Abstract
Rationale
Ontogenetic differences in the behavioral responsiveness to cocaine have often been attributed to the maturation of dopaminergic elements (e.g., dopamine transporters, D2High receptors, receptor coupling, etc.).
Objective
The purpose of this study was to determine whether ontogenetic changes in cocaine pharmacokinetics might contribute to age-dependent differences in behavioral responsiveness.
Methods
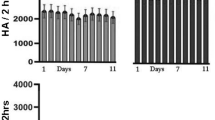
Male and female neonatal (PD 5), preweanling (PD 10 and PD 20), and adult (PD 70) rats were injected (IP) with cocaine or saline and various behaviors (e.g., locomotor activity, forelimb paddle, vertical activity, head-down sniffing, etc.) were measured for 90 min. In a separate experiment, the dorsal striata of young and adult rats were removed at 10 time points (0–210 min) after IP cocaine administration. Peak cocaine values, cocaine half-life, and dopamine levels were determined using HPLC.
Results
When converted to percent of saline controls, PD 5 and PD 10 rats were generally more sensitive to cocaine than older rats, but this effect varied according to the behavior being assessed. Peak cocaine values did not differ according to age or sex, but cocaine half-life in brain was approximately 2 times longer in PD 5 and PD 10 rats than adults. Cocaine pharmacokinetics did not differ between PD 20 and PD 70 rats.
Conclusions
Differences in the cocaine-induced behavioral responsiveness of very young rats (PD 5 and PD 10) and adults may be attributable, at least in part, to pharmacokinetic factors; whereas, age-dependent behavioral differences between the late preweanling period and adulthood cannot readily be ascribed to cocaine pharmacokinetics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams DR, Bruno JP (1992) Ontogeny of apomorphine-induced stereotypy and its D1 and D2 receptor mediation in rats depleted of dopamine as neonates. Dev Psychobiol 25:475–495
Alburges ME, Wamsley JK (1993) Effects on monoamine levels in rat CNS after chronic administration of cocaine. Investig Clin 34:181–192
Andersen SL (2003) Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:3–18
Badanich KA, Maldonado AM, Kirstein CL (2008) Early adolescents show enhanced acute cocaine-induced locomotor activity in comparison to late adolescent and adult rats. Dev Psychobiol 50:127–133
Becker JB, Molenda H, Hummer DL (2001) Gender differences in the behavioral responses to cocaine and amphetamine. Implications for mechanisms mediating gender differences in drug abuse. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937:172–187
Benuck M, Lajtha A, Reith ME (1987) Pharmacokinetics of systemically administered cocaine and locomotor stimulation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:144–149
Bolanos CA, Glatt SJ, Jackson D (1998) Subsensitivity to dopaminergic drugs in periadolescent rats: a behavioral and neurochemical analysis. Dev Brain Res 111:25–33
Bowman BP, Blatt B, Kuhn CM (1997) Ontogeny of the behavioral response to dopamine agonists after chronic cocaine. Psychopharmacology 129:121–127
Bowman BP, Vaughan SR, Walker QD, Davis SL, Little PJ, Scheffler NM, Thomas BF, Kuhn CM (1999) Effects of sex and gonadectomy on cocaine metabolism in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:1316–1323
Broaddus WC, Bennett JP (1990) Postnatal development of striatal dopamine function. I. An examination of D1 and D2 receptors, adenylate cyclase regulation and presynaptic dopamine markers. Dev Brain Res 52:265–271
Browne SP, Moore CM, Scheurer J, Tebbett IR, Logan BK (1991) A rapid method for the determination of cocaine in brain tissue. J Forensic Sci 36:1662–1665
Bystrowska B, Adamczyk P, Moniczewski A, Zaniewska M, Fuxe K, Filip M (2012) LC/MS/MS evaluation of cocaine and its metabolites in different brain areas, peripheral organs and plasma in cocaine self-administering rats. Pharmacol Rep 64:1337–1349
Cameron DL, Crosbie J, Crocker AD (1988) A fixed interval momentary sampling method for assessing on-going behaviours induced by dopamine receptor agonists. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 12:595–606
Camp LL, Rudy JW (1987) Behavioral activation in infant rats: pharmacological evidence for dopaminergic mediation. Psychobiology 15:317–328
Campbell BA, Lytle LD, Fibiger HC (1969) Ontogeny of adrenergic arousal and cholinergic inhibitory mechanisms in the rat. Science 166:635–637
