Abstract
The concentrations of iodine (I) and bromine (Br) were measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the plasma, kidney, heart, liver, and brain of control and thyroparathyroidectomized (TPTX) rats without and with an additional intake of either NaI or NaBr, 0.5 and 5 μmol/kg/d, respectively, for 21 d.
In all groups, the highest concentrations of I and Br were found in the plasma. TPTX did not modify the concentrations of I in tissues, but slightly increased Br in plasma (+33%) and kidney (+24%).
The additional intake of I with the drink induced an increase of I concentrations in the tissues tested (from 54 to 191%), except brain, both in control and TPTX rats. This additional intake of I also increased Br levels in the plasma of control (+24%) and TPTX rats (+53%).
The additional intake of Br with the drink induced an increase of Br levels in all the tested tissues, brain included (from 85 to 284%). The augmentation was higher in the tissues, particularly brain, of TPTX rats than of controls. The increase of Br in brain after an additional intake contrasts with the absence of increase of I given in the same conditions. This difference between I and Br probably results from the smaller radius of Br ion in comparison with I ion radius.
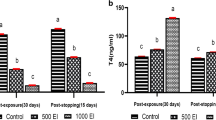
In conclusion, TPTX did not modify the distribution of I in the tested tissues, but slightly increased the concentrations of Br in plasma and kidney. Since the additional intake of Br decreased the level of T4 in plasma of TPTX rats, there is a reciprocal enhancing interaction between thyroid insufficiency and Br.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. X. R. Van Leeuwen, E. M. Den Tonkelaar, and M. J. Van Logten,Fd. Chem. Toxic. 21, 383 (1983).
J. G. Loeber, M. A. M. Franken, and F. X. R. Van Leeuwen,Fd. Chem. Toxic. 21, 391 (1983).
F. X. R. Van Leeuwen, R. Hanemaaijer, and J. G. Loeber,Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 12, 93 (1988).
W. Buchberger, W. Holler, and K. Winsaeur,J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 4, 25 (1990).
B. Sangster, J. L. Blom, V. M. Sekhuis, J. G. Loeber, A. G. Rauws, and J. C. Koedam,Fd. Chem. Toxic. 21, 409 (1983).
A. G. Rauws,Fd. Chem. Toxic. 21, 379 (1983).
P. Allain, Y. Mauras, Ch. Douge, and L. Jaunault,Analyst 115, 813 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krari, N., Berre, S. & Allain, P. Effects of thyroparathyroidectomy on the distribution of bromine and iodine in rat tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 32, 275–279 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784611
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784611