Abstract
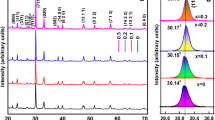
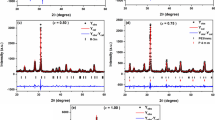
65(SrO·TiO2)−35(2SiO2·B2O3) wt% glass was synthesized. Differential thermal analysis study shows one exothermic peak which shifts towards higher temperature with increasing heating rate. Glass ceramics prepared by controlled crystallization of strontium titanate borosilicate glass produce uniform distribution of crystallites in a glassy matrix. Attempt was made to crystallize strontium titanate phase in this glass ceramic. Different phases precipitated out during ceramization have been identified by X-ray diffraction. It appears that due to high reactivity of SrO with B2O3, strontium borate crystallizes as principal phase followed by TiO2 (rutile) and Sr3Ti2O7 phases. Dielectric constant of these glass ceramics was observed to be more or less temperature independent over wide range of temperatures with low values of dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furukawa T and White W B 1980Phys. Chem. Glasses 21 85
Herczog A 1984J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 67 484
Kokubo T 1969Yogyo-Kyokai-Shi 77 293
Krogh-Moe J 1969J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1 269
Layton M M and Herczog A 1967J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 50 369
Lawless W N 1971Adv. Cryogenic Eng. 16 261
Lawless W N 1972aRev. Sci. Instrum. 42 561
Lawless W N 1972b US Patent 3649891
Mandal R K, Durgaprasad Ch, Parkash O and Kumar Devendra 1987Bull. Mater. Sci. 9 255
Marotta A, Buri A, Branda F and Saiello S 1982Adv. Ceram. 4 146
Mc Millan P W 1979Glass ceramics 2nd ed. (London: Academic Press)
Parkash O, Kumar Devendra and Rajgopalan R 1986Bull. Mater. Sci. 1 13
Smith R A 1986J. Non-Cryst. Solids 84 421
Swartz S L and Bhalla A S 1986Mater. Res. Bull. 21 1417
Swartz S L, Brevel E, Randall C A and Fox B H 1988aJ. Mater. Sci. 23 3997
Swartz S L, Bhalla A S, Cross L E and Lawless W N 1988bJ. Mater. Sci. 23 4004
Walrafen G E, Samanta S R and Krishnan P N 1980J. Chem. Phys. 72 113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, O.P., Kumar, D., Parkash, O.M. et al. Dielectric and microstructural behaviour of strontium titanate borosilicate glass ceramic system. Bull. Mater. Sci. 18, 577–585 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744843
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744843