Abstract
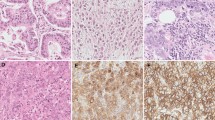
Apoptosis and immunoreactivity forbcl-2, p53, and Ki-67 were studied in 21 patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). The DNA nick end labeling method was used to assess apoptosis. The relationships between the different factors were analyzed, as were their relations to clinicopathological data, including survival. More than 80% of the tumors harbored apoptotic cells. Tumors in individuals who had died of the MTC disease had a higher percentage of apoptosis. All cases demonstrated immunoreactivity tobcl-2; disease-free individuals had a higher rate than those with recurrent disease. No obvious pattern could be discerned in the relation of p53 or Ki-67 to the outcome of the MTC disease. An inverse correlation betweenbcl-2 and apoptosis (r=−0.81;p<0.01) was demonstrated.bcl-2 was significantly (p=0.014) associated with apoptosis even after taking both p53 and Ki-67 into consideration, but these two factors were unrelated to apoptosis. None of the factors studied were correlated to crude survival, either in univariate or in multivariate analyses. This study established thatbcl-2 immunoreactivity is closely associated with apoptosis in MTC, suggesting that a downregulation of thebcl-2 protein is related to a more aggressive growth rate and might be a useful marker for the evaluation of MTC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandler D, El-naggar AK, Brisbay S, Redline RW, McDonnell TJ. Apoptosis and expression of the bcl-2 proto-oncogene in the fetal and adult human kidney: evidence for the contribution of bcl-2 expression to renal carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol 25:789–796, 1994.
Aihara M, Truong LD, Dunn JK, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT, Thompson TC. Frequency of apoptotic bodies positively correlates with gleason grade in prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 25:797–801, 1994.
Bourhis J, Bosq J, Wilson GD, Bressac B, Talbot M, Leridant AM, Dendale R, Janin N, Armand JP, Luboinski B, Malaise EP, Wibault P, Eschwege F. Correlation between p53 gene expression and tumor-cell proliferation in oropharyngeal cancer. Int J Cancer 57:458–462, 1994.
Cotter TG, Lennon SV, Glynn JG, Martin SJ. Cell death via apoptosis and its relationship to growth, development and differentiation of both tumour and normal cells. Anticancer Res 10:1153–1160, 1990.
Dobashi Y, Sakamoto A, Sugimura H, Mernyei M, Machinami R. Overexpression of p53 as possible prognostic factor in human thyroid carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 17:375–381, 1993.
Gerdes J, Li L, Schlueter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Gerlach C, Stahmer I, Kloth S, Brandt E, Flad HD. Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki67. Am J Pathol 138:867–873, 1991.
Hague A, Moorghen M, Hicks D, Chapman M, Paraskeva C. bcl-2 expression in human colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. Oncogene 9:3367–3370, 1994.
Ito K, Watanabe K, Nasim S, Sasano H, Sato S, Yajima A, Silverberg SG, Garrett CT. Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res 54:4667–4670, 1994.
Joensuu H, Pylkkänen L, Toikkanen S. bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 145:1191–1198, 1994.
Kushima R, Moritani S, Hattori T. Overexpression of p53 protein in gastric carcinomas: relationship with development, progression and mucin-histochemical differentiation. Cancer J 7:192–197, 1994.
Porter PL, Gown AM, Kramp SG, Coltrera MD. Widespread p53 overexpression in human malignant tumors: an immunohistochemical study using methacarn-fixed, embedded tissue. Am J Pathol 140:145–153, 1992.
Porter MJ, Field JK, Lee JCK, Leung SF, Lo D, Hasselt CAV. Detection of the tumour suppressor gene p53 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Hong Kong Chinese. Anticancer Res 14:1357–1360, 1994.
Skalova A, Lehtonen H, Boguslawsky KV, Leivo I. Prognostic significance of cell proliferation in mucoepidermoid carcinomas of the salivary gland: clinicopathological study using MIB 1 antibody in paraffin sections. Hum Pathol 25:929–935 1994.
Teh M, Wee A, Path MRC, Raju GC. An immunohistochemical study of p53 protein in gallbladder and extrahepatic bile duct/ampullary carcinomas. Cancer 74:1542–1545, 1994.
LeBrun DP, Wamke RA, Cleary ML. Expression of bcl-2 fetal tissues suggests a role in morphogenesis. Am J Pathol 142:743–753, 1993.
Novack DV, Korsmeyer SJ. bcl-2 protein expression during murine development. Am J Pathol 145:61–73, 1994.
Baer R. bcl-2 breathes life into embryogenesis. Am J Pathol 145:7–10, 1994.
