Abstract
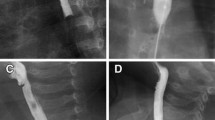
A 14-month-old boy with severe esophageal strictures following ingestion of potassium hydroxide is described. Initially, treatment was by surgical bougienage but following esophageal perforation, 65 balloon dilatations were performed over an 8-month period using a retrograde approach via a feeding gastrostomy without anesthesia or sedation. A further nine dilatations in the following 6 months were performed using a per-orla approach after establishment of full oral nutrition and removal of the gastrostomy. The main advantage of the retrograde approach was the large number of dilatations that could be performed without anesthesia in an infant. This has allowed nonoperative treatment of a high grade caustic esophageal stricture which would otherwise have required esophageal replacement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Middelkamp JN, Ferguson TB, Roper CL, Hoffman FD (1968) The management and problems of caustic burns in children. J Thorac Cardiovas Surg 57:3:341–347
Aschraft KW, Simon JL (1972) Accidental caustic ingestion in childhood: A review Texas Med 68:86–88
Kirsh MM, Peterson A, Brown JW, Orringer MB, Ritter F, Sloan H (1978) Treatment of caustic injuries of the esophagus: A ten-year experience. Ann Surg 188:5:675–678
Ferguson MK, Migliore M, Staszak VM, Little AG (1989) Early evaluation and therapy for caustic esophageal injury. Am J Surg 157: 116–120
Goldthorn JF, Ball WS, Wilkinson LG, Seigel RS, Kosloske AM (1984) Esophageal strictures in children: Treatment by serial balloon catheter dilatation. Radiology 153:3:655–658
Johnsen A, Ingemann L, Mauritzen K (1986) Balloon-dilatation of esophageal strictures in children. Pediatr Radiol 16:388–391
Ball WS, Strife JL, Rosenkrantz J, Towbin RB, Noseworthy J (1984) Esophageal strictures in children: Treatment by balloon dilatation. Radiology 150:263–264.
Dux AEW, Hall CM, Spitz L (1984) Technical notes: Balloon catheter dilatation of esophageal strictures in childrens. Br J Radiol 57:251–254
Starck E, Paolucci V, Herzer M, Crummy AB (1984) Esophageal stenosis: Treatment with balloon catheters. Radiology 153:3:637–640
Gaudreault P, Parent M, McGuigan MA, Chicoine L. Lovejoy FH (1983) Predictability of esophageal injury from signs and symptoms: A study of caustic ingestion in 378 children. Pediatrics 71:5:767–770
McLean GK, LeVeen RF (1989) Shear stress in the performance esophageal dilatation: Comparison of balloon dilatation and bougienage. Radiology 172:3:983–986
Dawson SL, Mueller PR, Ferrucci JT, Richter JM, Schapiro RH, Butch RJ, Simeone JF (1984) Severe esophageal strictures: Indications for balloon catheter dilatation. Radiology 153:3:631–635
Marshall F II (1979) Caustic burns of the esophagus: Ten-year results of aggressive care. South Med J 72:10:1236–1237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Philip Davies, R., Jane Linke, R. & Bruce Davey, R. Retrograde esophageal balloon dilatation: Salvage treatment of caustic-induced stricture. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 15, 186–188 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02735586
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02735586