits of soy proteins. J Agric Food Chem 49:1069–1086
Isanga J, Zhang G (2008) Soybean bioactive components and their implications to health a review. Food Rev Int 24:252–276
Jasti LS, Fadnavis NW, Addepally U, Daniels S, Deokar S, Ponrathnam S (2014) Comparison of polymer induced and solvent induced trypsin denaturation: the role of hydrophobicity. Colloids Surf B 116:201–205
Liener IE (1994) Implications of antinutritional components in soybean foods. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 34:31–67
Pessela BCCh, Mateo C, Fuentes M, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (2003) Reversible immobilization of a thermophilic β-galactosidase via ionic adsorption on PEI-coated Sepabeads. Enz Microb Technol 32:369–374
Saravitz DM, Siedow JN (1995) The lipoxygenase lsozymes in soybean [Glycine max (1.) Merr.] leaves changes during leaf development, after wounding, and following reproductive sink removal. Plant Physiol 107:535–543
Thudi L, Jasti LS, Swarnalatha Y, Fadnavis NW, Mulani K, Deokar S, Ponrathnam S (2012) Adsorption induced enzyme denaturation: the role of protein surface in adsorption induced protein denaturation on allyl glycidyl ether (AGE)-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDM) copolymers. Colloid Surf B 90:184–190
Timabud T, Sanitchon J, Pongdontri P (2013) A modified ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange assay for lipoxygenase activity in rice grains. Food Chem 141:2405–2411
Torres P, Batista FV (2012) Immobilization of β-galactosidase from Bacillus circulans onto epoxy-activated acrylic supports. J Mol Catal B Enzym 74:230–235
Torres R, Mateo C, Fuentes M, Tam A, Daminati M (2002) Reversible immobilization of invertase on Sepabeads coated with polyethyleneimine: optimization of the biocatalyst’s stability. Biotechnol Prog 18:1221–1226
Wang R, Zhou X, Chen Z (2008) High pressure inactivation of lipoxygenase in soy milk and crude soybean extract. Food Chem 106:603–611
Yuan SH, Chang SKC (2007) Selected odor compounds in soymilk as affected by chemical composition and lipoxygenases in five soybean materials. J Agric Food Chem 55:426–431
Yuan S, Chang SKC, Liu Z, Xu B (2008) Elimination of trypsin inhibitor activity and beany flavor in soy milk by consecutive blanching and ultrahigh-temperature (uht) processing. J Agric Food Chem 56:7957–7963
Acknowledgments
We thank CSIR, New Delhi for grant of Senior Research Fellowship to LSJ and DST, New Delhi for financial support (Grant No. SERB/MOFPI/0049/2012).
Supporting information
Supplementary Figure 1—SDS PAGE Electrophoresis.
Supplementary Figure 2—Recycling of polymer after protein desorption.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jasti, L.S., Lavanya, K. & Fadnavis, N.W. Adsorption induced denaturation: application to denaturation of soybean trypsin inhibitor (SBTI) and lipoxygenase (LOX) in soymilk. Biotechnol Lett 37, 147–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1659-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1659-2