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2005) Enhanced behavioral response to repeated-dose cocaine in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 183:218–225
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2007) A single high dose of cocaine induces differential sensitization to specific behaviors across adolescence. Psychopharmacology 193:247–260
Catlow BJ, Kirstein CL (2005) Heightened cocaine-induced locomotor activity in adolescent compared to adult female rats. J Psychopharmacol 19:443–447
Chao OY, Pum ME, Li JS, Huston JP (2012) The grid-walking test: assessment of sensorimotor deficits after moderate or severe dopamine depletion by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions in the dorsal striatum and medial forebrain bundle. Neuroscience 202:318–325
Charntikov S, Der-Ghazarian T, Herbert MS, Horn LR, Widarma CB, Gutierrez A, Varela FA, McDougall SA (2011) Importance of D1 and D2 receptors in the dorsal caudate-putamen for the locomotor activity and stereotyped behaviors of preweanling rats. Neuroscience 183:121–133
Delfs JM, Kelley AE (1990) The role of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in oral stereotypy induced by dopaminergic stimulation of the ventrolateral striatum. Neuroscience 39:59–67
Dewey SL, Chaurasia CS, Chen CE, Volkow ND, Clarkson FA, Porter SP, Straughter-Moore RM, Alexoff DL, Tedeschi D, Russo NB, Fowler JS, Brodie JD (1997) GABAergic attenuation of cocaine-induced dopamine release and locomotor activity. Synapse 25:393–398
Dickson PR, Lang CG, Hinton SC, Kelley AE (1994) Oral stereotypy induced by amphetamine microinjection into striatum: an anatomical mapping study. Neuroscience 61:81–91
Dourish CT, Cooper SJ, Philips SR (1985) Yawning elicited by systemic and intrastriatal injection of piribedil and apomorphine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 86:175–181
Eskow Jaunarajs KL, George JA, Bishop C (2012) L-DOPA-induced dysregulation of extrastriatal dopamine and serotonin and affective symptoms in a bilateral rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 218:243–256
Festa ED, Russo SJ, Gazi FM, Niyomchai T, Kemen LM, Lin SN, Foltz R, Jenab S, Quinones-Jenab V (2004) Sex differences in cocaine-induced behavioral responses, pharmacokinetics, and monoamine levels. Neuropharmacology 46:672–687
Franke RM, Belluzzi JD, Leslie FM (2007) Gestational exposure to nicotine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors influences cocaine-induced locomotion in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 195:117–124
Frantz K, Babcock D, Van Hartesveldt C (1996) The locomotor effects of a putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist in developing rats. Eur J Pharmacol 302:1–6
Frantz KJ, O’Dell LE, Parsons LH (2006) Behavioral and neurochemical responses to cocaine in periadolescent and adult rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:625–637
Fritz M, El Rawas R, Salti A, Klement S, Bardo MT, Kemmler G, Dechant G, Saria A, Zernig G (2011) Reversal of cocaine-conditioned place preference and mesocorticolimbic Zif268 expression by social interaction in rats. Addict Biol 16:273–284
Geisser S, Greenhouse SW (1958) An extension of Box’s results on the use of the F distribution in multivariate analysis. Ann Math Stat 29:885–891
Giorgi O, De Montis G, Porceddu ML, Mele S, Calderini G, Toffano G, Biggio G (1987) Developmental and age-related changes in D1-dopamine receptors and dopamine content in the rat striatum. Dev Brain Res 35:283–290
Grigoriadis N, Simeonidou C, Parashos SA, Albani M, Guiba-Tziampiri O (1996) Ontogenetic development of the locomotor response to levodopa in the rat. Pediatr Neurol 14:41–45
Gulley JM, Hoover BR, Larson GA, Zahniser NR (2003) Individual differences in cocaine-induced locomotor activity in rats: behavioral characteristics, cocaine pharmacokinetics, and the dopamine transporter. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:2089–2101
Hadfield MG, Milio C (1992) Cocaine and regional brain monoamines in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:395–403
Hall WG (1979) The ontogeny of feeding in rats: I. Ingestive and behavioral responses to oral infusions. J Comp Physiol Psychol 93:977–1000
Holson RR, Pearce B (1992) Principles and pitfalls in the analysis of prenatal treatment effects in multiparous species. Neurotoxicol Teratol 14:221–228
Hurd YL, Ungerstedt U (1989) Cocaine: an in vivo microdialysis evaluation of its acute action on dopamine transmission in rat striatum. Synapse 3:48–54
