Abstract
Study of the conversion of chlorophenols byRhodococcus opacus 1G,R. rhodnii 135,R. rhodochrous 89, andR. opacus 1cp disclosed the dependence of the conversion rate and pathway on the number and position of chlorine atoms in the aromatic ring. The most active chlorophenol converter, strainR. opacus 1cp, grew on each of the three isomeric monochlorophenols and on 2,4-dichlorophenol; the rate of growth decreased from 4-chlorophenol to 3-chlorophenol and then to 2-chlorophenol. The parameters of growth on 2,4-dichlorophenol were the same as on 3-chlorophenol. None of the strains studied utilized trichlorophenols. A detailed study of the pathway of chlorophenol transformation showed that 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 2,4-dichlorophenol were utilized by the strains via a modifiedortho-pathway. 2-Chlorophenol and 2,3-dichlorophenol were transformed by strainsR. opacus 1cp andR. rhodochrous 89 via corresponding 3-chloro- and 3,4-dichlorocatechols, which were then hydroxylated with the formation of 4-chloropyrogallol and 4,5-dichloropyrogallol; this route had not previously been described in bacteria. Phenol hydroxylase ofR. opacus 1G exhibited a previously undescribed catalytic pattern, catalyzing oxidative dehalogenation of 2,3,5-trichlorophenol with the formation of 3,5-dichlorocatechol but not hydroxylation of the nonsubstituted position 6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chubben, N.H.P., Vervoort, J., Borsma, M., and Rietjens, I.M.C.M., The Effect of Varying Halogen Substituents on the CytochromeP 450 Catalyzed Dehalogenation of 4-Halogenated Anilines to Aminophenol Metabolites,Biochem. Pharmacol., 1995, vol. 49, pp. 1235–1248.
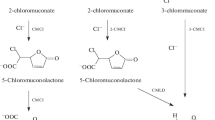
Schmidt, E. and Knackmuss, H.-J., Chemical Structure and Biodegradability of Halogenated Aromatic Compounds: Conversion of Chlorinated Muconic Acids into Maleylacetic Acid,Biochem. J., 1980, vol. 192, pp. 339–347.
Hofrichter, M., Gunter, T., and Fritsche, W., Metabolism of Phenol, Chloro- and Nitrophenols by thePenicillium strain Bi7/2 Isolated from Contaminated Soil,Biodegradation, 1992/1993, vol. 3, pp. 415–422.
Marr, J., Kremer, S., Sterner, O., and Anke, H., Transformation and Mineralization of Halophenols byPenicillium simplicissimum SK 9117,Biodegradation, 1996, vol. 7, pp. 165–171.
Zaborina, O.E., Baryshnikova, L.M., Baskunov, B.P., Golovlev, E.L., and Golovleva, L.A., Degradation of Pentachlorophenol in Soil by the Introduced StrainStreptomyces rochei 303 and Activated Soil Microflora,Mikrobiologiya, 1997, vol. 66, pp. 661–666.
Warhurst, A.M. and Fewson, C.A., Biotransformations Catalyzed by the GenusRhodococcus, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 1994, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 29–73.
Gorlatov, S.N., Mal’tseva, O.V., Shevchenko, V.I., and Golovleva, L.A., Degradation of Chlorophenols by a Culture ofRhodococcus erythropolis 1cp,Mikrobiologiya, 1989, vol. 58, pp. 647–651.
Bondar, V., Boersma, M.G., Golovlev, E.L., Vervoort, J., Van Berkel, W., Finkelstein, Z.I., Solyanikova, I.P., Golovleva, L.A., and Rietjens, I.M.C.M., 19 FMR Study on the Biodegradation of Fluorophenols by Various Rhodococcus Species,Biodegradation, 1998, vol. 9, pp. 1–12.
Eight Peak Index of Mass Spectra, 2nd ed., vol. 2, Table 2: Mass Spectr. Data Center, AWRE, Aldermaston, 1974, pp. 741–871.
Solyanikova, I.P., Golovlev, E.L., Lisnyak, O.V., and Golovleva, L.A., Isolation and Characterization of Pyrocatechases from Strains ofRhodococcus rhodnii 135 andR. rhodochrous 89: Comparison with Analogous Enzymes of the Common and Modified Pathways,Biokhimiya, 1999, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 982–989.
Polnish, E., Kneifel, H., Franzke, H., and Hofmann, K.H., Degradation and Dehalogenation of Monochlorophenols by the Phenol-assimilating YeastCandida maltosa, Biodegradation, 1991/1992, vol. 2, pp. 193–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finkel’shtein, Z.I., Baskunov, B.P., Golovlev, E.L. et al. Dependence of the conversion of chlorophenols by rhodococci on the number and position of chlorine atoms in the aromatic ring. Microbiology 69, 40–47 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02757255
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02757255