Abstract
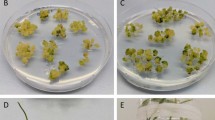
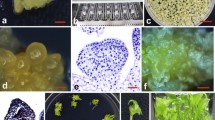
Although several reports on rice transformation have been published, producing transgenic plants ofIndica rice varieties is still problematic. We report an improved protocol for transformingIndica rice genotypes. An important agronomic MexicanIndica rice variety, Morelos A-92, was used. Calli derived from scutellum seeds were produced by using auxins and bombarded with 2 vectors, one harboring the reporteruidA gene and the other with thehptII gene conferring hygromycin resistance. The influence of the molar relation of these vectors (uidA-hptIII) in generating callus and plants expressing theuidA reporter gene was analyzed. Selection of bombarded calli was performed under 2 conditions: 50 mg/L of hygromycin with 3 subcultures and 80 mg/L of hygromycin with no subcultures. The best conditions were a 20∶1uidA-hptII molar vector relationship and selection at 80 mg/L of hygromycin, producing 14% of calli expressing GUS. The minimal callus size in regenerating plants was 3 mm. Transformed rice plants were generated with 4.6% efficiency, considering the initial number of bombarded calli. Heredity of theuidA gene behaved as a single locus in transformed rice plants. Homozygous plants were identified in the T1 generation by means of pollen staining.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cabrera-Ponce JL, Vegas-García A, and Herrera-Estrella L (1995) Herbicide resistant transgenic papaya plants produced by an efficient particle bombardment transformation method. Plant Cell Rep 15: 1–7.
Chávez-Bárcenas AT, Valdez-Alarcón JJ, Martínez-Trujillo M, Chen L, Xoconostle-Cázares B, Lucas WJ, and Herrera-Estrella L (2000) Tissue-specific and developmental pattern of expressión of the ricesps1 gene. Plant Physiol 124: 641–53.
Chen L, Marmey P, Taylor NJ, Brizard JP, Espinoza C, D'Cruz P, Huet H, Zhang S, Kochko A, Beachy TN, and Fauquet CM (1998) Expression and inheritance of multiple transgenes in rice plants. Nature Biotech 16: 1060–4.
Christou P, Ford T, and Kofrom M (1991) Production of transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants from agronomically importantIndica andJaponica varieties via electric discharge particle acceleration of exogenous DNA into immature zygotic embryos. Bio/Tech 9: 957–62.
Datta SK, Peterhans A, Datta K, and Potrykus (1990) I: Genetically engineered fertileIndica-rice recovered from protoplasts. Bio/Tech 8: 736–740.
Glaszmann JC and Arraudeau M (1986) Rice plant type variation: ‘japonica-javanica’ relationships. Rice Genet Newsl 3: 41–43.
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, and others (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. spp.Japonica). Science 296: 92–100.
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, and Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated byAgrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6: 271–282.
Kato S, Kosaka H, and Hara S (1928) On the affinity of rice varieties as shown by fertility of hybrid plants. Bull Sci Fac Agric. Kyushu Univ, Fukuoka, Japan 3: 132–147.
Klush G (1997) Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant Mol Biol 35: 25–34.
Kohli A, Leech M, Vain P, Laurie DA, and Chritou P (1998) Transgene organization in rice engineered through direct DNA transfer supports a two phase integration mechanism mediated by the establishment of integration hot spots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7203–7208.
Martínez-Trujillo M (2002) Análisis functional de regiones involucradas en la expresión del gen de Sacarosa-Fosfato Sintasa de arroz (Oryza sativa L.). Tesis de Doctorado. CINVESTAV-IPN. Irapuato, Guanajuato, México.
Salcedo-Aceves J (1993) Morelos A-92 variedad de arroz para el Estado de Morelos. SARH-INIF, Folleto Técnico No. 9. México.
Sivamani E, Shen P, Opalka N, Beachy RN, and Fauquet CM (1996) Selection of large quantities of embryogenic calli fromIndica rice seeds for production of fertile transgenic plants using the biolistic method. Plant Cell Rep 15: 322–327.
Stomp AM (1992) Histochemical localization of β-glucuronidase. In: Gallagher SR (ed), GUS Protocols: Using the GUS Gene as a Reporter of Gene Expression, pp 103–113, Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Toriyama K, Arimoto Y, Uchimiya H, and Hinata K (1988) Transgenic rice plants after direct gene transfer into protoplasts. Bio/Tech 6: 1072–1074.
Vain P, McMullen MD, and Finer JJ (1993) Osmotic treatment enhances particle bombardment-mediated transient and stable transformation of maize. Plant Cell Rep 12: 84–88.
Valdez M, Cabrera-Ponce JL, Sudhakar D, Herrera-Estrella L, and Christou P (1998) Transgenic Central America, West African and Asian elite rice varieties resulting from particle bombardment of foreign DNA into mature seed-derived explants utilizing three different bombardment devices. Ann Bot 82: 795–801.
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, and others (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. spp.indica). Science 296: 79–92.
Zhang HM, Yang H, Rech EL, Golds TJ, Davis AS, Mulligan BJ, Cocking EC, and Davey MR (1988) Transgenic rice plants produced by electroporation-mediated plasmid uptake into protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 7: 379–384.
Zhang W and Wu R (1988) Efficient regeneration of transgenic plants from rice protoplasts and correctly regulated expression of the foreign gene in the plants. Theor Appl Gen 76: 835–840.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez-Trujillo, M., Cabrera-Ponce, J.L. & Herrera-Estrella, L. Improvement of rice transformation using bombardment of scutellum-derived calli. Plant Mol Biol Rep 21, 429–437 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772592
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772592