Koek W, France CP, Javors MA (2012) Morphine-induced motor stimulation, motor incoordination, and hypothermia in adolescent and adult mice. Psychopharmacology 219:1027–1037
Kohler RJ, Perrine SA, Baker LE (2017) Concurrent repeated exposure to 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone and cocaine produce locomotor sensitization with minimal effects on brain monoamines. Neuropharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.10.019
Krolewski DM, Bishop C, Walker PD (2005) Intrastriatal dopamine D1 receptor agonist-mediated motor behavior is reduced by local neurokinin 1 receptor antagonism. Synapse 57:1–7
Kummer KK, Hofhansel L, Barwitz CM, Schardl A, Prast JM, Salti A, El Rawas R, Zernig G (2014) Differences in social interaction- vs. cocaine reward in mouse vs. rat. Front Behav Neurosci 8:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00363
Lal S, Feldmüller F (1975) Effect of amphetamine and apomorphine on brain monoamines and behaviour in the immature and young adult rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 218:239–251
Lal S, Sourkes TL (1973) Ontogeny of stereotyped behaviour induced by apomorphine and amphetamine in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 202:171–182
Lanier LP, Isaacson RL (1977) Early developmental changes in the locomotor response to amphetamine and their relation to hippocampal function. Brain Res 126:567–575
Lau CE, Imam A, Ma F, Falk JL (1991) Acute effects of cocaine on spontaneous and discriminative motor functions: relation to route of administration and pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:444–456
Laviola G, Adriani W, Terranova ML, Gerra G (1999) Psychobiological risk factors for vulnerability to psychostimulants in human adolescents and animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:993–1010
Lin MY, Walters DE (1994) Dopamine D2 autoreceptors in rats are behaviorally functional at 21 but not 10 days of age. Psychopharmacology 114:262–268
Liu K, Steketee JD (2016) The role of adenylyl cyclase in the medial prefrontal cortex in cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats. Neuropharmacology 111:70–77
Maldonado AM, Kirstein CL (2005a) Cocaine-induced locomotor activity is increased by prior handling in adolescent but not adult female rats. Physiol Behav 86:568–572
Maldonado AM, Kirstein CL (2005b) Handling alters cocaine-induced activity in adolescent but not adult male rats. Physiol Behav 84:321–326
Martin-Fardon R, Arnaud M, Rousseau É, Kamenka J-M, Privat A, Vignon J (1996) N-[1-(2-benzo(b)thiophenyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine (BTCP) and cocaine induce similar effects on striatal dopamine: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats. Neurosci Lett 211:179–182
McDougall SA, Kozanian OO, Greenfield VY, Horn LR, Gutierrez A, Mohd-Yusof A, Castellanos KA (2011) One-trial behavioral sensitization in preweanling rats: differential effects of cocaine, methamphetamine, methylphenidate, and D-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 217:559–571
McDougall SA, Nuqui CM, Quiroz AT, Martinez CM (2013) Early ontogeny of D-amphetamine-induced one-trial behavioral sensitization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 104:154–162
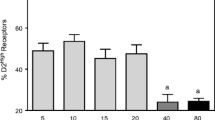
McDougall SA, Eaton SE, Mohd-Yusof A, Crawford CA (2015) Age-dependent changes in cocaine sensitivity across early ontogeny in male and female rats: possible role of dorsal striatal D2High receptors. Psychopharmacology 232:2287–2301
Milesi-Hallé A, Hendrickson HP, Laurenzana EM, Gentry WB, Owens SM (2005) Sex- and dose-dependency in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of (+)-methamphetamine and its metabolite (+)-amphetamine in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209:203–213
Milesi-Hallé A, McMillan DE, Laurenzana EM, Byrnes-Blake KA, Owens SM (2007) Sex differences in (+)-amphetamine- and (+)-methamphetamine-induced behavioral response in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:140–149
Moody CA, Spear LP (1992) Ontogenetic differences in the psychopharmacological responses to separate and combined stimulation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors during the neonatal to weanling age period. Psychopharmacology 106:161–168
National Research Council (2010) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. National Academies Press, Washington
Pinheiro Carrera PM, Brunhara FC, Schwarting RK, Tomaz C (1998) Drug conditioning induced by intrastriatal apomorphine administration. Brain Res 790:60–66
