Abstract
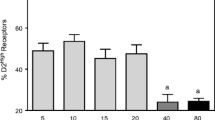
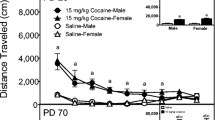
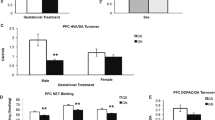
It has been reported from this laboratory that prenatal cocaine exposure results in the postnatal transient alterations of rat striatal dopamine uptake sites examined from postnatal 0–32 wk. The present study aims to examine whether this will result in a direct/indirect stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors. Pregnant rats were dosed orally with cocaine hydrochloride (60 mg/kg/d) from gestational day (GD) 7–21. Control animals received an equivalent volume of water. The striatum from the offspring at postnatal 0–32 wk was examined. The radioligand [3H]sulpiride was used for the Scatchard analysis of the D2 receptors, and the changes in the levels of mRNA for the D2 receptor were studied using Northern blot analysis. Results from the present study revealed that in the control group, there was an age-dependent increase in the number of D2 receptor sites (B max:44.00±2.12 to 178.00±45.10 fmol/mg protein) and in the levels of D2 mRNA from PN0–32 wk with the most rapid increase occurring during the first 4 wk of postnatal development. Prenatal cocaine exposure resulted in only a significant decrease (p<0.001) in the number of D2 receptor sites at PN0 wk and in a 10% increase in mRNA levels at PN3, 4, and 12 wk. It was concluded from this study that prenatal cocaine exposure resulted in minimal postnatal changes in the dopamine D2 receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams R. M., Burchfield D. J., Gerhardt K. J., and Peters J. M. (1992) Effect of cocaine on electrocortical activity in fetal sheep.Dev. Brain Res. 70, 97–102.
Bilitzke P. J. and Church M. W. (1992) Prenatal cocaine and alcohol exposures affect rat behavior in a stress test (the porsolt swim test).Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 359–364.
Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H. M., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., and Civelli O. (1988) Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA.Nature 336, 783–787.
Burchfield D. J., Graham E. M., Abrams R. M., and Gerhardt K. J. (1990) Cocaine alters behavioral states in fetal sheep.Dev. Brain Res. 56, 41–45.
Carroll F. I., Lewin A. H., Boja J. W., and Kuhar M. J. (1992) Cocaine receptor: biochemical characterization and structure-activity relationships of cocaine analogues at the dopamine transporter.J. Med. Chem. 35, 969–981.
Chasnoff I. J., Burns W. J., Schnoll S. H., and Burns K. A. (1985) Cocaine use in pregnancy.N. Engl. J. Med. 313, 666–669.
Chasnoff I. J., Burns K. A., Burns W. J., and Schnoll S. H. (1986) Prenatal drug exposure: effects on neonatal and infant growth and development.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 9, 291–293.
Chasnoff I. J., Burns K. A., and Burns W. J. (1987) Cocaine in pregnancy: perinatal morbidity and mortality.Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 9, 291–293.
Chasnoff I. J., Griffith D. R., MacGregor S., Dirkes K., and Burns K. A. (1989) Temporal patterns of cocaine use in pregnancy.JAMA 261, 1741–1744.
Chasnoff I. J., Landress H. J., and Barrett M. E. (1990) The prevalence of illicit-drug or alcohol use during pregnancy and discrepancies in mandatory reporting in Pinellas County, FL.N. Engl. J. Med. 322, 1202–1206.
Church M. W. and Overbeck G. W. (1990) Prenatal cocaine exposure in the Long-Evans rat: III. Developmental effects on the brainstem auditory-evoked potential.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 12, 345–351.
Church M. W., Holmes P. A., Overbeck G. W., Tilak J. P., and Zajac C. S. (1991) Interactive effects of prenatal alcohol and cocaine exposures on postnatal mortality, development and behaviour in the Long-Evans rat.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 377–386.
Coles C. D., Platzman K. A., Smith I., James M. E., and Falek A. (1992) Effects of cocaine and alcohol use in pregnancy on neonatal growth and neurobehavioral status.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 23–33.
Corwin M. J., Lester B. M., Sepkoski C., McLaughlin S., Kayne H., and Golub H. L. (1992) Effects of in utero cocaine exposure on newborn acoustical cry characteristics.Pediatrics 89, 1199–1203.
Davis M. (1985) Cocaine: excitatory effects on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle.Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 86, 31–36.
Dow-Edwards D. L. (1989) Long-term neurochemical and neurobehavioral consequences of cocaine use during pregnancy.Ann NY Acad. Sci. 562, 280–289.
