Abstract
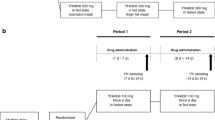
The absorption and metabolism of zinc in a commercial form for oral use (Rubozinc®, 15 mg zinc as gluconate) were investigated in 10 subjects by a kinetic study of the serum zinc profile after administration of 45 mg zinc under three conditions: after an overnight fast, during a standardized breakfast, and 2 h after this meal. The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated by a method suitable to the characterization of rebound effects (recycling of the element in the gastrointestinal tract). In fasting state, the parameters were comparable to those previously collected in the same subjects with oral 45 mg zinc as sulfate, except with very significantly higherC max and area under curve (AUC), showing a better bioavailability for zinc in the commercial form. The light meal perturbed the absorption process as evidenced by the significant increases in the lag time (+180%), thet max (+57%), and the lag times for the first two cycles during the meal. However, the parameters returned to normal values 2 h after the meal. TheC max only moderately decreased during the meal (31%) as did the AUC (−28%). An important delay in the absorption of zinc in the commercial form when taken during a meal was therefore demonstrated, but the effect on zinc bioavailability was only moderate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. M. Hambidge, C. E. Casey, and N. F. Krebs,Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, vol. 2, W. Mertz, ed., Academic, Orlando, FL, 1986, pp. 1–137.
A. Favier,Le Zinc en Médecine et en Biologie, A. Favier, J. Arnaud, and H. Faure, eds., Editions Médicales Internationales, Paris, 1987, pp. 3–20.
J. Nève and A. Peretz,J. Pharm. Belg. 43, 466 (1988).
R. J. Cousins,Physiol. Rev. 65, 238 (1985).
A. S. Prasad,Ann. Rev. Nutr. 5, 341 (1985).
H. Ronaghy,Wld. Rev. Nutr. Diet. 54, 237 (1987).
B. Dreno, P. Amblard, P. Agache, S. Sirot, and P. Litoux,Acta Derm. Venerol. 69, 541 (1989).
C. L. Keen and M. E. Gershin,Ann. Rev. Nutr. 10, 415 (1990).
C. H. Cho,Drug Develop. Rev. 17, 185 (1989).
G. Escolar and O. Bulbena,Drugs Expl. Clin. Res. 15, 83 (1989).
G. A. Eby, D. R. Davis, and W. W. Halcomb,Antimicrob. Agents Chemotherap. 25, 20 (1984).
G. Hill, J. Brewer, A. S. Prasad, C. Hydrick, and D. Hartmann,Hepatol. 7, 522 (1987).
G. Hill, J. Brewer, J. Juni, A. S. Prasad, and R. D. Dick,Am. J. Med. Sci. 29, 344 (1986).
National Research Council, Recommended Dietary Allowances, 10th ed., National Academy Press, Washington, 1989.
P. B. Moser and C. J. Gundeson, (1982),Nutr. Res. 3, 279.
J. J. Keyzer, E. Oosting, B. G. Wolthers, and F. Muskiet,Pharm. Weekbl. 5, 252 (1983).
A. Pecoud, P. Conzel, and J. L. Schelling,Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 17, 469 (1975).
F. J. Oelshlegel and G. J. Brewer,Zinc Metabolism, Current Aspects in Health and Disease, G. J. Brewer and A. S. Prasad, eds., Alan R. Liss, New York, 1977, pp. 299–311.
J. Nève, M. Hanocq, A. Peretz, F. Abi Khalil, F. Pelen, J. P. Famaey, and J. Fontaine,Eur. J. Drug. Metabl. Pharmacokin, in press (1991).
J. C. Smith, J. T. Holbrook, and D. E. Danford,J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 4, 627 (1985).
J. Nève, L. Molle, M. Hanocq, P. M. Sinet, and R. Van Geffel,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 5, 75 (1983).
A. Peretz, J. Nève, and J. P. Famaey,J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 3, 103 (1989).
J. Versieck, L. Vanballenberghe, A. De Kessel, J. Hoste, B. Wallaeys, J. Vandenhaute, N. Baeck, A. Steyaert, J. Byrne, and F. Sunderman,Clin. Chim. Acta 204, 63 (1988).
E. Couturier, A. van Onderbergen, D. Bosson, and J. Nève,J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 2, 245 (1988).
F. Abi Khalil, J. Dubois, M. Hanocq, and G. Atassi,Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokin. 11, 51 (1986).
F. Abi Khalil, M. Hanocq, and J. Dubois,Eur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokin. in press (1991).
G. W. Snedecor, and W. G. Cochran,Statistical Methods 7th ed. Iowa State University, Ames, IA, 1980.
M. G. Kendall and A. Stewart,The Advanced Theory of Statistics, vol. 2., Griffin and Co., London, 1968.
S. S. Southon, S. J. Fairweather-Tait, and T. Hazell,Proc. Nutr. Soc. 47, 27 (1988).
R. Aamodt, W. Rumble, G. Johnston, E. Markley, and R. Henkin,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32, 559 (1979).
R. Aamodt, W. Rumble, A. Babcock, D. Foster, and R. Henkin,Metab. 31, 326 (1982).
J. Turnlund, N. Durkin, F. Costa, and S. Margen,J. Nutr. 116, 1239 (1986).
M. Wastney and R. Henkin,J. Nutr. 119, 1438 (1989).
L. S. Valberg, P. Flanagan, J. Brennan, and M. Chamberlain,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 41, 37 (1985).
J. P. Labaune,Handbook of Pharmacokinetics, Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1989.
J. G. Wagner,Biopharmaceutics and Relevant Pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence, Hamilton, IL, 1971.
S. A. Barrie, J. V. Wright, J. E. Pissorno, E. Kutter, and P. C. Barron,Agents Actions 21, 223 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nève, J., Hanocq, M., Peretz, A. et al. Absorption and metabolism of oral zinc gluconate in humans in fasting state, during, and after a meal. Biol Trace Elem Res 32, 201–212 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784604
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784604