Rowlett JK, Mattingly BA, Bardo MT (1991) Neurochemical and behavioral effects of acute and chronic treatment with apomorphine in rats. Neuropharmacology 30:191–197
Schindler CW, Carmona GN (2002) Effects of dopamine agonists and antagonists on locomotor activity in male and female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:857–863
Schramm-Sapyta NL, Walker QD, Caster JM, Levin ED, Kuhn CM (2009) Are adolescents more vulnerable to drug addiction than adults? Evidence from animal models. Psychopharmacology 206:1–21
Sell SL, Scalzitti JM, Thomas ML, Cunningham KA (2000) Influence of ovarian hormones and estrous cycle on the behavioral response to cocaine in female rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:879–886
Shalaby IA, Spear LP (1980) Psychopharmacological effects of low and high doses of apomorphine during ontogeny. Eur J Pharmacol 67:451–459
Simon P, Dupuis R, Costentin J (1994) Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav Brain Res 61:59–64
Snyder KJ, Katovic NM, Spear LP (1998) Longevity of the expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine in preweanling rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:909–914
Spear LP (1979) The use of psychopharmacological procedures to analyse the ontogeny of learning and retention: issues and concerns. In: Spear NE, Campbell BA (eds) Ontogeny of learning and memory. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, pp 135–156
Spear LP, Brake SC (1983) Periadolescence: age-dependent behavior and psychopharmacological responsivity in rats. Dev Psychobiol 16:83–109
Spear LP, Brick J (1979) Cocaine-induced behavior in the developing rat. Behav Neural Biol 26:401–415
Tirelli E (2001) Day-by-day maturation of the long-term expression of cocaine sensitization acquired before weaning in the rat. Behav Neurosci 115:1101–1110
Treit D, Fundytus M (1989) Thigmotaxis as a test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31:959–962
Ujike H, Tsuchida K, Akiyama K, Fujiwara Y, Kuroda S (1995) Ontogeny of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:613–617
van Harren F, Garcea M, Anderson KG, Tebbett IR (1997) Cocaine and benzoylecgonine in serum microsamples of intact and gonadectomized male and female Wistar rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:421–424
Varela FA, Der-Ghazarian T, Lee RJ, Charntikov S, Crawford CA, McDougall SA (2014) Repeated aripiprazole treatment causes dopamine D2 receptor up-regulation and dopamine supersensitivity in young rats. J Psychopharmacol 28:376–386
Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2008) Cocaine increases stimulated dopamine release more in periadolescent than adult rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 30:412–418
Walker QD, Morris SE, Arrant AE, Nagel JM, Parylak S, Zhou G, Caster JM, Kuhn CM (2010) Dopamine uptake inhibitors but not dopamine releasers induce greater increases in motor behavior and extracellular dopamine in adolescent rats than in adult male rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335:124–132
White DA, Michaels CC, Holtzman SG (2008) Periadolescent male but not female rats have higher motor activity in response to morphine than do adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 89:188–199
Yu ZJ, Lim DK, Hoskins B, Rockhold RW, Ho IK (1990) Effects of acute and subacute cocaine administration on the CNS dopaminergic system in Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats: I. Levels of dopamine and metabolites. Neurochem Res 15:613–619
Zhou L, Sun WL, Weierstall K, Minerly AC, Weiner J, Jenab S, Quinones-Jenab V (2016) Sex differences in behavioral and PKA cascade responses to repeated cocaine administration. Psychopharmacology 233:3527–3536
Acknowledgements
We thank Danielle E. Humphrey for help with injecting the rats, and Christopher P. Plant for help with the assays. We also thank Nancy R. Zahniser and Gaynor A. Larson for their assistance in setting up the cocaine assay.
Funding
This research was supported by NIGMS training grant GM083883 (MGA and ATQ) and NIDA training grant DA033877 (AMY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, S.A., Apodaca, M.G., Mohd-Yusof, A. et al. Ontogeny of cocaine-induced behaviors and cocaine pharmacokinetics in male and female neonatal, preweanling, and adult rats. Psychopharmacology 235, 1967–1980 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4894-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4894-8