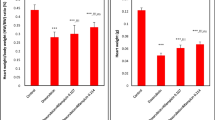
Abstract
The influence of selenium (Se) deficiency on the acute cardiotoxicity induced by the anticancer drug adriamycin (ADR) has been studied in rats by electrocardiography.
Two categories were formed by feeding groups of rats a Se-supplemented and a Se-deficient diet. The supplemented animals were taken as normals. The two categories were treated with iv injections of saline solution containing ADR at doses of 0, 7.5, and 15 mg/kg body wt.
The cardiac Se concentration and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity in the Se-deficient groups were <2% lower than in the normals.
The normal groups showed significant widening of the SaT and QaT durations when given 15 mg/kg ADR. The Se-deficient groups exhibited a dose-dependent widening of the SaT and QaT duration at 7.5 and 15 mg/kg and narrowing of the PQ duration at 15 mg/kg ADR. No heart rate or QRS duration changes were detected in both categories.
Our results suggest that an imbalance of the antioxidant system is associated with Se deficiency and that Se plays a role in preventing the cardiac functional disorder attributable to oxygen free radical formation induced by ADR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. F. Burk, Protection against free radical injury by selenoenzymes,Pharmacol. Ther. 45, 383–385 (1990).
H. W. Lane, A. O. Barroso, D. Englert, S. J. Dudrick, and B. S. MacFadyen, Jr., Selenium status of seven chronic intravenous hyperalimentation patients,JPEN 6, 426–431 (1982).
S. S. Baker, R. H. Lerman, S. H. Kery, K. S. Crocker, E. F. Hirsh, and H. Cohen, Selenium deficiency with total parenteral nutrition: reversal of biochemical and functional abnormalities by selenium supplementation: a case report,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 38, 769–774 (1983).
S. Jacobson and L-O. Plantin, Concentration of selenium in plasma and erythrocytes during total parenteral nutrition in Crohn's disease,Gut 26, 50–54 (1985).
H. W. Lane, C. A. Lotspeich, C. E. Moore, J. Ballard, S. T. Dudrick, and D. C. Warren, The effect of selenium supplementation on selenium status of patients receiving chronic total parenteral nutrition,JPEN 11, 177–182 (1987).
H. J. Cohen, M. R. Brown, D. Hamilton, J. Lyons-Patterson, N. Avissar, and P. Liegey, Glutathione peroxidase and elenium deficiency in patients receiving home parenteral nutrition: time course for development of deficiency and repletion of enzyme activity in plasma and blood cells,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49, 132–139 (1989).
K. Sando, M. Hoki, R. Nezu, Y. Takagi, and A. Okada, Platelet glutathione peroxidase activity in long-term total parenteral nutrition with and without selenium supplementation,JPEN 16, 54–58 (1992).
A. M. van Rij, C. D. Thomson, J. M. McKenzie, and M. F. Robinson, Selenium deficiency in total parenteral nutrition,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32, 2076–2085 (1979).
C. L. Kien and H. E. Ganther, Manifestations of chronic selenium deficiency in a child receiving total parenteral nutrition,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 37, 319–328 (1983).
R. J. Baptista, B. R. Bistrian, G. L. Blackburn, D. G. Miller, C. D. Champagne, and L. Buchanan, Utilizing selenious acid to reverse selenium deficiency in total parenteral nutrition patients,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 39, 816–820 (1984).
R. D. Watson, R. A. Cannon, G. S. Kurland, K. L. Cox, and R. C. Frates, Selenium responsive myositis during prolonged home total parenteral nutrition in cystic fibrosis,JPEN 9, 58–60 (1985).
R. A. Johnson, S. S. Baker, J. T. Fallon, E. P. Maynard III, J. N. Ruskin, Z. Wen, K. Ge, and H. J. Cohen, An occidental case of cardiomyopathy and selenium deficiency,N. Engl. J. Med. 304, 1210–1212 (1981).
C. R. Fleming, J. T. Lie, J. T. McCall, J. F. O'Brien, E. E. Baillie, and J. L. Thistle, Selenium deficiency and fatal cardiomyopathy in a patient on home parenteral nutrition,Gastroenterology 83, 689–693 (1982).
R. A. Quercia, S. Korn, D. O'Neill, J. E. Dougherty, M. Ludwig, R. Schweizer, and R. Sigman, Selenium deficiency and fatal cardiomyopathy in a patient receiving long-term home parenteral nutrition,Clin. Pharm. 3, 531–535 (1984).
