Summary
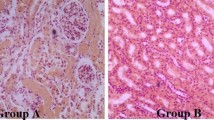
Statistical observations were performed in 139 cases of constitutional hyperbilirubinemia which were reported during 7 years from 1963 to 1969 in Japan. Male was predominant in Dubin Johnson syndrome (Dubin-Johnson), but there was no difference with sex in Rotor’s type of hyperbilirubinemia (Rotor) and Gilbert’s disease (Gilbert). The age, at which jaundice first noticed, was distributed in the youngest among patient with Rotor, and age was young in Rotor, Gilbert and Dubin-Johnson as in order. The mean total bilirubin level in serum showed the highest value in Rotor and it showed higher in Dubin-Johnson than in Gilbert. Abnormal retention of BSP a 45 minutes wsa observed in 80% of Dubin-Johnson and in all cases of Rotor. The secondary rise of BSP in serum was observed in almost all cases of Dubin-Johnson during from 120 minutes to 180 minutes after an injection. Of other liver function tests there were no common changes. Of cholecystography one third of the cases in Dubin-Johnson demonstrated a visualized gallbladder both on oral and intravenous method, while in Rotor the positive rate increased on oral method more than on intravenous method. The black colored liver and the lipofuscin-like pigments in liver cells were observed in all patients of Dubin-Johnson, except patients with hepatic inflammatory changes. In Rotor and in Gilbert the pigments were observed in several patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuda, M.: Idiopathic jaundice in Japan (Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Gilbert’s disease). Jap. J. Gastroenterol. 59:55, 1962.
Arias, I.M.: Bilirubin glucuronide formation in vitro: Demonstration of a defect in Gilbert’s disease. Science 126:563, 1957.
Schmid, R.: Jaundice and bilirubin metabolism. Bull. N.Y. Acad. Med. 35:755, 1959.
Billing, B.H., Williams, R., Richards, T.G.: Defects in hepatic transport of bilirubin in congenital hyperbilirubinemia : An analysis of plasma bilirubin disappearance curves. Clin. Sci. 27:245, 1964.
Mandema, E., Fraiture, W.H., Nieweg, H.O., Arends, A.: Familial chronic idiopathic jaundice (Dubin-Sprinz Disease), with a note on bromsulphalein metabloism in this disease. Amer. J. Med. 28:42, 1960.
Hunter, F.M., Sparks, R.D., Flinner, R.L.: Hepatitis with resulting mobilization of hepatic pigment in a patient with Dubin-Johnson Syndrome. Gastroenterology 47:631, 1964.
Tsuneoka, K., Nomura, M., Okumura, E., Aoyagi, T., Takabatake, Y., Katayama, S.: Dubin-Johnson Syndrome. Report of 3 cases. Jap. J. Clin. Med. 16:1188, 1958.
Takahashi, T.: Dubin-Johnson Syndrome (“Chronic idiopathic jaundice”). SaishinIgaku 14:413, 1959.
Tasaka, S., Araki, Y., Iwamoto, J. Taoka, K.: Dubin-Johnson Syndrome and Gilbert’s disease. Acta. Hep. Jap. 1:54, 1960.
Yamagata, S., Wakui, K., Komatsu, T., Kiriu, N.: Recent aspects of hereditary nonhemolytic jaundice. J. Clin. Sci. 5:696, 1969.
Dubin, I.N., Johnson, F.B.: Chronic idiopathic jaundice with unidentified pigment in liver cell. A new clinico-pathologic entity with a report of 12 cases. Medicine 23:155, 1954.
Schillinger, H.: Dubin-Johnson Syndrome. Med. Klin. 62:201, 1967.
Meulengracht, E.: Icterus intermittens juvenilis. Klin. Wschr. 18:118, 1939.
Dameshek, W., Singer, K.: Familial nonhomelytic jaundice, constitutional hepatic dysfunction with indirect van den Bergh reaction. Arch. Int. Med. 67:259, 1941.
Rotor, A.B., Manahan, L., Florentin, A.: Familial nonhemolytic jaundice with direct van den Bergh reaction. Acta. Med. Philip. 5:37, 1948.
Powell, L.W., Hemingway, E., Billing, B.H., Sherlock, S.: Idiopathic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert’s syndrome). A study of 42 families. New Eng. J. Med. 277:1108, 1967.
Rozendaal, H.M., Comfort, M.W., Snell, A.M.: Slight and latent jaundice. The significance of elevated concentrations of bilirubin giving an indirect van den Berghreaction.
John, G.G., Knudtson, K.P.: Chronic idiopathic jaundice: two cases occurring in siblings, with histochemical studies. Amer.J. Med. 21:138, 1956.
Takeuchi, J., Sugioka, G.: Rotor type of hyperbilirubinemia. Sogo-Igaku 19:350, 1962.
Okumura, E., Kunishima, O., Minagawa, A.: Rotor type of hyperbilirubinemia. Rotor’s disease and Rotor Syndrome. Saishin-Igaku 18:1114, 1963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namihisa, T., Yamaguchi, K. The constitutional hyperbilirubinemia in Japan studies on the 139 cases reported during the period from 1963 to 1969. Gastroenterol Jpn 8, 311–321 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02779108
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02779108