Dow-Edwards D. L., Freed L. A., and Fico T. A. (1990) Structural and functional effects of prenatal cocaine exposure in adult rat brain.Dev. Brain Res. 57, 263–268.
Eisen L. N., Field T. M., Bandstra E. S., Roberts J. P., Morrow C., Larson K., and Steele B. M. (1991) Perinatal cocaine effects on neonatal stress behavior and performance on the Brazelton scale.Pediatrics 88, 477–480.
Foss J. A. and Riley E. P. (1991) Failure of acute cocaine administration to differentially affect acoustic startle and activity in rats prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 547–551.
Frank D. A., Zuckerman B. S., Amaro H., Aboagye K., Bauchner H., Cabral H., Fried L., Hingson R., Kayne H., Levenson S. M., Parker S., Reece H., and Vinci R. (1988) Cocaine use during pregnancy: prevalence and correlates.Pediatrics 82, 888–895.
Freedman S. B., Mustafa A., Poat J., Senior K., Want C., and Woodruff G. N. (1981) A study on the localization of3H-sulpiride binding sites in rat striatal membranes.Neuropharmacology 20, 1151–1155.
Freier M. C., Griffith D. R., and Chasnoff I. J. (1991) In utero drug exposure: developmental follow-up and maternal-infant interaction.Sem. Perinatol. 15, 310–316.
Fung Y. K., Reed J. A., and Lau Y. S. (1989) Prenatal cocaine exposure fails to modify neurobehavioral responses and the striatal dopaminergic system in newborn rats.Gen. Pharmacol. 20, 686–693.
Gingras J. L., Weese-Mayer D. E., Hume R. F. Jr., and O’Donnell K. J. (1992) Cocaine and development: mechanisms of fetal toxicity and neonatal consequences of prenatal cocaine exposure.Early Hum. Dev. 31, 1–24.
Graham W. C., Clarke C. E., Boyce S., Sambrook M. A., Crossman A. R., and Woodruff G. N. (1990) Autoradiographic studies in animal models of hemi-parkinsonism reveal dopamine D2 but not D1 receptor supersensitivity. II. Unilateral intracarotid infusion of MPTP in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis).Brain Res. 514, 103–110.
Henderson M. G. and McMillen B. A. (1990) Effects of prenatal exposure to cocaine or related drugs on rat developmental and neurological indices.Brain Res. Bull. 24, 207–212.
Henderson M. G., McConnaughey M. M., and McMillen B. A. (1991) Long-term consequences of prenatal exposure to cocaine or related drugs: effects on rat brain monoaminergic receptors.Brain Res. Bull. 26, 941–945.
Heyser C. J., Miller J. S., Spear N. E., and Spear L. P. (1992) Prenatal exposure to cocaine disrupts cocaine-dinduced conditioned place preference in rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 57–64.
Hutchings D. E., Fico T. A., and Dow-Edwards D. L. (1989) Prenatal cocaine: maternal toxicity, fetal effects and locomotor activity in rat offspring.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 65–69.
Jastrow T. R., Richfield E., and Gnegy M. E. (1984) Quantitative autoradiography of3H-sulpiride binding sits in rat brain.Neurosci. Lett. 51, 47–53.
Johns J. M., Means L. W., Means M. J., and McMillen B. A. (1992a) Prenatal exposure to cocaine I: affects on gestation, development, and activity in Sprague-Dawley rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 337–342.
Johns J. M., Means M. J., Anderson D. R., Means L. W., and McMillen B. A. (1992b) Prenatal exposure to cocaine II: effects on open-field activity and cognitive behavior in Sprague-Dawley rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 343–349.
Joyce J. N., Marshall J. F., Bankiewicz K. S., Kopin I. J., and Jacobwitz D. M. (1986) Hemiparkinsonism in a monkey after unilateral internal carotid artery infusion of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is associated with regional ipsilateral changes in striatal dopamine D2 receptor density.Brain Res. 382, 360–364.
Kuhar M. J., Ritz M. C., and Boja J. W. (1991) The dopamine hypothesis of the reinforcing properties of cocaine.TINS 14, 299–302.
Le Moal M. and Simon H. (1991) Mesocorticolimbic dopaminergic netowrk: functional and regulatory roles.Physiol. Rev. 71, 155–234.
Little B. B., Snell L. M., Palmore M. K., and Gilstrap L. C. III (1988) Cocaine use in pregnant women in a large public hospital.Am. J. Perinatol. 5, 206–207.