Gusterson B, Anbazhagan R, Waren W, Midgely C, Lane P, O’Hare M, Stamps A, Carter R, Jayatilake H. Expression of p53 in pre-malignant and malignant squamous epithelium. Oncogene 6:1785–1789, 1992.
Key G, Becker MHG, Baron B, Duchrow M, Schluter C, Flad HD, Gerdes J. New Ki-67-equivalent murine monoclonal antibodies (MIB 1–3) generated against bacterially expressed parts of the Ki-67 cDNA containing three 62 base pair repetitive elements encoding for the Ki-67 epitope. Lab Invest 68:629–636, 1993.
Reinariz JJ, George E, Lindgren BR, Niehans GA. Expression of p53, transforming growth factor alpha, epidermal growth factor receptor, and c-erbB-2 in endometrial carcinoma and correlation with survival and known predictors of survival. Hum Pathol 25:1075–1083, 1994.
Sasano H, Garrett CT. Oncogenes in gynecological tumors. Curr Top Pathol 85:357–372, 1992.
Roncalli M, Viale G, Grimelius L, Johansson H, Wilander E, Alfano RM, Springall D, Battezzati PM, Polak JM, Coggi G. Prognostic value of N-myc immunoreactivity in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 74:134–141, 1994.
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501, 1992.
Rosai J, Carcangiu ML, Delellis RA. Tumors of the thyroid gland. Atlas of tumor pathology. 3rd ser. Washington, DC: Fascicle 5, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1992; 207–240.
Bergholm U. Medullary thyroid carcinoma in Sweden. Compr Summ Uppsala Diss Faculty Med 189:1–32, 1989.
Quinn CM, Wright NA. The clinical assessment of proliferation and growth in human tumours: evaluation of methods and applications as prognostic variables. J Pathol 160:93–102, 1990.
Duncan AMV, Heddle JA, Blakey DH. Mechanism of induction of nuclear anomalies by γ-radiation in the colonic epithelium of the mouse. Cancer Res 45:250–252, 1985.
Lee FD. Importance of apoptosis in the histopathology of drug related lesions in the large intestine. J Clin Pathol 46:118–122, 1993.
Willingham MC, Bhalla K. Transient mitotic phase localization of bcl-2 oncoprotein in human carcinoma cells and its possible role in prevention of apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem 42:441–450, 1994.
Hockenbery DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin XM, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer J. bcl-2 functions in an anti-oxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell 75:241–251, 1993.
Pezzella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar MF, Dunnill MS, Pierce CB, Harris A, Gatter KC, Mason DY. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med 329:690–694, 1993.
Korsmeyer SJ. bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood 80:879–886, 1992.
Nakagawa K, Yarnamura K, Maeda S, Ichihashi M. bcl-2 expression in epidermal keratinocytic diseases. Cancer 74:1720–1724, 1994.
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LWK, Hsieh JT, Tu SM, Campbell ML. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 52:6940–6944, 1992.
Viale G, Roncalli M, Grimelius, Graziani D, Johansson H, Bergholm U. Prognostic value of bcl-2 immunoreactivity in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol 26:945–950, 1995.
Kanavaros P, Loannidou D, Tzardi M, Datseris G, Katsantonis J, Delidis G, Tosca A. Mycosis fungoides: expression of C-myc p62, p53, bcl-2 and PCNA proteins and absence of association with Epstein-Barr virus. Pathol Res Pract 190:767–774, 1994.
Pezzella F, Morrison H, Jones M, Lane D, Harris AJ, Mason DY. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Histopathology 22:39–44, 1993.
Marin MC, Hsu B, Meyn RE, Donehower LA, El-naggar AK, McDonnell TJ. Evidence that p53 and bcl-2 are regulators of a common cell death pathway important for in vivo lymphomagenesis. Oncogene 9:3107–3112, 1994.
Shaw P, Bovey R, Tardy S, Sahli R, Sordat B, Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4495–4499, 1992.
Dobashi Y, Sugimura H, Sakamoto A, Mernyei M, Mori M, Oyama T, Machinami R. Stepwise participation of p53 gene mutation during differentiation of human thyroid carcinomas. Diagn Mol Pathol 3:9–14, 1994.
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B, Reed J. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 9:1799–1805, 1994.
Pelosi G, Bresaola E, Rodella S, Manfrin E, Piubello Q, Schiavon I, Iannucci A. Expression of proliferation cell nuclear antigen, Ki-67 antigen, estrogen receptor protein, and tumor suppressor p53 gene in cytologic samples of breast cancer: an immunochemical study with clinical, pathological, and histologic correlations. Diagn Cytopathol 11:131–140, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Johansson, H., Bergholm, U. et al. Apoptosis and expression of the proto-oncogenesbcl-2 and p53 and the proliferation factor Ki-67 in human medullary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Pathol 7, 37–45 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739913
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739913