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge, Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: an overview, inMethods in Enzymology, vol. 186, L. Packer and A. N. Glazer, eds., Academic, San Diego, pp. 1–85 (1990).
L. Lenaz and J. P. Page, Cardiotoxicity of adriamycin and related anthracyclines,Cancer Treat. Rev. 3, 111–120 (1976).
P. K. Singal, C. M. R. Deally, and L. E. Weinberg, Subcellular effects of adriamycin in the heart: a concise review,J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 19, 817–828 (1987).
C. A. Maggi and A. Meli, Suitability of urethane anesthesia for physiopharmacological investigations in various systems: 2. Cardiovascular system,Experientia 42, 292–297 (1986).
K. Sekine, M. Kimura, and Y. Itokawa, Method for the determination of selenium in biological samples by hydrogen selenide evolution electrothermal atomic absorption,Jpn. J. Hyg. 39, 807–811 (1984).
D. E. Paglia and W. N. Valentine, Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70, 158–169 (1967).
J. Goodman and P. Hochstein, Generation of free radicals and lipid peroxidation by redox cycling of adriamycin and daunomycin,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 77, 797–803 (1977).
F. Villani, E. Monti, F. Piccinini, L. Favalli, E. Lanza, A. R. Dionigi, and P. Poggi, Relationship between doxorubicin-induced ECG changes and myocardial alterations in rats,Tumori 72, 323–329 (1986).
S. T. Hu, E. Brandle, and G. Zbinden, Inhibition of cardiotoxic, nephrotoxic and neurotoxic effects of doxorubicin by ICRF-152,Pharmacology 26, 210–220 (1983).
G. Zbinden and E. Brandle, Toxicologic screening of daunorubicin (NSC-82151), adriamycin (NSC-123127) and their derivatives in rats,Cancer Chemother. Rep. 59, 707–715 (1975).
R. A. Jensen, E. M. Acton, and J. H. Peters, Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in the rat: comparison of ECG, transmembrane potential and structural effects,J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 6, 186–200 (1984).
R. A. Jensen, E. M. Acton, and J. H. Peters, Electrocardiographic and transmembrane potential effects of 5-iminodaunorubicin in the rat,Cancer Res. 44, 4030–4039 (1984).
R. Danesi, N. Bernardini, A. Marchetti, M. Bernardini, and M. D. Tacca, Protective effects of fructose-1, 6-diphosphate on acute and chronic doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats,Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 25, 326–332 (1990).
N. Koukay, S. Mouhieddine, M. J. Richard, J. Arnaud, J. De Leiris, and A. Favier, Influence of selenium on lipid peroxidation and cardiac functions in chronically adriamycin-treated rats,Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 264, 353–359 (1990).
J. G. Fischer, R. L. Tackett, E. W. Howerth, and M. A. Johnson, Copper and selenium deficiencies do not enhance the cardiotoxicity in rats due to chronic doxorubicin treatment,J. Nutr. 122, 2128–2137 (1992).
X. Chen, A. Xue, V. C. Morris, V. J. Ferrans, E. H. Herman, A. El-Hage, and O. A. Levander, Effect of selenium deficiency on the chronic toxicity of adriamycin in rats,J. Nutr. 116, 2453–2465 (1986).
T. Facchinetti, F. Delaini, M. Salmona, M. B. Donati, S. Feuerstein, and A. Wendel, The influence of selenium intake on chronic adriamycin toxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats,Toxicol. Lett. 15, 301–307 (1983).
K. V. Dimitrov, M. B. Hay, S. Siew, D. A. Hudler, L. J. Charamella, and D. E. Ullrey, Abrogation of adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by selenium in rabbits.Am. J. Pathol. 126, 376–383 (1987).
J. A. Butler, P. D. Whanger, and N. M. Patton, Effects of feeding selenium deficient diets to rhesus monkeys (macaca mulatta),J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 7, 43–56 (1988).
Z. Zhu, M. Kimura, and Y. Itokawa, Effect of selenium and protein deficiency on selenium and glutathione peroxidase in rats,Biol. Trace Element Res. 36, 15–23 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuda, A., Kimura, M. & Itokawa, Y. Influence of selenium deficiency on the acute cardiotoxicity of adriamycin in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 57, 157–167 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02778199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02778199