Lowry O.H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Pandall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
McMillen B. A., Johns J. M., Bass E. W., and Means L. W. (1991) Learning and behaviour of adult rats exposed to cocaine through-out gestation.Teratology 43, 495.
Meyer J. S. and Dupont S. A. (1993) Prenatal cocaine administration stimulates fetal brain tyrosine hydroxylase activity.Brain Res. 608, 129–137.
Minabe Y., Ashby C. R. Jr., Heyser C., Spear L. P., and Wang R. Y. (1992) The effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on spontaneously active midbrain dopamine neurons in adult male offspring: an electrophysiological study.Brain Res. 586, 152–156.
Mofenson H. C. and Caraccio T. R. (1987) Cocaine.Pediatr. Ann. 16, 864–874.
Munson P. J. and Rodbard D. (1980) LIGAND: a versatile computerized approach for the characterization of ligand binding systems.Anal. Biochem. 107, 220–239.
Neerhof M. G., MacGregor S. N., and Sullivan T. P. (1989) Cocaine abuse during pregnancy: peripartum prevalence and perinatal outcome.Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 161, 633–638.
Neuspiel D. R., Hamel S. C., Hochberg E., Greene J., and Campbell D. (1991) Maternal cocaine use and infant behavior.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 229–233.
Nomura Y., Oki K., and Segawa T. (1982) Ontogenetic development of the striatal [3H]spiperone binding: regulation by sodium and guanine nucleotide in rats.J. Neurochem. 38, 902–908.
O’Malley P. M., Bachman J. G., and Johnston L. D. (1988) Period, age, and cohort effects on substance use among young Americans: a decade of change, 1976–1986.Am. J. Public Health 78, 1315–1321.
Oro A. S. and Dixon S. D. (1987) Perinatal cocaine and amphetamine exposure: maternal and neonatal correlates.J. Pediatr. 111, 571–578.
Peris J. and Zahniser N. R. (1989) Persistent augmented dopamine release after acute cocaine requires dopamine receptor activation.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 32, 71–76.
Peris J., Coleman-Hardee M., and Millard W. J. (1992) Cocaine in utero enhances the behavioral response to cocaine in adult rats.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 42, 509–515.
Richardson G. A. and Day N. L. (1991) Maternal and neonatal effects of moderate cocaine use during pregnancy.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 455–460.
Riley E. P. and Foss J. A. (1991) Exploratory behavior and locomotor activity: a failure to find effects in animals prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 553–558.
Ritz M. C., Lamb R. J., Goldberg S. R., and Kuhar M. J. (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporter are related to the self administration of cocaine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248, 1010–1017.
Sambrook J. M., Fritsch E. F., and Maniatas T. (1989)Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Scalzo F. M., Ali S. F., Frambes N. A., and Spear L. P. (1990) Weanling rats exposed prenatally to cocaine exhibit an increase in striatal D2 dopamine binding associated with an increase in ligand affinity.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 37, 371–373.
Schneider J. W., Griffith D. R., and Chasnoff I. J. (1989) Infants exposed to cocaine in utero: implications of developmental assessment and intervention.IYC 2, 25–36.
Smith R. F., Mattran K. M., Kurkjian M. F., and Kurtz S. L. (1989) Alterations in offspring behaviour induced by chronic prenatal cocaine dosing.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 35–38.
Sobrian S. K., Burton L. E., Robinson N. L., Ashe W. K., James H., Stokes D. L., and Turner L. M. (1990) Neurobehavioral and immunological effects of prenatal cocaine exposure in rat.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 37, 617–629.
Spear L. P., Kirstein C. L., Bell J., Yoottanasumpun V., Greenbaum R., O’Shea J., Hoffman H., and Spear N. E. (1989) Effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on behavior during the early postnatal period.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 57–63.
Stadlin A., Choi H. L., and Tsang D. (1994) Postnatal changes in [3H]mazindol-labelled dopamine uptake sites in the rat striatum following prenatal cocaine exposure.Brain Res. 637, 345–348.
Wiggins R. C. (1992) Pharmacokinetics of cocaine in pregnancy and effects on fetal maturation.Clin. Pharmacokinet. 22, 85–93.
Zmitrovich A. C., Hutchings D. E., Dow-Edwards D. L., Malowany D., and Church S. (1992) Effects of prenatal exposure to cocaine on the restactivity cycle of the preweanling rat.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 43, 1059–1064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stadlin, A., Choi, H.L., Keung Tsim, K.W. et al. Prenatal cocaine exposure revealed minimal postnatal changes in rat striatal dopamine D2 receptor sites and mRNA levels in the offspring. Mol Neurobiol 11, 67–76 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740685
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740685