Abstract
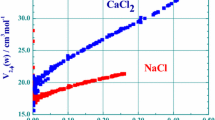
The thermodynamic route of establishing phase diagrams is a relatively recent activity, considering that till about the fifties most phase diagrams were determined by the measurement of certain physical property or quantitative microscopy using light optics or x-ray diffraction. The thermodynamic formalism used by Kaufman and Bernstein is explained and illustrated with examples of the development of hypothetical binary phase diagrams. The calculation of ternary phase diagrams can begin with the binary phase diagram data as a first approximation. However, to calculate a reasonably accurate ternary phase diagram a certain amount of ternary solution data is necessary. Various empirical equations have been proposed in the literature to express ternary thermodynamic data.
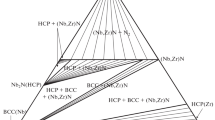
Calculation of simple ternary isothermal sections is illustrated with the examples of Mo-V-W and Cd-Sn-Pb systems. The numerical techniques which involve the differentiation of thermodynamic parameters with respect to composition get more involved with the number of components becoming 3 or more. A simpler approach has been applied recently to find the minimum position on the Gibbs free energy surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansara I 1979Int. Metall. Rev. 238 20
Balakrishna S S and Mallik A K 1979 ICMS-77 Varanasi, Indian Inst. of Met, Varanasi p. 107
Balakrishna S S and Mallik A K 1980Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 33 155
Bhansali A and Mallik A K 1985 (Communicated)
Counsell J F, Lees E B and Spencer P J 1971Met. Sci. J. 5 210
Chart T G, Counsell J F, Jones G P, Slough W and Spencer J P 1975Int. Metall. Rev. 20 57
Gaye H and Lupis C H P 1975Metall. Trans. 4 685
Gorman L W and Hinman J E 1962Technometrics 4 463
Hardy H K 1953Acta Metall. 1 202
Hillert M 1970Phase transformations (Ohio: Am. Soc. for Metals)
Kohler F 1960Monatsh. Chem. 91 738
Kaufman L and Bernstein H 1970Computer calculations of phase diagrams (New York: Academic Press)
Kubaschewski O and Barin I 1974Pure Appl. Chem. 38 469
Kaufman L and Nesor H 1978Calphad (Computer coupling of phase diagrams and thermochemistry)2 81
Kaufman L 1978Calphad (Computer coupling of phase diagrams and thermochemistry)2 117
Nelder J A and Mead R 1965Comput. J. 7 308
Pelton A D and Bale C W 1977Calphad (Computer coupling of phase diagrams and thermochemistry)1 253
Pelton A D and Thompson W T 1975Prog. Solid State Chem. 10 119
Rudman P S 1969Advances in materials research (New York: Interscience) Vol. 4
Scheffe H 1958J. R. Stat. Soc. B20 344
Toop G W 1965Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME,233 850
Wagner C 1954Acta Metall. 2 242
White J L, Orr R L and Hultgren R 1977Acta Metall. 5 747
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallik, A.K. Computer calculations of phase diagrams. Bull. Mater. Sci. 8, 107–121 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744176
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744176